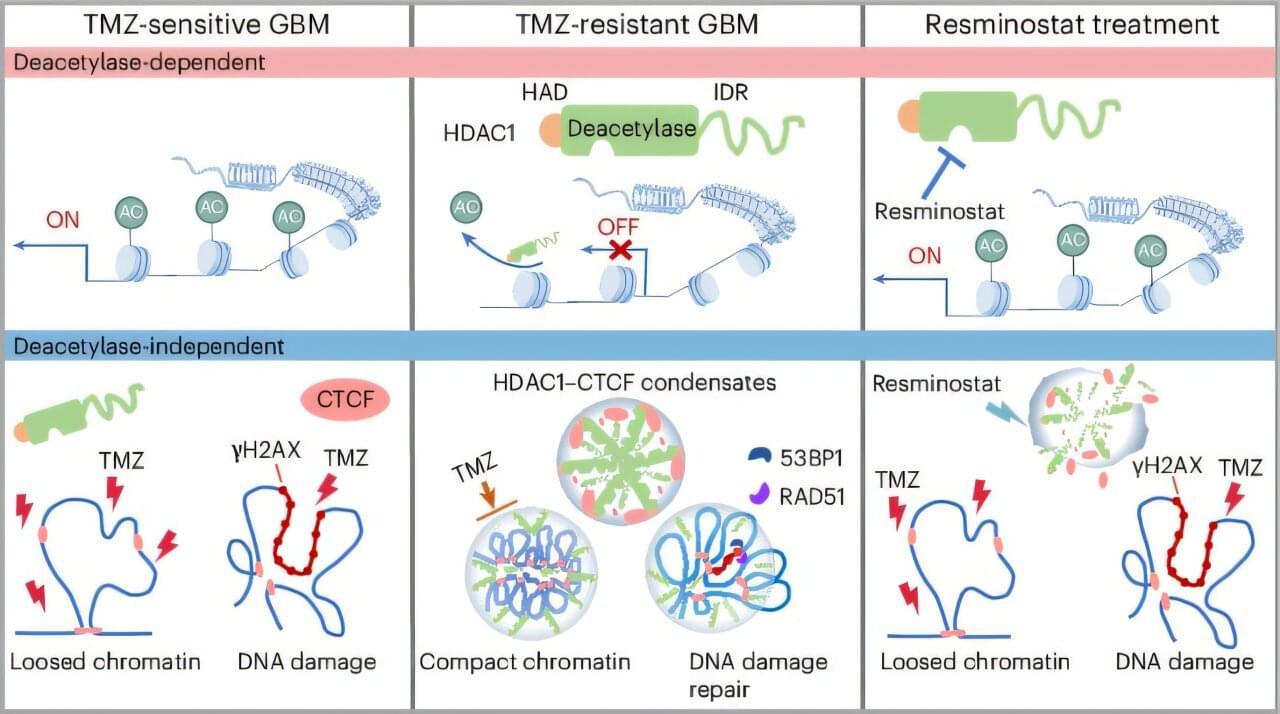
Glioblastoma (GBM) is one of the most common and aggressive primary brain tumors in adults, carrying an extremely poor prognosis and a median overall survival typically less than two years. Temozolomide (TMZ) is currently the only chemotherapeutic agent widely used in clinical practice. However, around 90% of cases experience tumor recurrence due to acquired resistance. How to overcome TMZ resistance remains a challenge.
In a study published in Nature Chemical Biology, Dr. Dong Peng’s team from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and collaborators from Sun Yat-sen University have discovered that TMZ treatment induces the formation of HDAC1-CTCF condensates in GBM cells. The team identified the small-molecule compound resminostat as a therapeutic agent capable of targeting these condensates.
Through three-dimensional (3D) super-resolution imaging independently developed by Dr. Dong’s team, the researchers observed a significant reduction in chromatin accessibility in TMZ-resistant GBM cells. The team characterized their 3D genomic structural features, and revealed that the decreased chromatin accessibility in resistant cells is primarily attributed to TMZ-induced formation of HDAC1-CTCF condensates, which accumulate on chromatin and restrict local accessibility.