MIT Associate Professor Phillip Isola studies the ways in which intelligent machines “think” and perceive the world, in an effort to ensure AI is safely and effectively integrated into human society.
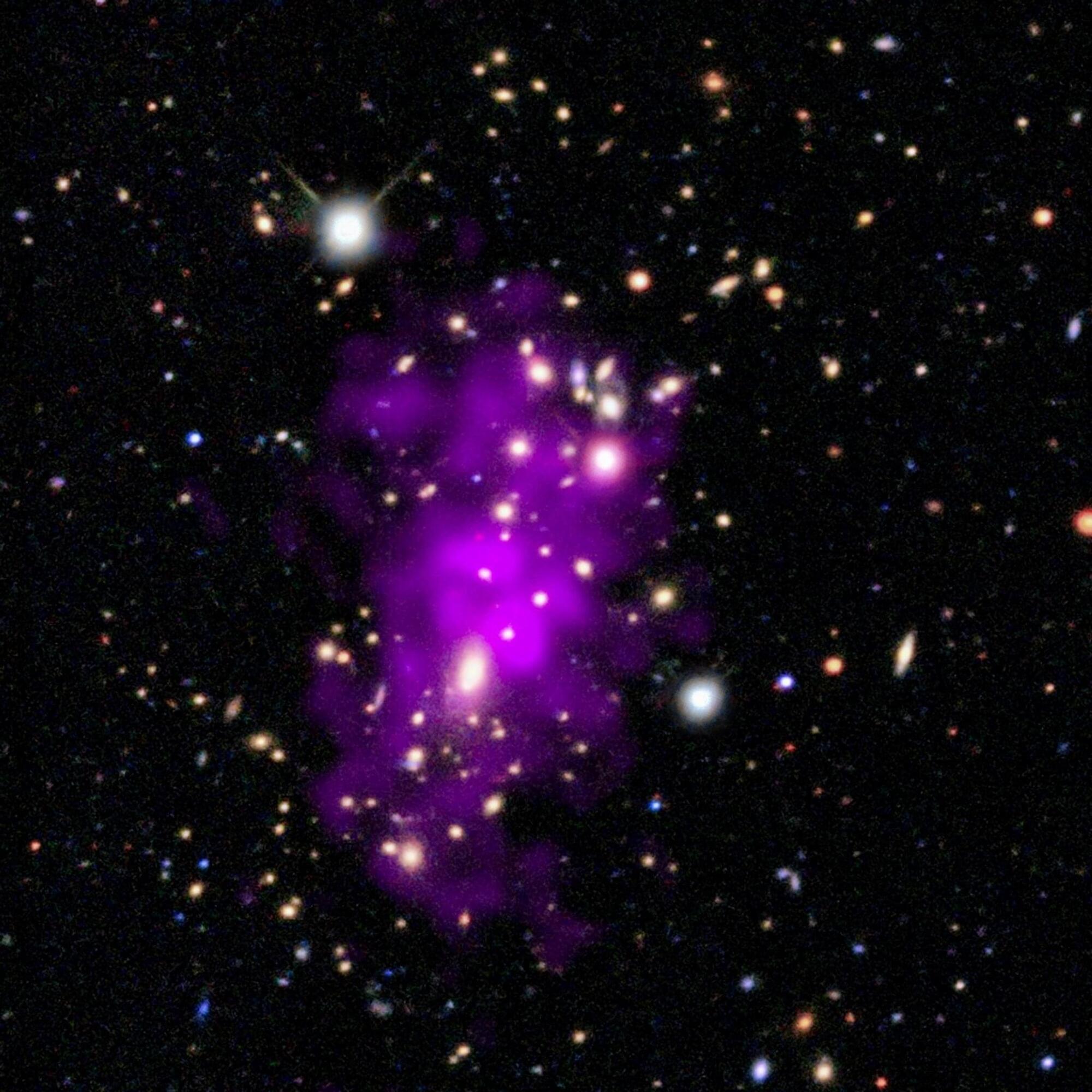



