Real-time, single-cell imaging reveals ERK signaling dynamics in response to T cell receptor stimulation.

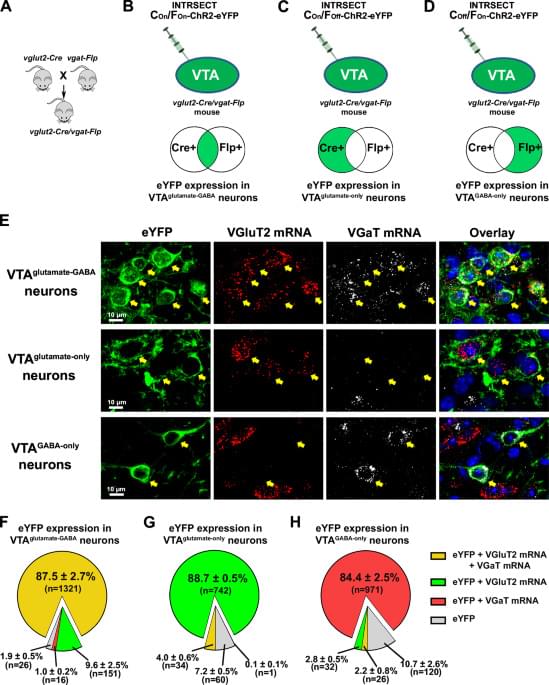
The way the brain develops can shape us throughout our lives, so neuroscientists are intensely curious about how it happens. A new study by researchers in The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT that focused on visual cortex development in mice, reveals that an important class of neurons follows a set of rules that while surprising, might just create the right conditions for circuit optimization.
During early brain development, multiple types of neurons emerge in the visual cortex (where the brain processes vision). Many are “excitatory,” driving the activity of brain circuits, and others are “inhibitory,” meaning they control that activity. Just like a car needs not only an engine and a gas pedal, but also a steering wheel and brakes, a healthy balance between excitation and inhibition is required for proper brain function.
During a “critical period” of development in the visual cortex, soon after the eyes first open, excitatory and inhibitory neurons forge and edit millions of connections, or synapses, to adapt nascent circuits to the incoming flood of visual experience. Over many days, in other words, the brain optimizes its attunement to the world.
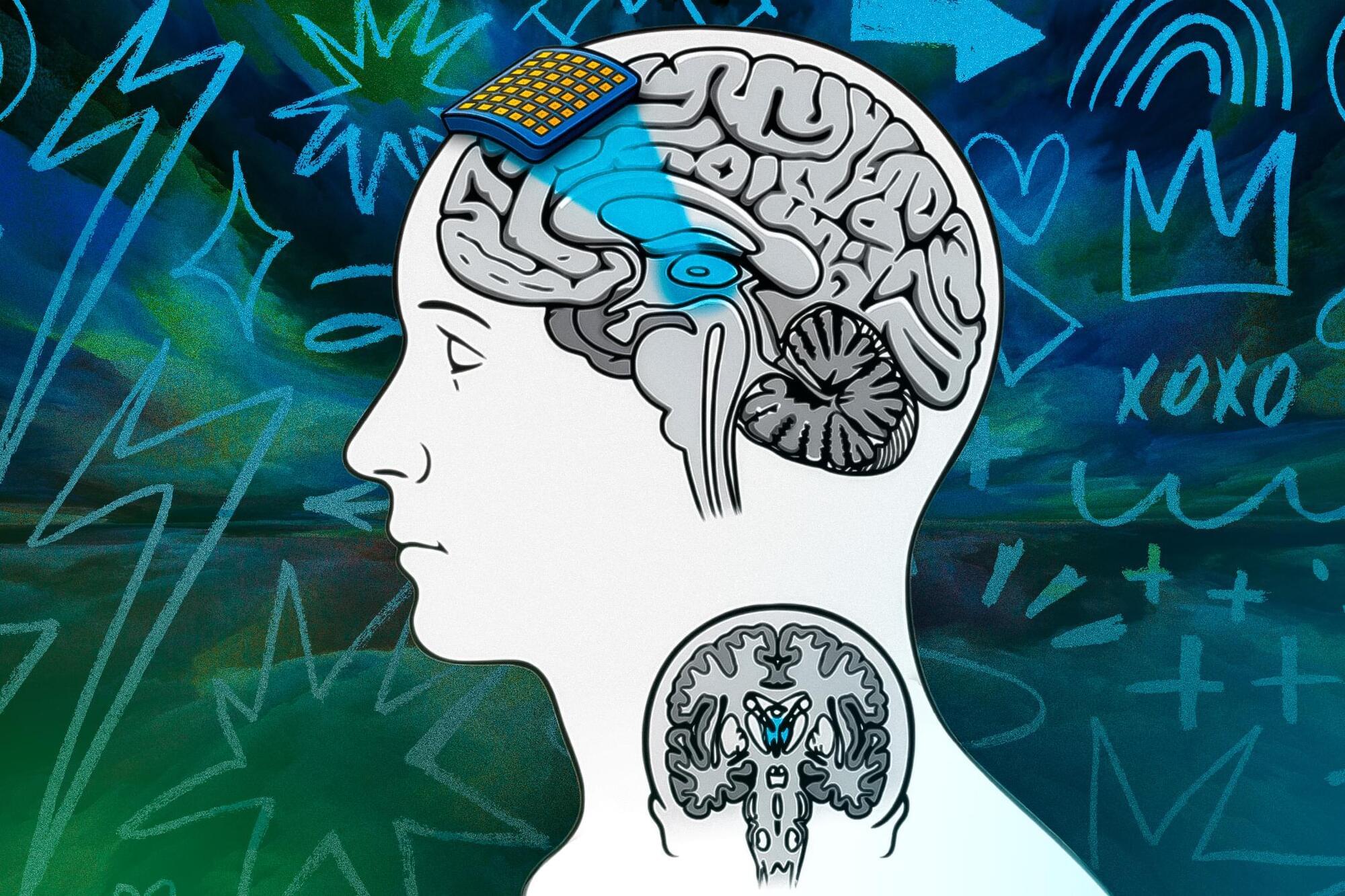
The technology has entered use in recent years, but it isn’t yet fully integrated into research. Now, two MIT researchers are planning experiments with it, and have published a new paper they term a “roadmap” for using the tool to study consciousness.
