The four-star system features three stars in stable orbits, plus a fourth at a distance equal to Jupiter’s orbit around our Sun.


The survival of the human species may depend on an accelerated sprint to settle space. Watch and see why.
Tired of toxins in your consumer products? https://switchwithgreg.com/
GoldBacks from Galactic/Green Greg’s affiliate link:
https://www.defythegrid.com/goldbacks… coupon code GreenGregs for 1% off.

Coming soon!
India is preparing to enter a new phase of human space exploration, with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) targeting its first crewed spaceflight mission in 2027 and crewed lunar missions under the Chandrayaan programme by 2028, according to senior officials, TV BRICS reports.
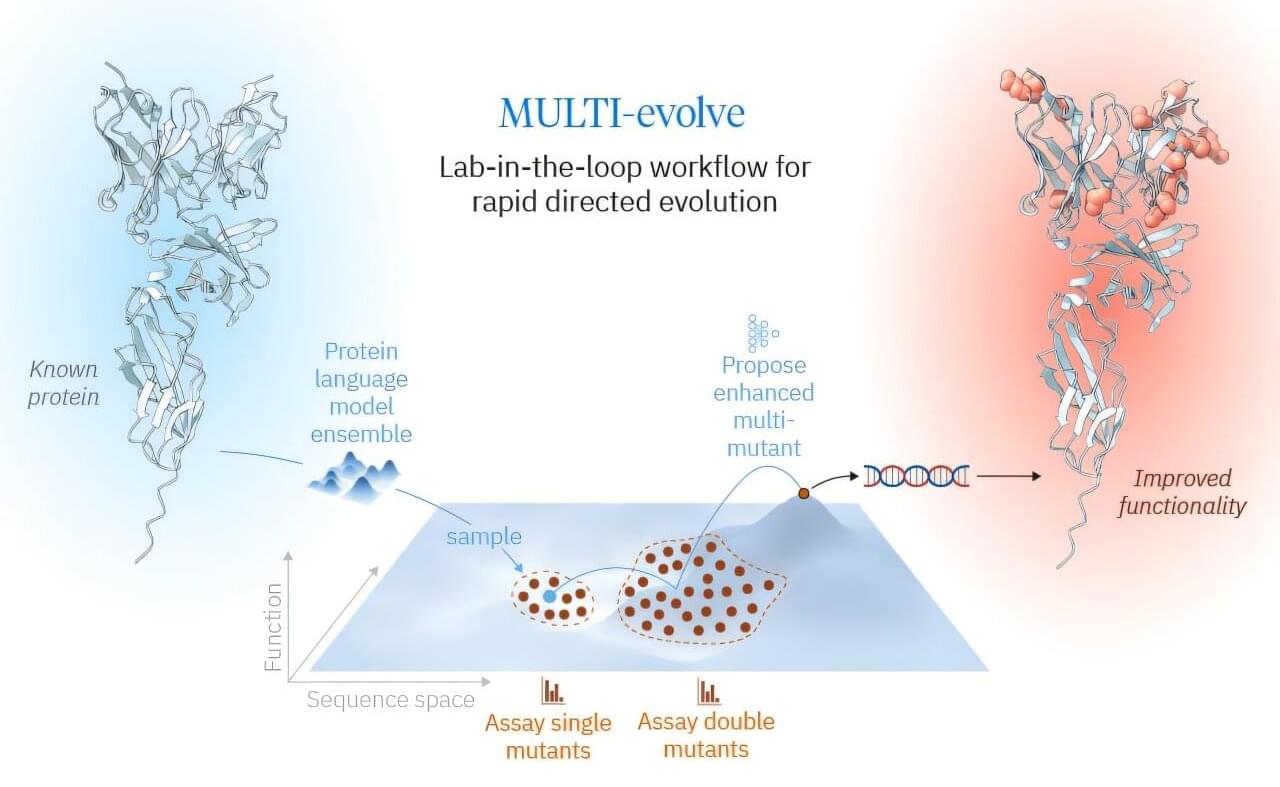
The search space for protein engineering grows exponentially with complexity. A protein of just 100 amino acids has 20100 possible variants—more combinations than atoms in the observable universe. Traditional engineering methods might test hundreds of variants but limit exploration to narrow regions of the sequence space. Recent machine learning approaches enable broader searches through computational screening. However, these approaches still require tens of thousands of measurements, or 5–10 iterative rounds.
With the advent of these foundational protein models, the bottleneck for protein engineering swings back to the lab. For a single protein engineering campaign, researchers can only efficiently build and test hundreds of variants. What is the best way to choose those hundreds to most effectively uncover an evolved protein with substantially increased function? To address this problem, researchers have developed MULTI-evolve, a framework for efficient protein evolution that applies machine learning models trained on datasets of ~200 variants focused specifically on pairs of function-enhancing mutations.
