Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 122 (51) e2518999122, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2518999122 (2025).
Copy.

Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 122 (51) e2518999122, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2518999122 (2025).
Copy.
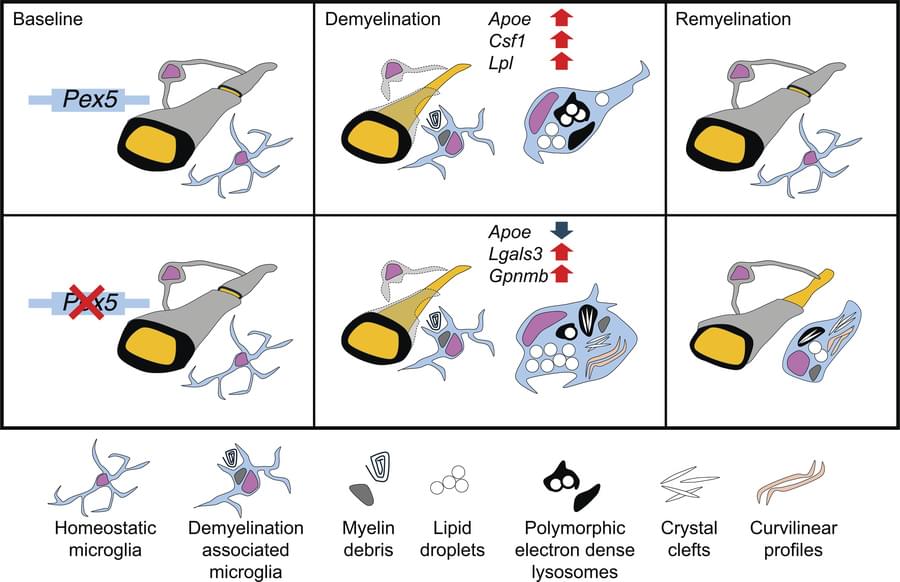
Jian Hu & team use mouse models to show peroxisomes license myelin debris degradation in myeloid cells, which enables debris clearance and remyelination after myelin damage:
The figure shows TEM micrographs of phagocytes in which PEX5 loss (bottom panel) aggregates lipid droplets and crystal accumulation.
1Department of Cancer Biology, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas, USA.
2University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center UTHealth Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Houston, Texas, USA.
3University of Puerto Rico School of Medicine, San Juan, Puerto Rico.

Tubular biomarkers linked to sodium avidity in heart failure—may give insights into causes of diuretic resistance. @UCSDCardiology
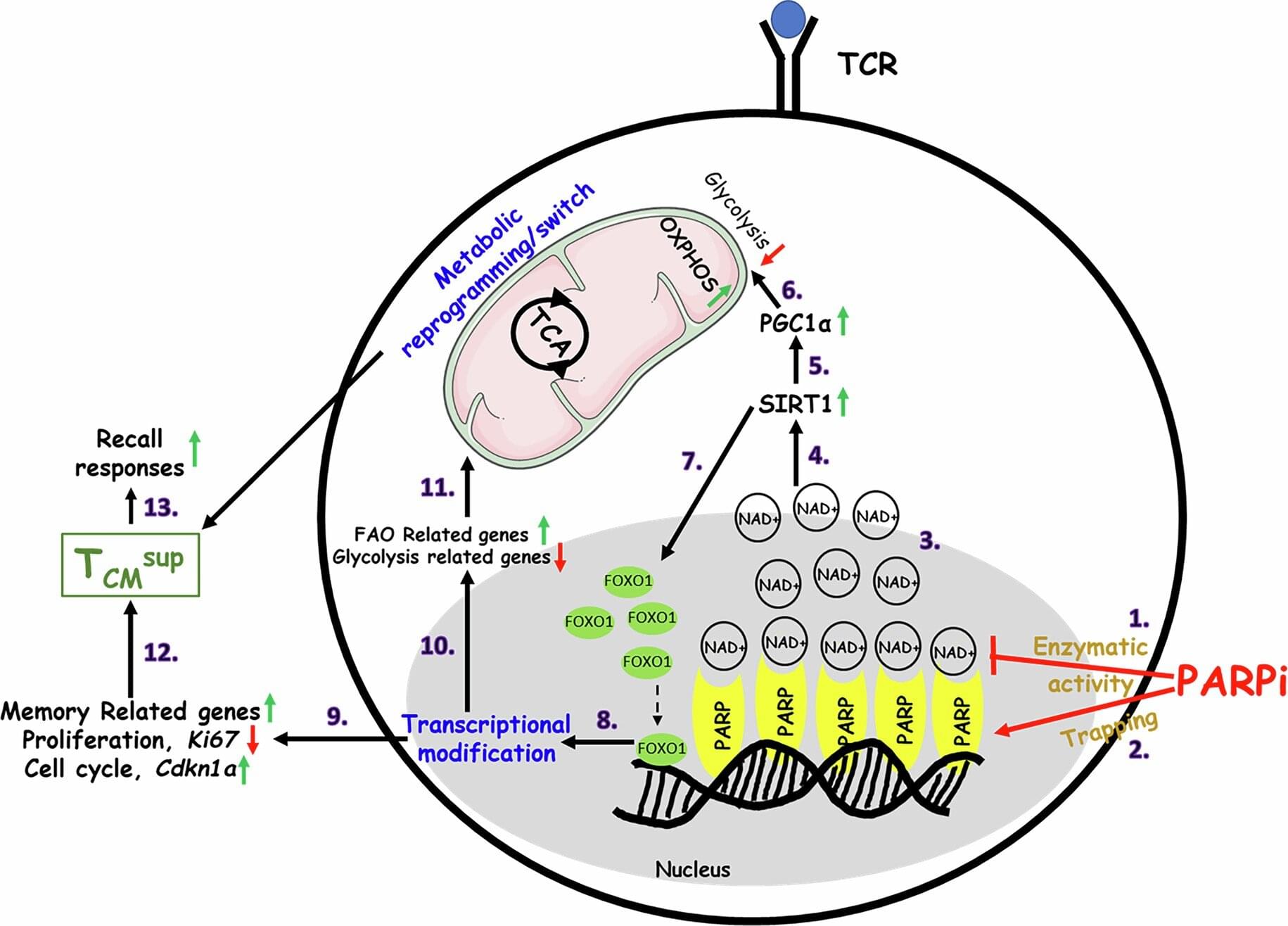
Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers have identified a new way to reprogram T cells, which are infection and tumor-fighting white blood cells, so that they have a superior memory, thereby making them more effective in killing cancer cells.