“Transcranial focused ultrasound will let you stimulate different parts of the brain in healthy subjects, in ways you just couldn’t before,” says Daniel Freeman, an MIT researcher and co-author of a new paper on the subject. “This is a tool that’s not just useful for medicine or even basic science, but could also help address the hard problem of consciousness. It can probe where in the brain are the neural circuits that generate a sense of pain, a sense of vision, or even something as complex as human thought.”
Transcranial focused ultrasound is noninvasive and reaches deeper into the brain, with greater resolution, than other forms of brain stimulation, such as transcranial magnetic or electrical stimulation.
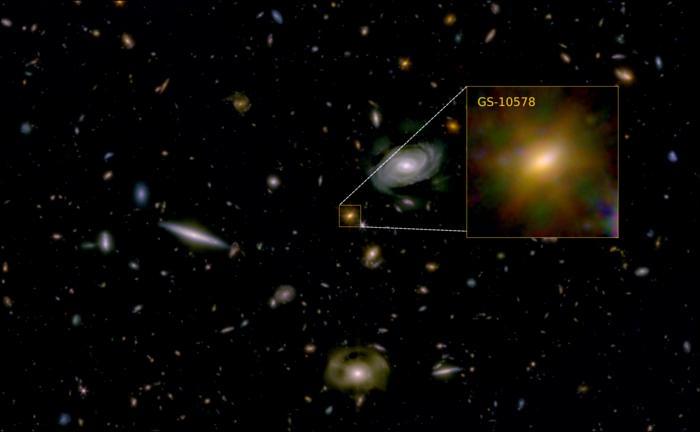
Dr. Francesco D’Eugenio: “The galaxy looks like a calm, rotating disc. That tells us it didn’t suffer a major, disruptive merger with another galaxy.”
What were galaxies like in the early universe? This is what a recent study published in Nature Astronomy hopes to address as an international team of scientists investigated the formation and evolution of the first galaxies after the Big Bang. This study has the potential to help scientists better understand the conditions of the early universe and what this could mean for the development of life throughout the cosmos.
For the study, the researchers used a combination of data obtained from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and the Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA) located in Chile to examine “Pablo’s Galaxy” (officially designated as GS-10578) and is estimated to have existed approximately three billion years after the Big Bang. For context, the Big Bang is estimated to have occurred approximately 13.8 billion years ago. Using this data, the researchers discovered that Pablo’s Galaxy had a very short lifespan due to a lack of star formation from the galaxy’s black hole heated all of the cold gas, preventing new stars from forming.