Published in Science, this work represents Arc Institute’s first lab-in-the-loop framework for biological design, where computational prediction and experimental design are tightly integrated from the outset, reflecting a broader investment in AI-guided research.

At the entrance to Starbase in south Texas, a glowing sign now welcomes visitors with the words “Gateway to Mars.” The display sits in front of SpaceX facilities where giant Starship rockets are being assembled with one bold purpose in mind: Elon Musk wants to build a self-sustaining city on Mars.
In recent years he has begun to put numbers on that dream. Musk has repeatedly said that building the first sustainable city on Mars would require around 1,000 Starship rockets and roughly 20 years of launch campaigns, moving up to 100,000 people per favorable Earth-Mars alignment and eventually reaching about one million settlers plus millions of tons of cargo.
It sounds like science fiction with a project plan. Yet the language he uses, “sustainable city,” is very familiar to climate and energy experts here on Earth. So what does sustainability really mean on a frozen, air-thin world and how does that huge effort interact with the environmental crisis on our own planet?
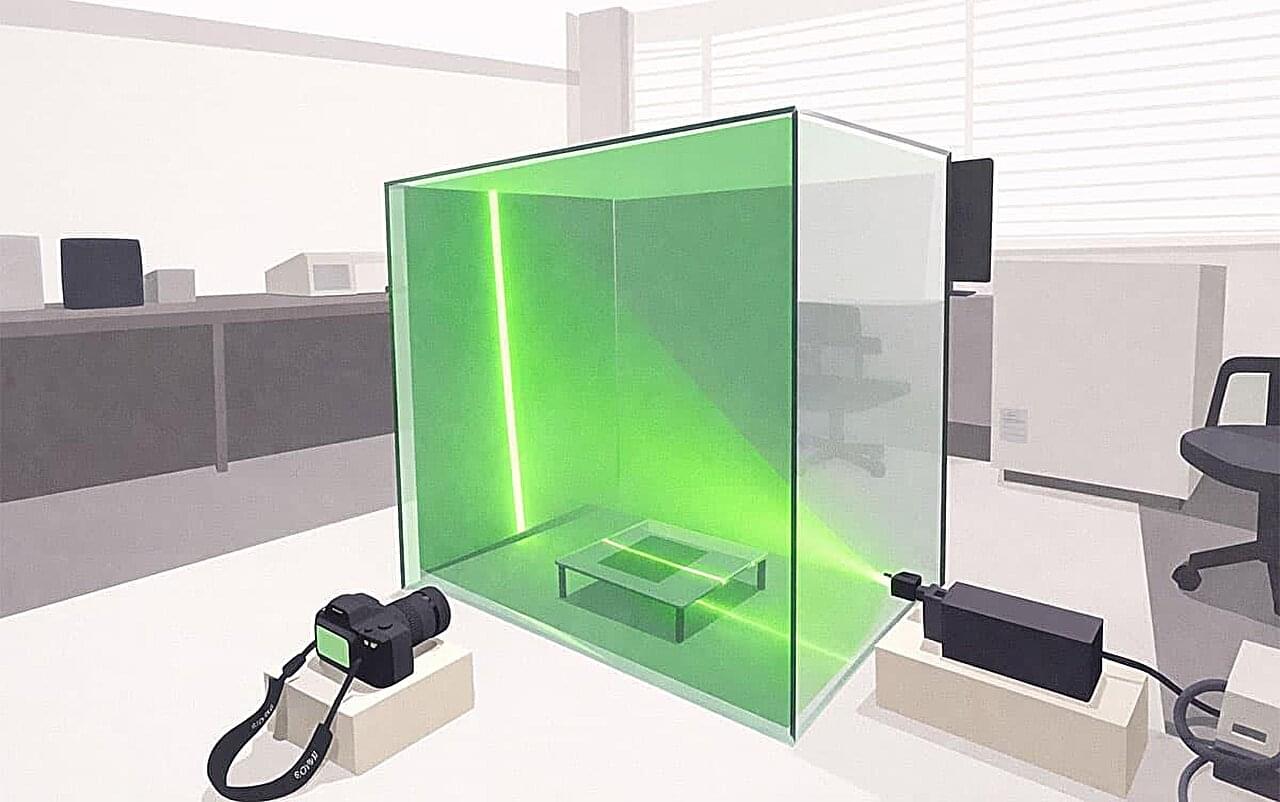
Acoustic streaming generated by airborne ultrasonic phased arrays plays a critical role in the performance of advanced ultrasonic technologies, including midair haptic feedback, odor delivery, and acoustic levitation. Researchers at University of Tsukuba have developed a predictive model for acoustic streaming in phased arrays by integrating three-dimensional acoustic and fluid simulations.
Airborne ultrasonic phased arrays focus ultrasonic waves at prescribed locations in space and dynamically steer them, enabling applications such as noncontact tactile feedback, odor transport, and the levitation of small objects.