The finding, published January 12, 2026, in Nature Immunology, amplifies a known strategy of blocking the cellular activity of PARP, an enzyme that detects DNA abnormalities in cells and repairs them.
“This opens the door to a new area of research in understanding how our immune system works, and as importantly, it opens the way for the development of new strategies for the treatment of cancer,” says Samir N. Khleif, MD, director of The Center for Advanced Immunotherapy Research and the director of Loop Immuno-Oncology Research Laboratory at Georgetown’s Lombardi.
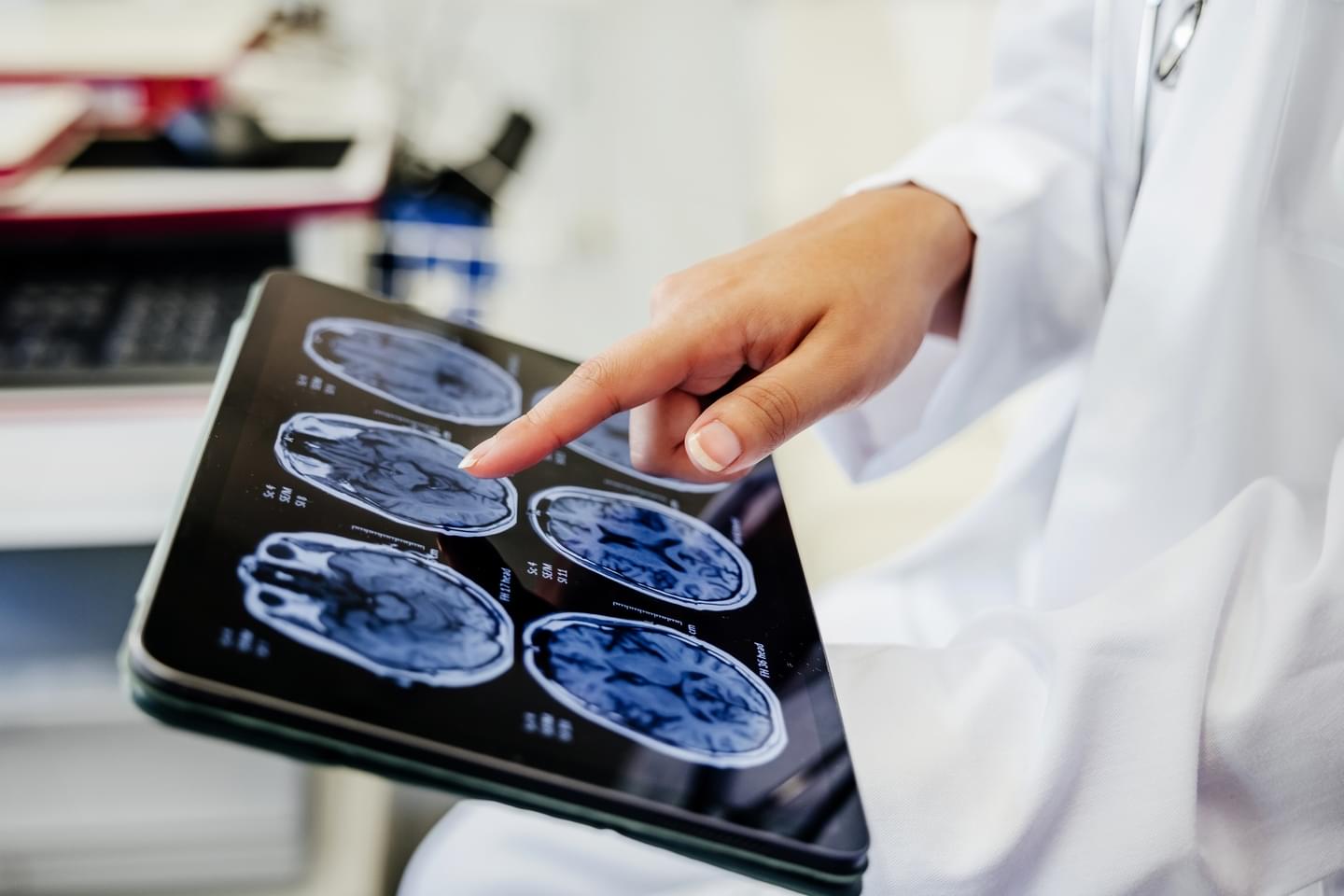

The devastating illness deteriorates your brain’s ability to think, remember things and can even alter your behaviour.
While some studies have discovered that engaging in a pretty gross habit or reaching a daily step count can reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease (AD), for over a century, scientists have considered it an irreversible illness. This is why research has focused on preventing or slowing its progression, rather than recovery.
However, a new study challenges this long-held belief by testing whether brains already severely afflicted with advanced AD could recover.
Building on the foundational Nobel Prize-winning work, researchers at Berkeley Lab and its DOE user facilities continue to push MOF technology to address major global challenges.
For example, at the ALS, a team led by Yaghi traced how MOFs absorb water and engineered new versions to harvest water from the air more efficiently – an important step in designing MOFs that could help ease water shortages in the future. Yaghi is launching this technology through the company Waha, Inc, and working with scientists from the Energy Technologies Area to apply water-absorbing MOFs for in-building technologies and industrial applications.
Another team, led by joint Berkeley Lab and UC Berkeley scientist Jeffrey Long, used the ALS to study how flexible MOFs hold natural gas, with potential to boost the driving range of an adsorbed-natural-gas car – an alternative to today’s vehicles. An international team of scientists used the ALS to study the performance of a MOF that traps toxic sulfur dioxide gas at record concentrations; sulfur dioxide is typically emitted by industrial facilities, power plants, and trains and ships, and is harmful to human health and the environment. Others have used the facility to design luminous MOFs, or LMOFs, glowing crystals that can capture mercury and lead to clean contaminated drinking water.
