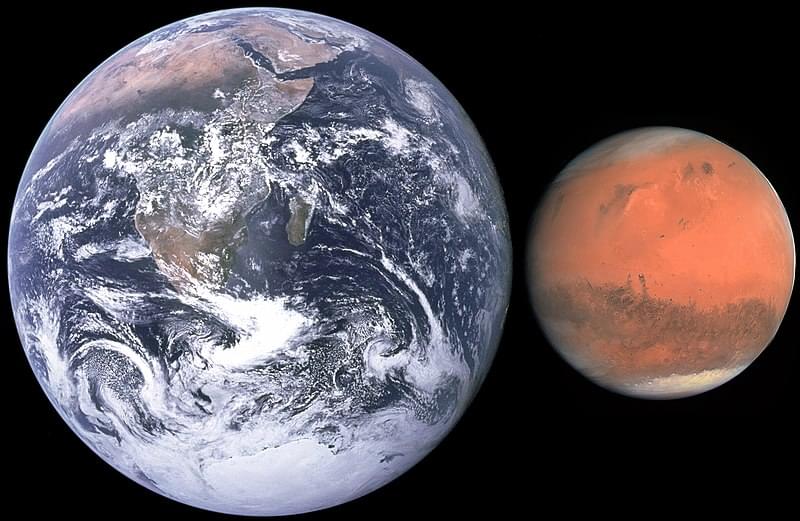
“I knew Mars had some effect on Earth, but I assumed it was tiny,” said Dr. Stephen Kane.
How does Mars influence Earth’s climate cycles? This is what a recent study published in the Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific hopes to address as a trio of researchers from the United States, United Kingdom, and Australia investigated how the gravitational interactions between Earth and Mars help alter the former’s climate evolution. This study has the potential to help scientists better understand how external processes influence planetary habitability and what this could mean for finding life beyond Earth.
For the study, the researchers used a series of computer models to simulate Earth Milankovitch cycles, which are changes in Earth’s eccentricity (orbit shape), obliquity (axial tilt), and precession (axial wobble) over hundreds of thousands of years. Specifically, the researchers aspired to ascertain how gravitational interactions with Mars could influence these cycles, including climate evolution like ice ages.
In the end, the researchers found that Mars not only influences Earth’s orbital patterns and behavior, but that the solar system’s architecture influences each other’s orbital patterns, and this could have implications for searching for Earth-like exoplanets. This comes despite Mars being approximately half the size of Earth.