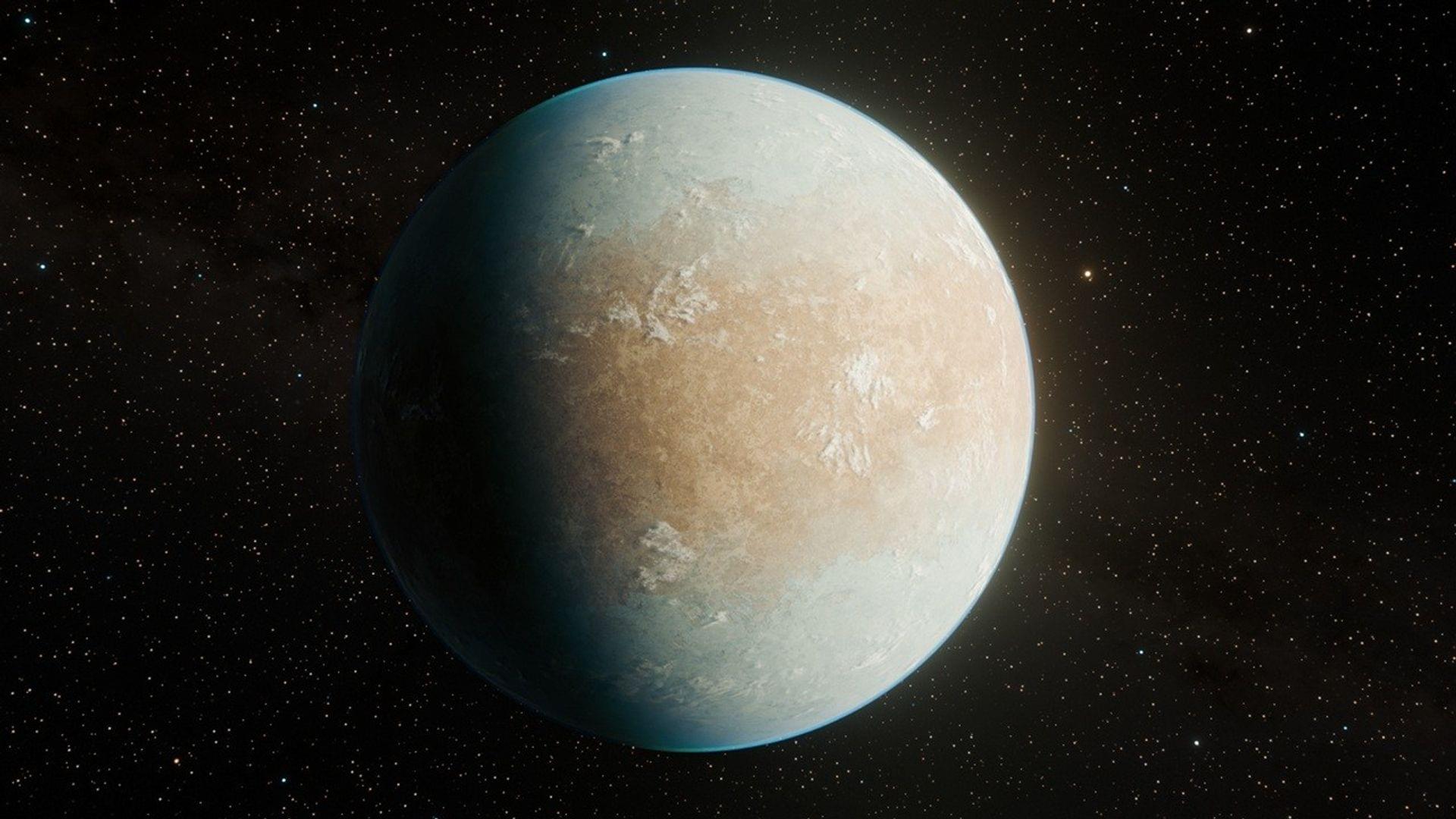
Astronomers have found an Earth-sized exoplanet, HD 137,010 b, orbiting a nearby Sun-like star but likely far too cold to be habitable.
How any Earth-sized exoplanets exist, and how do we find them? This is what a recent study published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters hopes to address as a team of scientists announced the discovery of an Earth-sized exoplanet orbiting a K-dwarf star, the latter of which is smaller and cooler than our Sun. This discovery has the potential to help scientists not only better understand the formation and evolution of Earth-like worlds, but also the methods used to find them.
For the discovery, the researchers analyzed data obtained from the NASA Kepler K2 mission about HD 137,010 b, which is located approximately 146 light-years from Earth. While the data was collected in 2017 using the transit method, which is when astronomers observe a dip in starlight as the planet crosses in front of its star, astronomers only recently were able to analyze the data to confirm this dip in starlight was an exoplanet. Despite the transit only lasting 10 hours, the astronomers estimate this means HD 137,010 b has an approximate orbital period of 355 days and an approximate radius of 1.06 Earths.