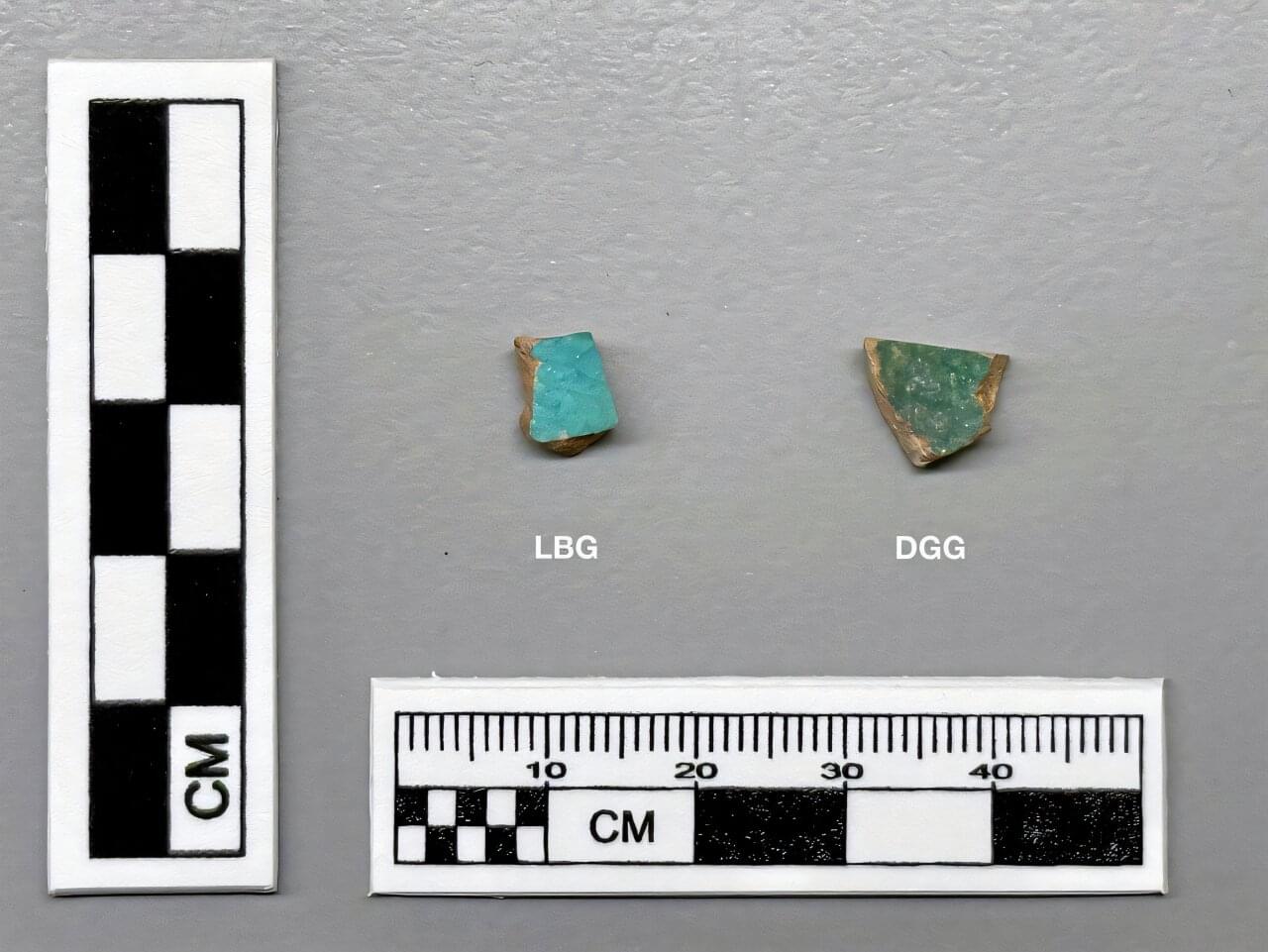

In a study published in the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, Dr. Ellery Frahm and his colleagues analyzed two unusual blue-green glazed ceramic sherds discovered in the Gobi Desert in 2016.
Their analysis reveals that the two sherds, originating in small seasonal herding camps, were high-value goods traded from the Persian empire, likely during the Early Islamic period, providing important insight into the far-flung connections and trade networks these nomadic communities were a part of.

Inside the body, a 24-hour rhythm, known as the circadian rhythm, quietly coordinates when we sleep, wake, eat, and recover. This internal timing system helps keep organs and hormones working in sync.
When it becomes disrupted, the effects may extend well beyond poor sleep, with growing evidence suggesting consequences for long-term brain health.
A large 2025 study of more than 2,000 people with an average age of 79 found that those with a strong circadian rhythm had an almost halved risk of developing dementia. Circadian rhythms regulate daily processes, including sleep timing, hormone release, heart rate, and body temperature.
