Grid storage batteries, for their part, collect excess power from various green energy sources, like wind farms. They can be charged and then discharged at times of higher demand and lower supply. Having plentiful, economical batteries is a key factor in pitching this kind of facility to nations and communities that are considering using renewables, or larger portions of renewables.
But setting up a mine to extract the massive deposit of lithium in Thacker Pass is not a simple task: it will require a wholly new process to separate the lithium from its natural clay deposit.
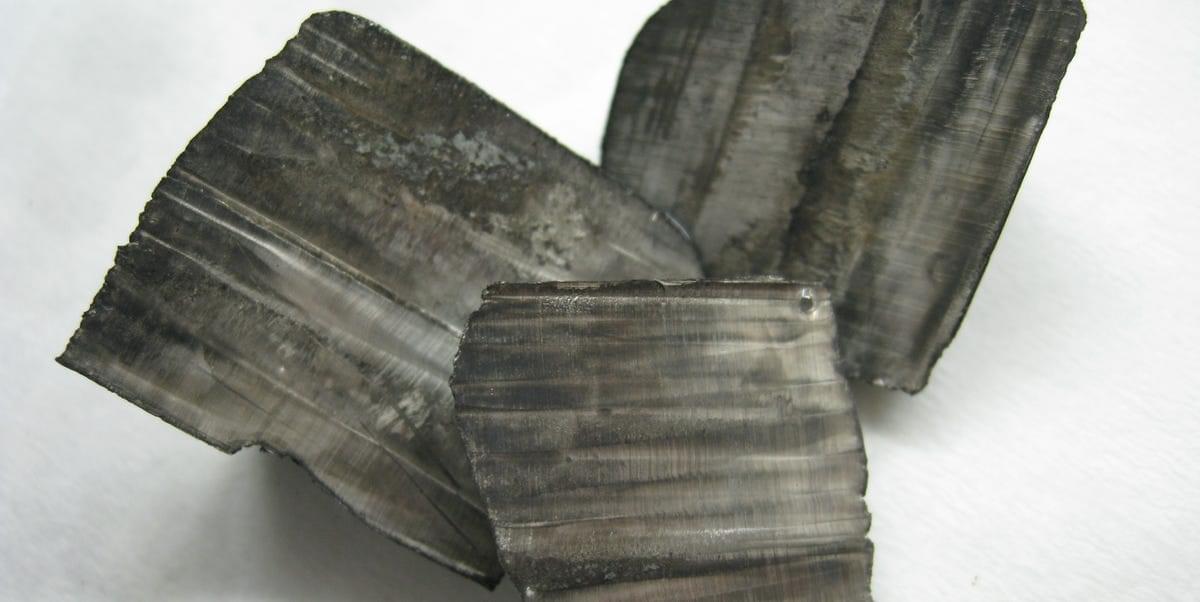
Lithium is all around us. The U.S. Geological Survey estimates there are 89 million tons of lithium in deposits on Earth, just two one-thousandths of 1 percent of Earth’s elemental abundance. Experts believe more than half of that lithium can be found in one triangular area of desert in western South America; but Thacker Pass in the United States, we now know, could contain as much as 40 million tons of lithium.