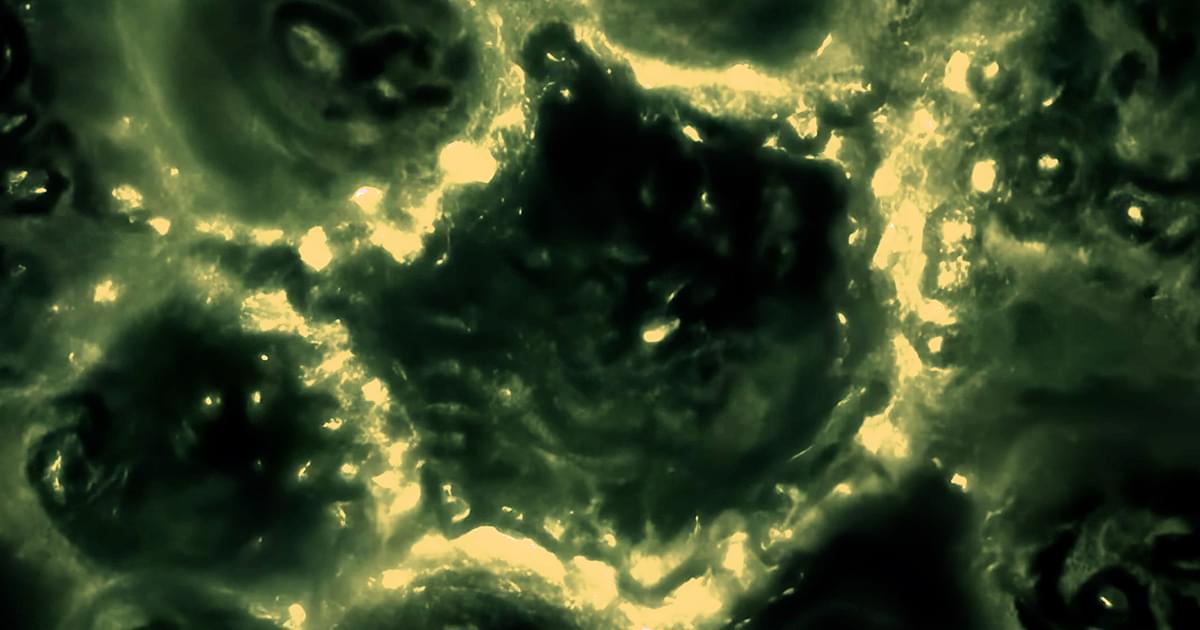
According to the new results, as epithelial tissue grows, cells are packed more tightly together, which increases the electrical current flowing through each cell’s membrane. A weak, old, or energy-starved cell will struggle to compensate, triggering a response that sends water rushing out of the cell, shriveling it up and marking it for death. In this way, electricity acts like a health checkup for the tissue and guides the pruning process.
“This is a very interesting discovery — finding that bioelectricity is the earliest event during this cell-extrusion process,” said the geneticist GuangJun Zhang of Purdue University, who studies bioelectrical signals in zebra fish development and wasn’t involved in the study. “It’s a good example of how a widening electronic-signaling perspective can be used in fundamental biology.”
The new discovery adds to the growing assortment of bioelectrical phenomena that scientists have discovered playing out beyond the nervous system, from bacteria swapping signals within a biofilm to cells following electric fields during embryonic development. Electricity increasingly appears to be one of biology’s go-to tools for coordinating and exchanging information between all kinds of cells.

Scientists have identified a promising target for treatment of a devastating autoimmune disease affecting the brain.
The discovery could lead to the development of new therapies for a disease triggered by an attack on one of the key neurotransmitter receptors in the brain, the NMDA receptor. It also raises the potential for a blood test to detect a signal of the condition and enable earlier treatment with existing therapies.
The study from Oregon Health & Science University is published in Science Advances.
