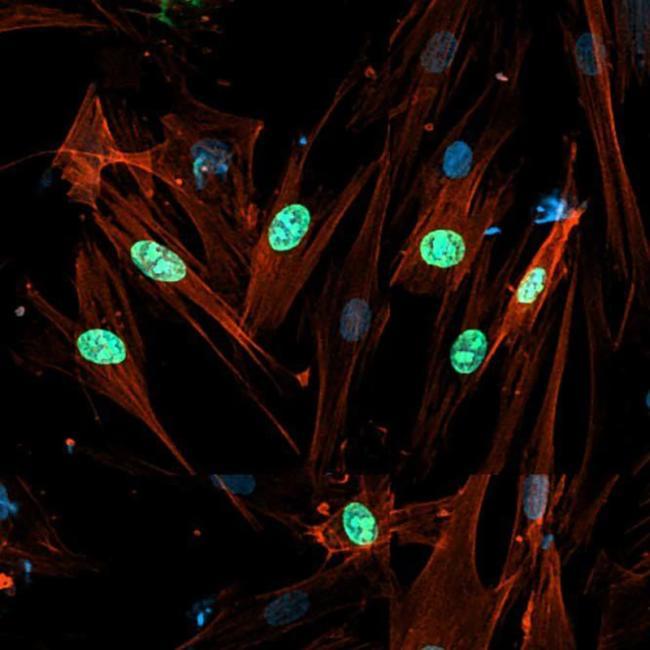
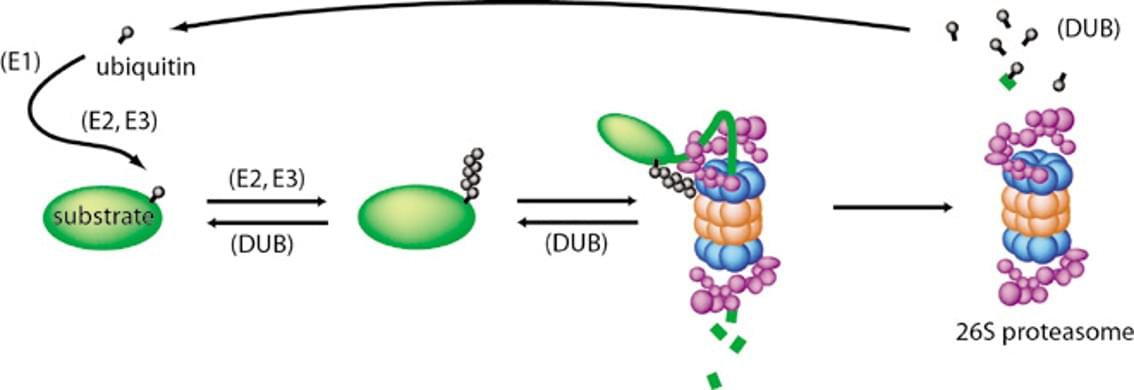
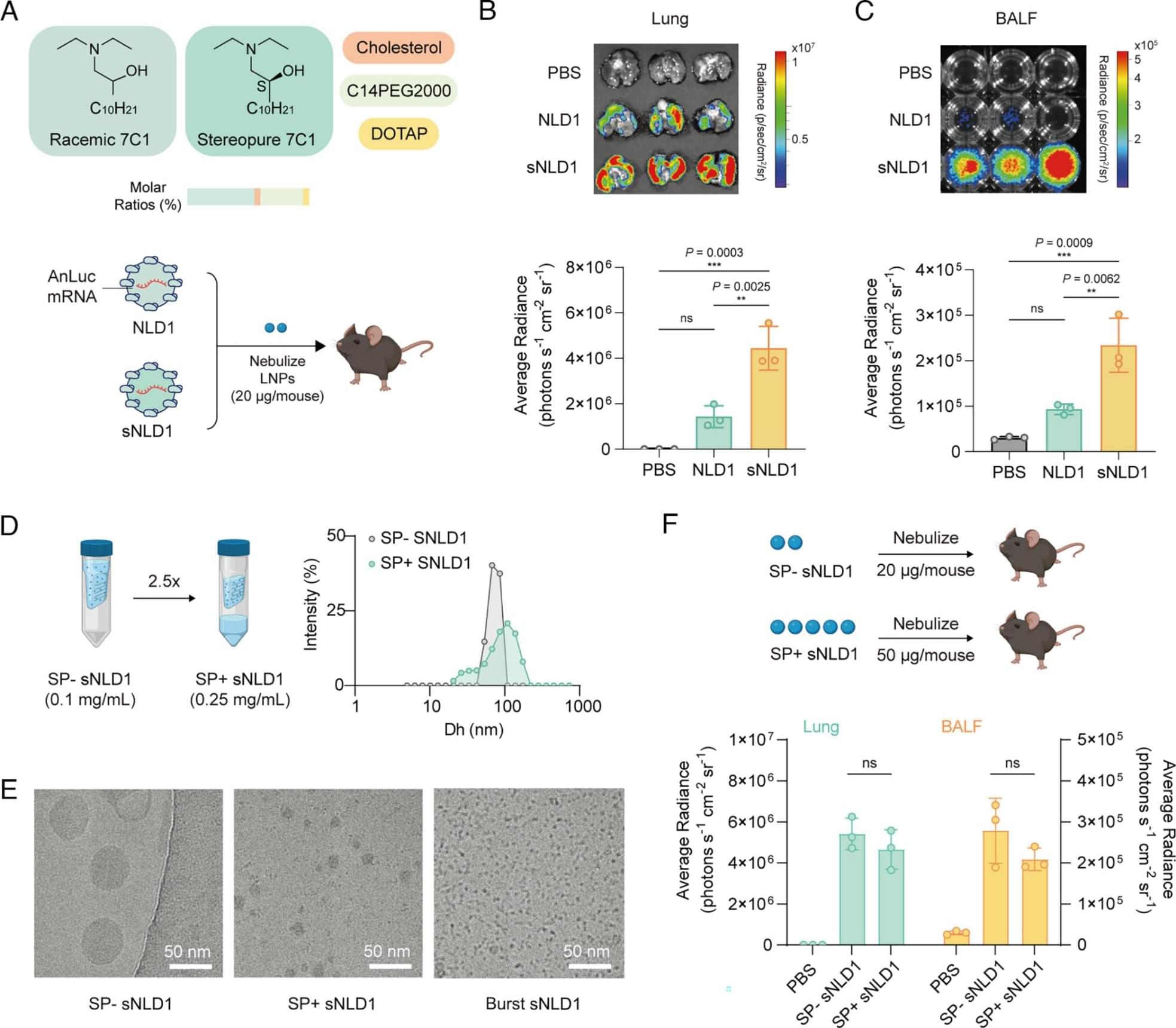
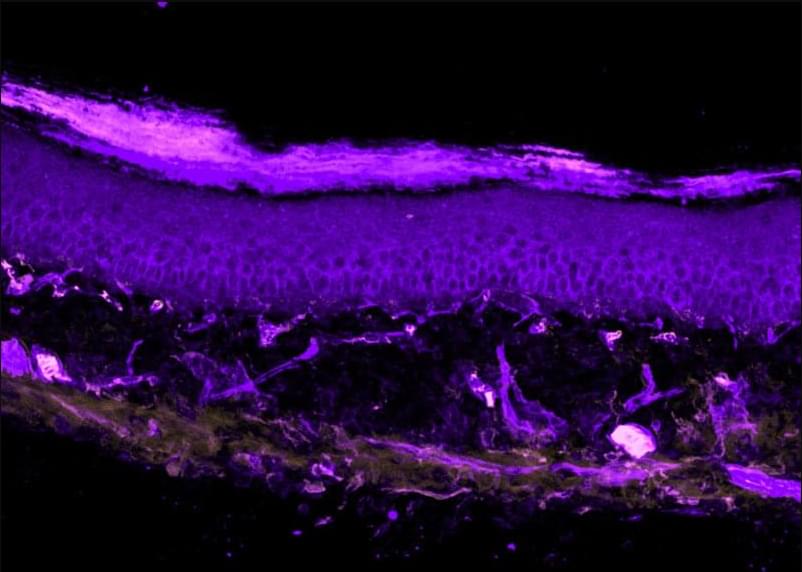
Although cancer is a common cause of death in domestic cats, little is known about the range of cancer genes in cat tumors, and how this range might compare with the oncogenome in people.
Now, researchers in Science have sequenced cancer genes in 493 samples from 13 different types of feline cancer and matched healthy control tissue, gaining a clearer picture of the cat oncogenome and comparing the genes to known cancer-causing mutations in humans.
Cancer is a common cause of morbidity and mortality in domestic cats. Because the mutational landscape of domestic cat tumors remains uncharacterized, we performed targeted sequencing of 493 feline tumor–normal tissue pairs from 13 tumor types, focusing on the feline orthologs of ~1000 human cancer genes. TP53 was the most frequently mutated gene, and the most recurrent copy number alterations were loss of PTEN or FAS or gain of MYC. By identifying 31 driver genes, mutational signatures, viral sequences, and tumor-predisposing germline variants, our study provides insight into the domestic cat oncogenome. We demonstrate key similarities with the human oncogenome, confirming the cat as a valuable model for comparative studies, and identify potentially actionable mutations, aligning with a “One Medicine” approach.