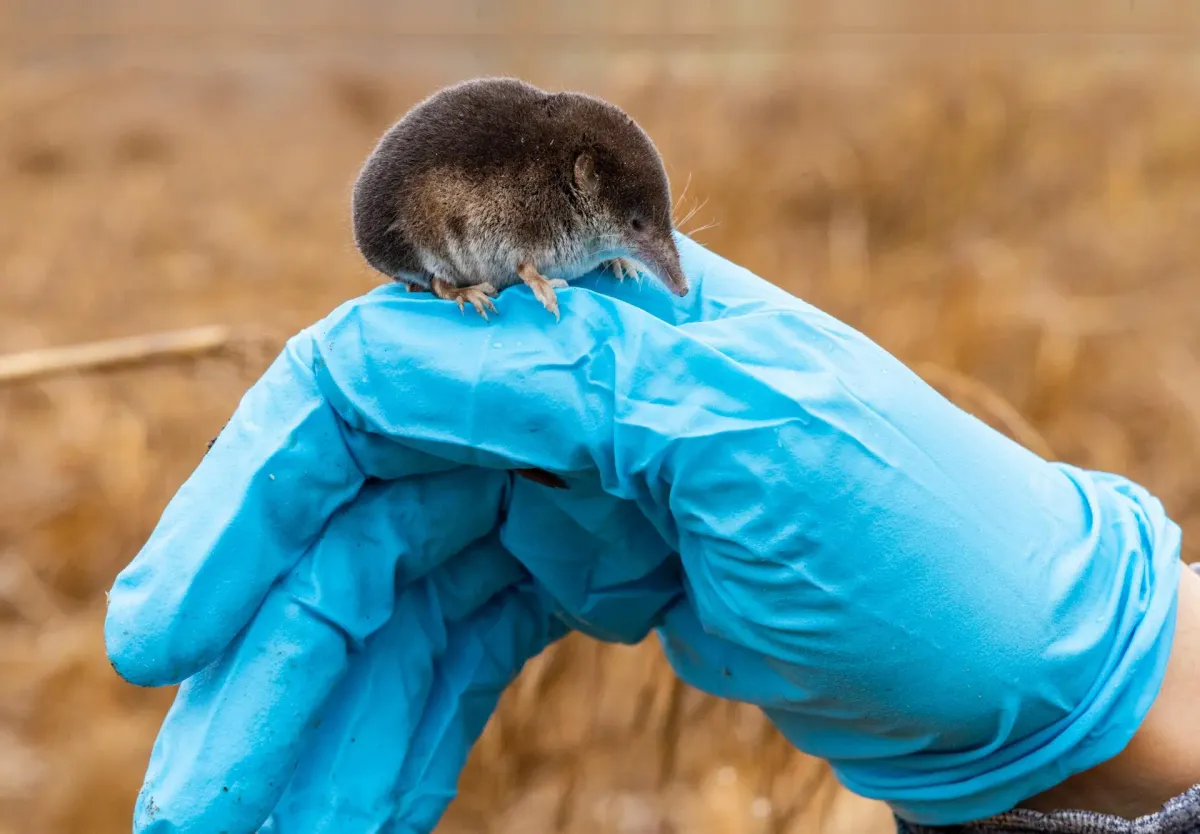
Researchers discovered that the common shrew can shrink itself during the winter
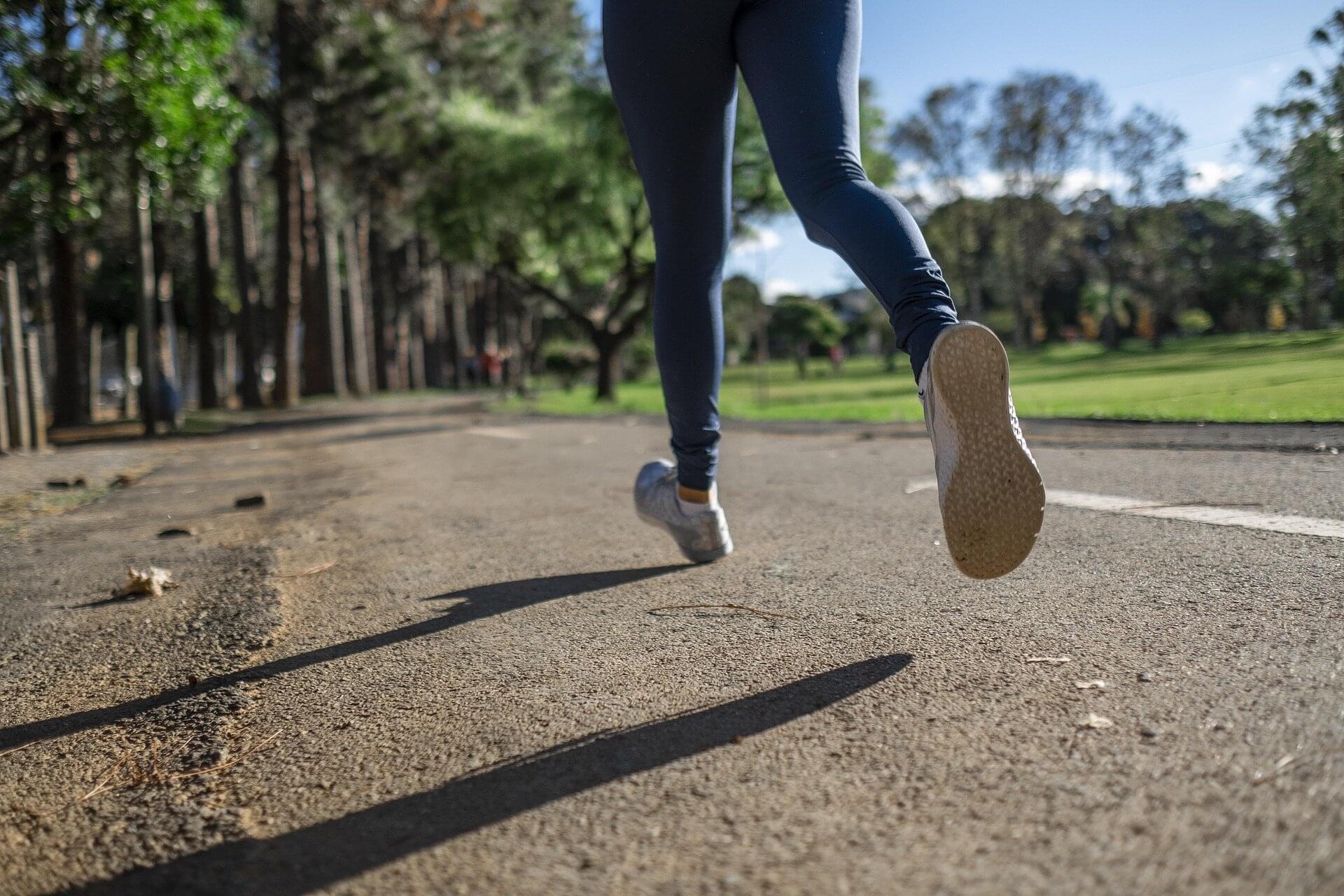




As many of us embark on an exercise or gym routine for the new year, research reveals that just 10 minutes of intense exercise could help fight cancer.
Short bursts of energetic activity can trigger rapid molecular changes in the bloodstream, shutting down bowel cancer growth and speeding up DNA damage repair, a new study has shown.
Researchers at Newcastle University have found that exercise increases the concentration of several small molecules in the blood—many linked to reducing inflammation, improving blood vessel function, and metabolism.
Can Alzheimer’s be reversed? Dr. Insoo Hyun explains how scientists at Case Western Reserve University are exploring that possibility by restoring NAD+, a vi…
The androids of the future will be the distant results of synthetic biology and not silicon.
🚀 Step into a world of boundless innovation as we take you on a journey through the awe-inspiring technologies that await humanity in the 22nd century! 🌌 From advancements in space exploration to mind-boggling leaps in artificial intelligence, this captivating video offers a glimpse into the cutting-edge breakthroughs that will redefine the very fabric of human existence.
🌐 Witness the birth of extraterrestrial civilizations as humans venture further into space, exploring distant planets and establishing self-sustaining colonies. Experience the seamless integration of artificial intelligence into our daily lives, transforming how we interact with technology and creating new possibilities for societal progress. Prepare to be amazed by quantum computing’s extraordinary power, revolutionizing problem-solving and opening doors to scientific discoveries previously deemed impossible.
