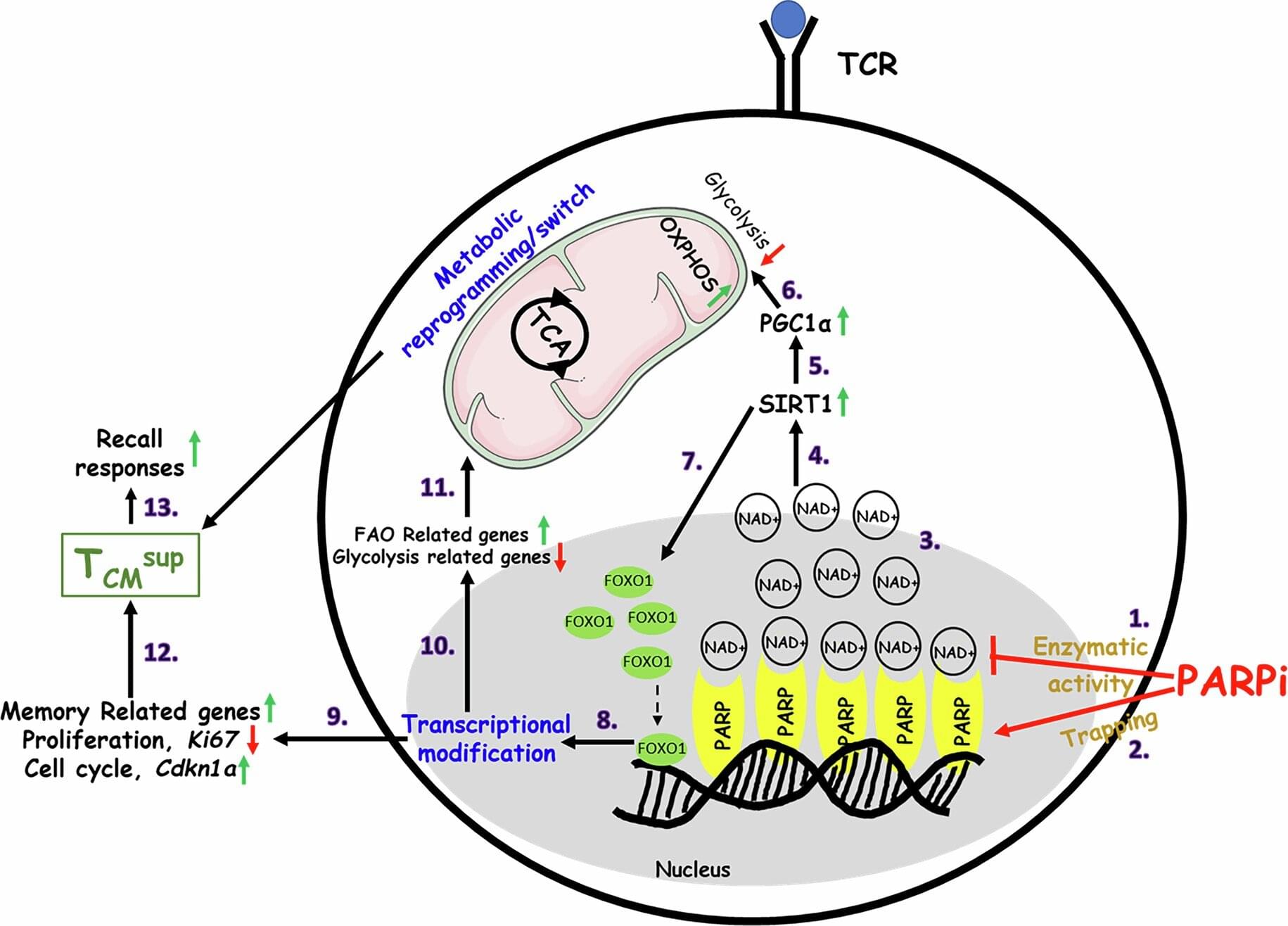
Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers have identified a new way to reprogram T cells, which are infection and tumor-fighting white blood cells, so that they have a superior memory, thereby making them more effective in killing cancer cells.
The finding, published January 12, 2026, in Nature Immunology, amplifies a known strategy of blocking the cellular activity of PARP, an enzyme that detects DNA abnormalities in cells and repairs them.
“This opens the door to a new area of research in understanding how our immune system works, and as importantly, it opens the way for the development of new strategies for the treatment of cancer,” says Samir N. Khleif, MD, director of The Center for Advanced Immunotherapy Research and the director of Loop Immuno-Oncology Research Laboratory at Georgetown’s Lombardi.