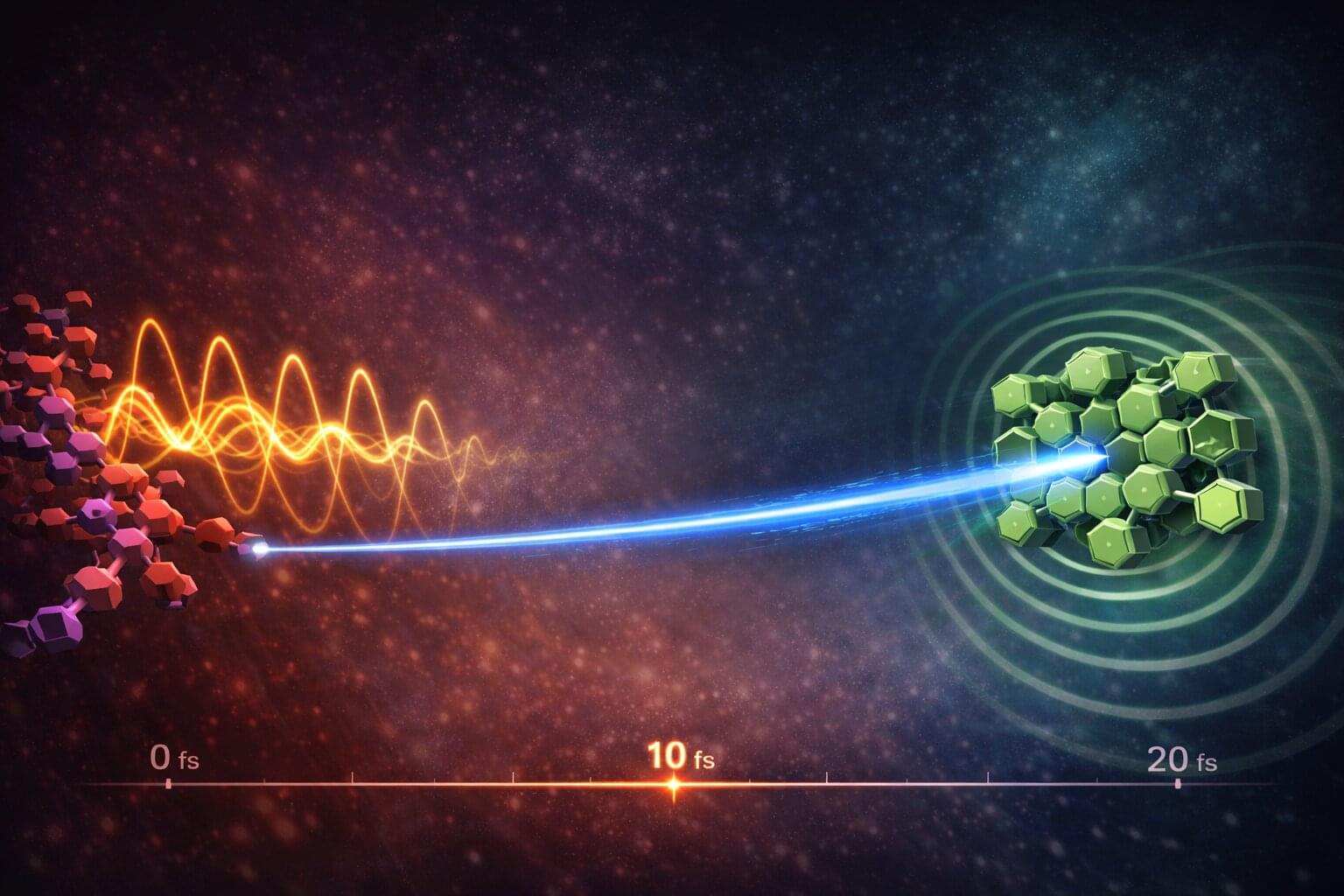
Electrons can be “kicked across” solar materials at almost the fastest speed nature allows, scientists have discovered, challenging long-held theories about how solar energy systems work. The finding could help researchers design more efficient ways of harvesting sunlight and converting it into electricity. The research is published in Nature Communications.
In experiments capturing events lasting just 18 femtoseconds —less than 20 quadrillionths of a second—researchers at the University of Cambridge observed charge separation happening within a single molecular vibration.
“We deliberately designed a system that—according to conventional theory—should not have transferred charge this fast,” said Dr. Pratyush Ghosh, Research Fellow, at St John’s College, Cambridge, and first author of the study. “By conventional design rules, this system should have been slow, and that’s what makes the result so striking.