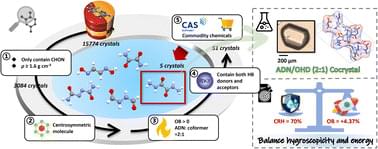
Researchers developed a faster, more targeted way to design ionic cocrystals (ICCs) of the energetic oxidizer ammonium dinitramide (ADN).
Using high‑throughput virtual screening with the CSD Python interface and RDKit, followed by quick experimental tests, they identified and synthesized a new ADN cocrystal with oxalyl dihydrazide (OHD).
Read the full paper here.
Ionic cocrystals (ICCs) offer a promising strategy to tailor the properties of energetic oxidizers like ammonium dinitramide (ADN). However, the current design process of ADN-based ICCs remains heavily reliant on empirical trial-and-error methods, which significantly impedes development efficiency and presents a fundamental challenge in balancing energy performance and hygroscopicity. Herein, we leverage a high-throughput virtual screening strategy to identify coformers of ADN cocrystals that meet requirements for structures and performances, integrating the CSD Python interface and RDKit via custom Python scripts. Combined with rapid experimental screening, the first ADN cocrystal with balanced hygroscopicity and energy is successfully synthesized using a commercially available coformer oxalyl dihydrazide (OHD). The resulting ADN/OHD cocrystal exhibits a positive oxygen balance of +4.37%, enhanced moisture resistance and thermal stability. Moreover, compared to pure ADN, ADN/OHD delivers a 27.6% higher specific impulse, along with excellent green processability and engineering scalability. This work establishes a rational and scalable approach for developing perchlorate-free oxidizer cocrystals with well-balanced properties, and also provides a generalizable paradigm for the performance-oriented design of ICCs.