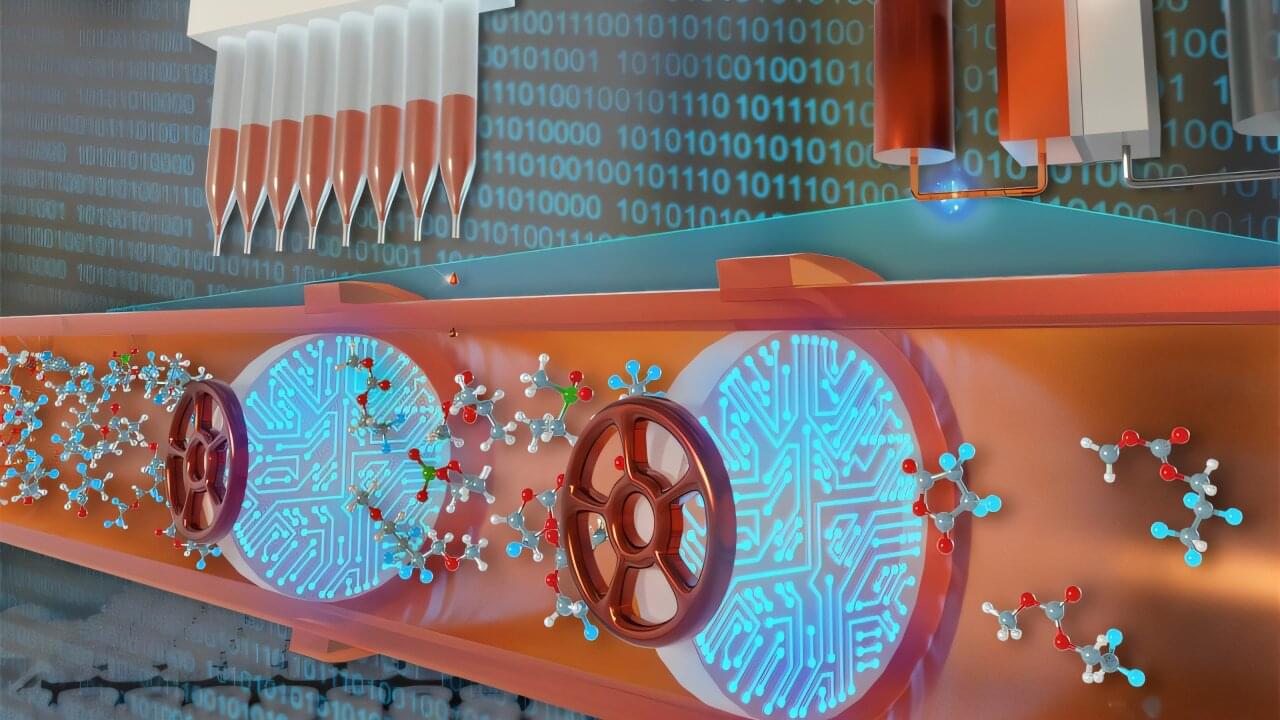
In numerous scientific fields, high-throughput experimentation methods combined with artificial intelligence (AI) show great promise to accelerate innovation and scientific discovery.
Case in point: In just five months, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory used robotics, automation and AI to conduct more than 6,000 experiments on chemicals in a type of rechargeable energy storage called organic redox flow batteries (RFBs). Such a monumental effort would have taken five to eight years with traditional experimentation.
Organic RFBs use carbon-based—that is, organic—molecules instead of traditional metal ions. Through their work, the researchers made a crucial finding about these batteries: A fundamental barrier at the molecular level limits their stability. The insight is expected to inspire exciting new directions in battery chemical research.

Bird Flu 2026
Researchers analyzed 17,500 genomes using Bayesian phylodynamics. Mapped origin, spread, and evolutionary timeline with precision.
The infrastructure failure: Of 1,722 D1.1 sequences, 9% have complete metadata (date + location).
We’re tracking a super-spreader blind.
#OpenScience #DataScience
“Avian Flu in North America: The D1.1 Evolutionary Leap” explores the emergence of a game-changing H5N1 virus variant that has fundamentally altered North America’s disease landscape since mid-2024. Through accessible explanation of cutting-edge genomic science, this episode reveals how the D1.1 genotype achieved unprecedented spread, infected all seven documented host categories including humans, and represents a major evolutionary shift. The podcast examines the massive computational effort behind tracking viral evolution, exposes critical gaps in our surveillance infrastructure, and confronts a paradigm-shifting reality: the Americas have become a primary engine of H5N1 evolution, reversing decades of global health assumptions.