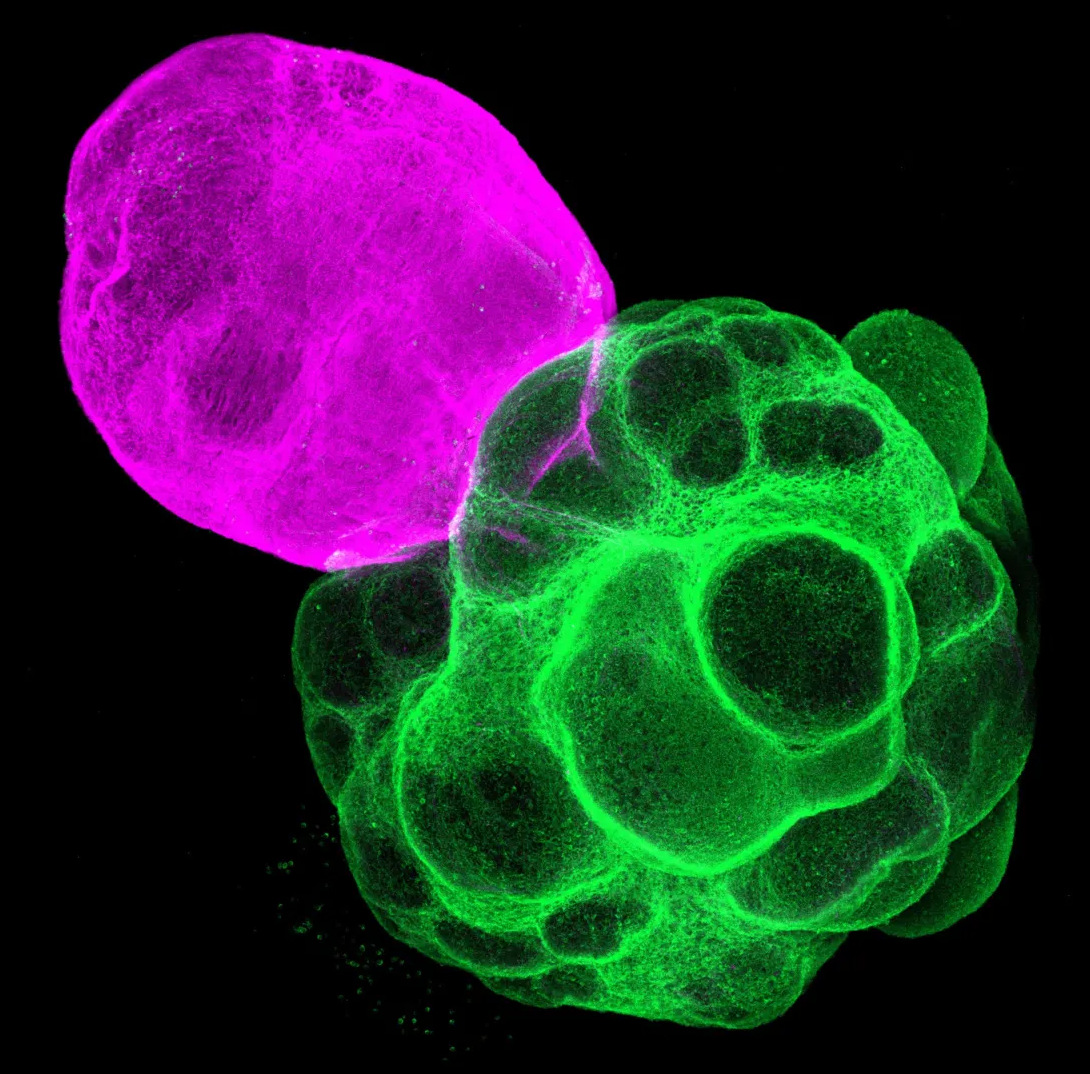
To assess how this interaction affected development, the team compared gene expression in the cortical region of the assembloid with that of a standalone cortical organoid. The cortical tissue connected to the thalamus showed signs of greater maturity, indicating that thalamus cortex communication promotes cortical growth and development.
Thalamic Signals Drive Neural Synchrony
The scientists also examined how signals traveled through the assembloid. They found that neural activity spread from the thalamus into the cortex in wave like patterns, creating synchronized activity across cortical networks.