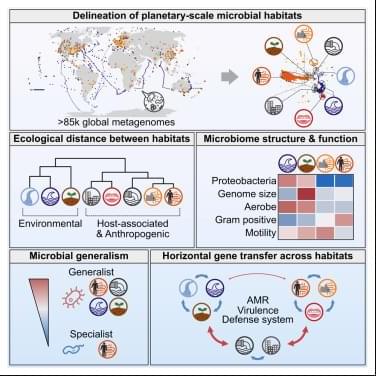
The sun is the basis for photosynthesis, but not all plants thrive in strong sunlight. Strong sunlight constrains plant diversity and plant biomass in the world’s grasslands, a new study shows. Temperature, precipitation, and atmospheric nitrogen deposition have less impact on plant diversity. These results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences by a research team led by Marie Spohn from the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences.
The steppes of North America, the Serengeti savanna, the Svalbard tundra and natural pastures in the Alps are examples of habitats that are described as grasslands, with the common feature that there are no trees and the vegetation is dominated by grasses and other herbaceous plants. The diversity of plant species in these grasslands varies considerably, but the question of what controls plant diversity has challenged researchers for decades.
Last year, in a study on grasslands, Spohn from SLU and colleagues found that soil properties and climate factors, such as temperature, did not explain variations in plant diversity. “This finding surprised me,” says Spohn. “And that’s when I started wondering about the importance of sunlight for plant diversity in grasslands and decided to start a new project that would explore this relationship.”