Celebrate the New Year with the “Champagne Cluster,” a galaxy cluster seen in this new image from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and optical telescopes.
Astronomers discovered this galaxy cluster on Dec. 31, 2020. The date, combined with the bubble-like appearance of the galaxies and the superheated gas seen with Chandra observations (represented in purple), inspired the scientists to nickname the galaxy cluster the Champagne Cluster, a much easier-to-remember name than its official designation of RM J130558.9+263048.4.
The new composite image shows that the Champagne Cluster is actually two galaxy clusters in the process of merging to form an even larger cluster.
(Cell Reports 42, 112925; August 29, 2023)
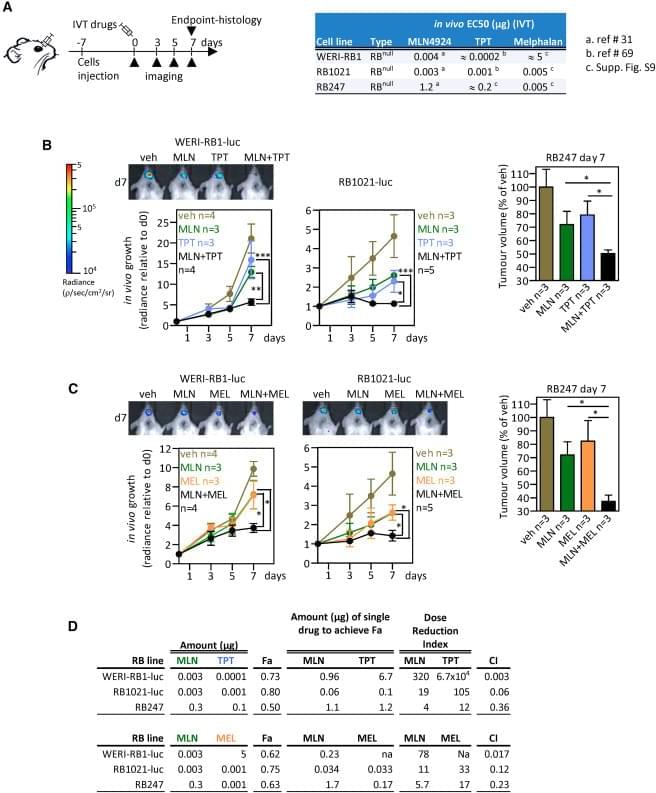
The authors were made aware of an image duplication in their published paper. The representative photo in Figure 5B is the same as the image in Fig. 4g of Aubry et al., 2020, Oncogene 39, p. 5338–5357. The assays involved treating xenografts of the RB1021-luc retinoblastoma line, using either MLN4924 (MLN) and topotecan (TPT; Cell Reports) or the RAD51 inhibitor B02 and TPT (Oncogene). These assays were run and analyzed concurrently in 2018. For the Xenogen measurements of tumor growth, we first quantified the signal and recorded the values in tables. After all the mice were assessed, appropriate mice were placed together for representative images. Thus, the quantification, which was performed correctly, and acquisition/storage of the representative image, which was not, were performed separately. Our review of image files revealed that the representative image of the B02 + TPT series of mice was accidentally duplicated using the file name for the MLN + TPT series of mice.


Creating mini mitochondria factories helped recharge damaged cells in a dish, providing proof-of-concept work that could pave the way to new regenerative medicine therapies
Wang and Wu et al. identify soluble interleukin-6 receptor (sIL-6R) as a key exerkine determining the efficacy of exercise in diabetes prevention, which is modulated by microbiome-dependent leucine through a gut-adipose tissue axis. Pharmacological or dietary interventions targeting adipocyte-secreted sIL-6R may help to improve the metabolic outcomes in those exercise non-responders.
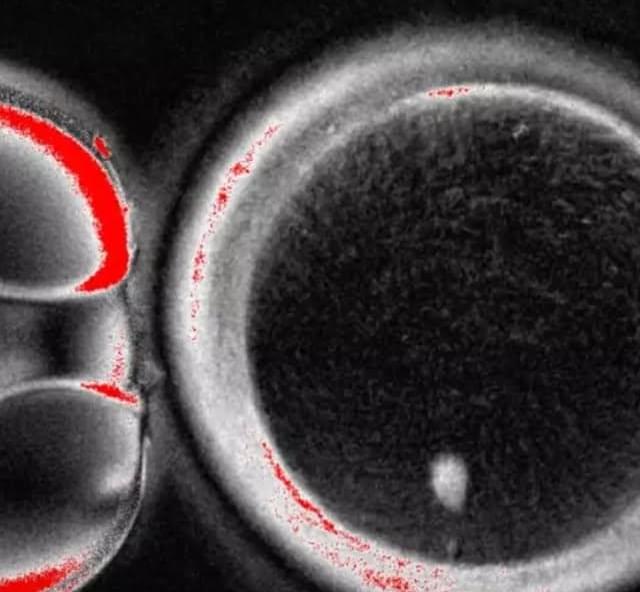
Marking a first in reproductive science. The process involved transferring skin cell nuclei into donated eggs and stimulating them to behave like natural oocytes, some of which developed into early embryos in the lab. While none progressed beyond a few days and major safety hurdles remain, the study suggests a future path that could one day help women with infertility and expand options in reproductive medicine.
#science #medicine #genetics #fertility #research

Researchers have created a protein that can detect the faint chemical signals neurons receive from other brain cells. By tracking glutamate in real time, scientists can finally see how neurons process incoming information before sending signals onward. This reveals a missing layer of brain communication that has been invisible until now. The discovery could reshape how scientists study learning, memory, and brain disease.