🌿 Delve into the world of sustainable marvels, where eco-friendly innovations mend our relationship with the environment and pave the way for a greener, more harmonious future. Explore the ethical implications of biotechnology advancements, which offer insights into longevity and human potential. This video paints an inspiring picture of the limitless possibilities and profound transformations that lie ahead in the remarkable world of 22nd-century technologies. Like, share, and subscribe to our channel for more captivating glimpses of the ever-evolving world of tomorrow. 🌟🔮🌠 #FutureTechnologies #22ndCenturyInnovations #EmbracingTomorrow

PersonaPlex runs in a dual stream configuration. One stream tracks user audio, the other stream tracks agent speech and text. Both streams share the same model state, so the agent can keep listening while speaking and can adjust its response when the user interrupts. This design is directly inspired by Kyutai’s Moshi full duplex framework.
NVIDIA Researchers released PersonaPlex-7B-v1, a full duplex speech to speech conversational model that targets natural voice interactions with precise persona control.
Conventional voice assistants usually run a cascade. Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) converts speech to text, a language model generates a text answer, and Text to Speech (TTS) converts back to audio. Each stage adds latency, and the pipeline cannot handle overlapping speech, natural interruptions, or dense backchannels.
PersonaPlex replaces this stack with a single Transformer model that performs streaming speech understanding and speech generation in one network. The model operates on continuous audio encoded with a neural codec and predicts both text tokens and audio tokens autoregressively. Incoming user audio is incrementally encoded, while PersonaPlex simultaneously generates its own speech, which enables barge in, overlaps, rapid turn taking, and contextual backchannels.

Sharing my latest Forbes article: by Chuck Brooks.
Thanks for reading and sharing!
#cybersecurity #tech #ai #quantum #space Forbes
Artificial intelligence and quantum computing are no longer speculative technologies. They are reshaping cybersecurity, economic viability, and managing risk in real time.
When we talk about the universe, we usually imagine space filled with galaxies, stars, and matter expanding endlessly in all directions. It feels natural to think of the universe as a vast container — a place where everything exists. But modern theoretical physics suggests that this picture may be deeply misleading.
In this video, we explore a more fundamental question: what is the universe really made of? Is it space? Matter? Energy? Or something far more abstract than our everyday intuition allows?
Drawing on ideas associated with Leonard Susskind, this long-form exploration challenges the assumption that the universe is a physical stage where reality takes place. Instead, physics increasingly points toward a universe defined not by objects and locations, but by information, relationships, and boundaries.
Black hole physics, quantum theory, and modern cosmology have forced scientists to rethink the foundations of reality. In some of the deepest descriptions of nature, space and time no longer appear as fundamental ingredients. What we experience as a three-dimensional universe may be an emergent structure — a convenient description rather than the true underlying reality.
Rather than focusing on equations, this video emphasizes intuition and conceptual understanding. Through thought experiments and simple analogies, we examine why the universe feels like a place, why that picture works so well at human scales, and why it may break down at the most fundamental level.
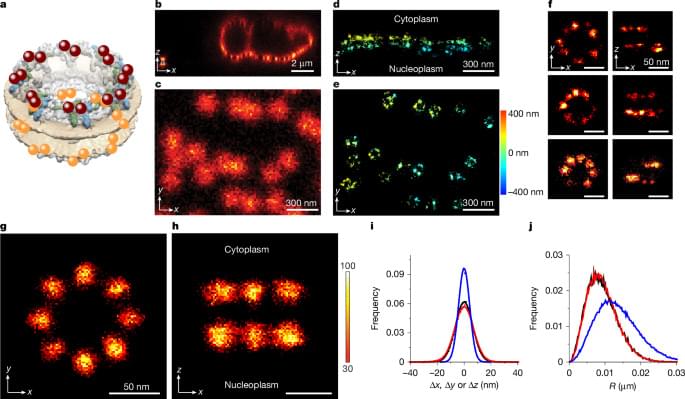
Interesting paper where Sau et al. used MINFLUX super-resolution microscopy to track the passage of proteins across nuclear pores. They found that import and export pathways did not take separate tracks and that the proteins almost completely avoided the central region of the pore during [ https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-08738-0](https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-08738-0)
High spatiotemporal precision tracking using 3D MINFLUX shows that nuclear import and export occur in overlapping regions of the central pore, providing insight into transport across the nuclear pore complex.