Despite the nonnegligible influence of acoustic streaming—steady airflow induced by high-intensity sound fields—on tactile perception and the stability of levitated objects, reliable prediction and modeling of this phenomenon have remained challenging.
SpaceX, in collaboration with xAI, plans to build a lunar base called Moonbase Alpha using advanced technologies such as mass drivers, solar power, and Starship, aiming to make human activity on the moon visible, affordable, and sustainable ##
## Questions to inspire discussion.
Launch Infrastructure Economics.
🚀 Q: What launch costs could SpaceX’s moon infrastructure achieve? A: Mature SpaceX moon operations could reduce costs to $10/kg to orbit and $50/kg to moon surface, enabling $5,000 moon trips for people under 100kg (comparable to expensive cruise pricing), as mentioned by Elon Musk.
⚡ Q: How could lunar mass drivers scale satellite deployment? A: Lunar mass drivers using magnetic rails at 5,600 mph could launch 10 billion tons of satellites annually with 2 terawatts of power, based on 2023 San Jose State study updating 1960s-70s mass driver literature.
Starship Capabilities.

Activation of endothelial cells causes a monocyte recruitment cascade involving rolling, adhesion, activation and transendothelial migration (Figure 1). Selectins, especially P-selectin, mediate the initial rolling interaction of monocytes with the endothelium (32). Monocyte adherence is then promoted by endothelial cell immunoglobulin-G proteins including VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 (32). Potent chemoattractant factors such as MCP-1 and IL-8 then induce migration of monocytes into the subendothelial space (33-35). Ly6hi monocytes, versus Ly6lo, preferentially migrate into the subendothelial space to convert to proinflammatory macrophages in mice (36-38). The enhanced migration of Ly6hi versus Ly6lo monocytes likely results from increased expression of functional P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (39). In addition, the number of blood monocytes originating from the bone marrow and spleen, especially Ly6hi cells, increases in response to hypercholesterolemia (36). Furthermore, hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis increase monocytosis in humans (40,41). Importantly, increased numbers of inflammatory CD14++ CD16+ monocytes independently predicted cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and stroke in patients undergoing elective coronary angiography (42). Intimal macrophages also result from proliferation of monocyte/macrophages, especially in more advanced lesions (43). During the initial fatty streak phase of atherosclerosis (Figure 1), the monocyte-derived macrophages internalize the retained apoB-containing lipoproteins, which are degraded in lysosomes, where excess free cholesterol is trafficked to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to be esterified by acyl CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT), and the resulting cholesteryl ester (CE) is packaged into cytoplasmic lipid droplets, which are characteristic of foam cells (42) (Figure 2) (44,45). Modification of apoB lipoproteins via oxidation and glycation enhances their uptake through a number of receptors not down-regulated by cholesterol including CD36, scavenger receptor A, and lectin-like receptor family (see details below) (Figure 2) (46,47). Enzyme-mediated aggregation of apoB lipoproteins enhances uptake via phagocytosis (Figure 2) (48,49). In addition, native remnant lipoproteins can induce foam cell formation via a number of apoE receptors (LRP1 and VLDLR) (Figure 2) (50,51). Uptake of native LDL by fluid phase pinocytosis may also contribute to foam cell formation (Figure 2) (52,53).
Macrophage Cholesterol Metabolism. Native LDL is recognized by the LDL receptor (LDLR). The LDL is endocytosed and trafficked to lysosomes, where the cholesteryl ester (CE) is hydrolyzed to free cholesterol (FC) by the acid lipase. The FC is transported to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to be esterified by acyl CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT). Increased FC in an ER regulatory pool initiates a signaling cascade resulting in down-regulation of the LDL receptor. Cholesterol regulation of the LDLR prevents foam cell formation via this receptor in the setting of hypercholesterolemia. ApoB containing lipoproteins that also contain apoE (apoE remnants, VLDL) can cause cholesterol accumulation via interaction of apoE with apoE receptors including the LRP1 and the VLDL receptor, which are not regulated by cellular cholesterol. Uptake of native LDL by fluid phase pinocytosis may also contribute to foam cell formation.
Questions to inspire discussion AI Model Performance & Capabilities.
🤖 Q: How does Anthropic’s Opus 4.6 compare to GPT-5.2 in performance?
A: Opus 4.6 outperforms GPT-5.2 by 144 ELO points while handling 1M tokens, and is now in production with recursive self-improvement capabilities that allow it to rewrite its entire tech stack.
🔧 Q: What real-world task demonstrates Opus 4.6’s agent swarm capabilities?
A: An agent swarm created a C compiler in Rust for multiple architectures in weeks for **$20K, a task that would take humans decades, demonstrating AI’s ability to collapse timelines and costs.
🐛 Q: How effective is Opus 4.6 at finding security vulnerabilities?