Spain’s Ministry of Science (Ministerio de Ciencia) announced a partial shutdown of its IT systems, affecting several citizen- and company-facing services.


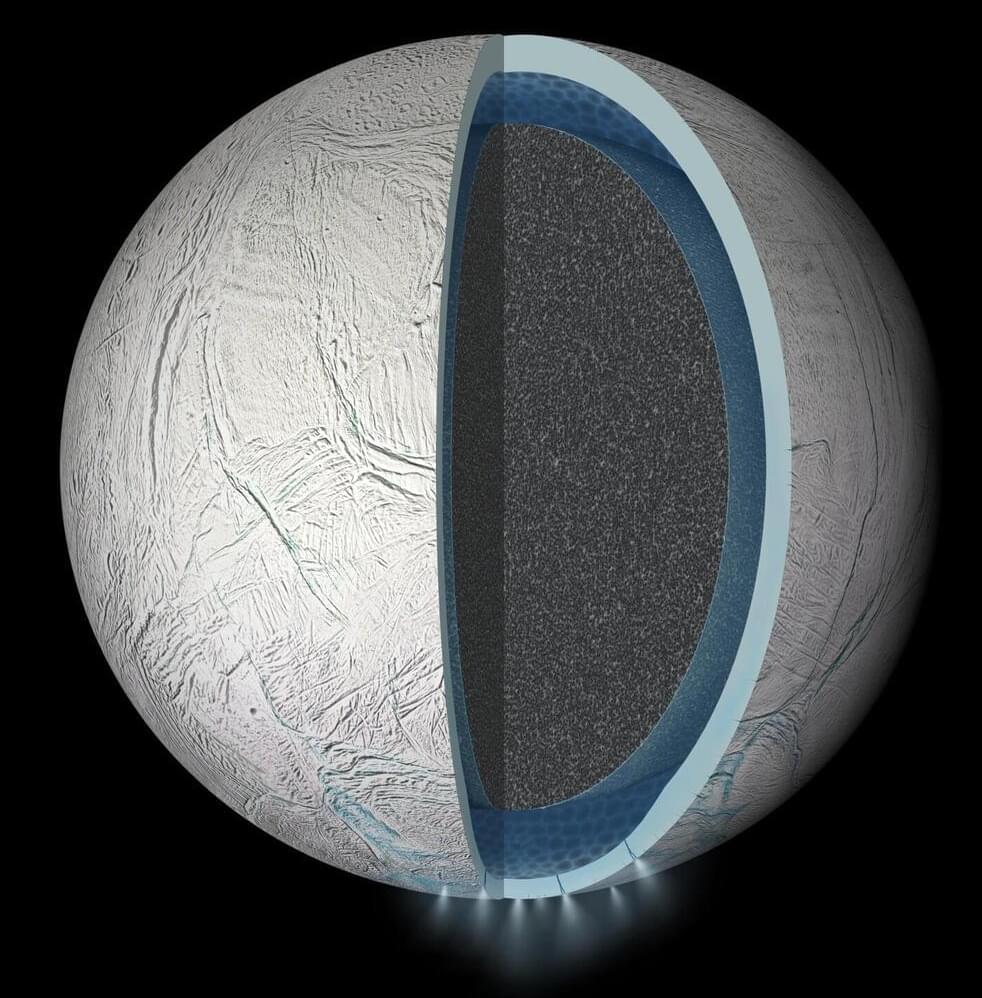
Through new experiments, researchers in Japan and Germany have recreated the chemical conditions found in the subsurface ocean of Saturn’s moon, Enceladus. Published in Icarus, the results show that these conditions can readily produce many of the organic compounds observed by the Cassini mission, strengthening evidence that the distant world could harbor the molecular building blocks of life.
Beneath its thick outer shell of ice, astronomers widely predict that Saturn’s sixth largest moon hosts an ocean of liquid water in its south polar region. The main evidence for this ocean is a water-rich plume which frequently erupts from fractures in Enceladus’ surface, leaving a trail of ice particles in its orbital paths which contributes to one of its host planet’s iconic rings.
Between 2004 and 2017, NASA’s Cassini probe passed through this E-ring and plume several times. Equipped with instruments including mass spectrometers and an ultraviolet imaging spectrograph, it detected a diverse array of organic compounds: from simple carbon dioxide to larger hydrocarbon chains, which on Earth are essential molecular precursors to complex biomolecules.
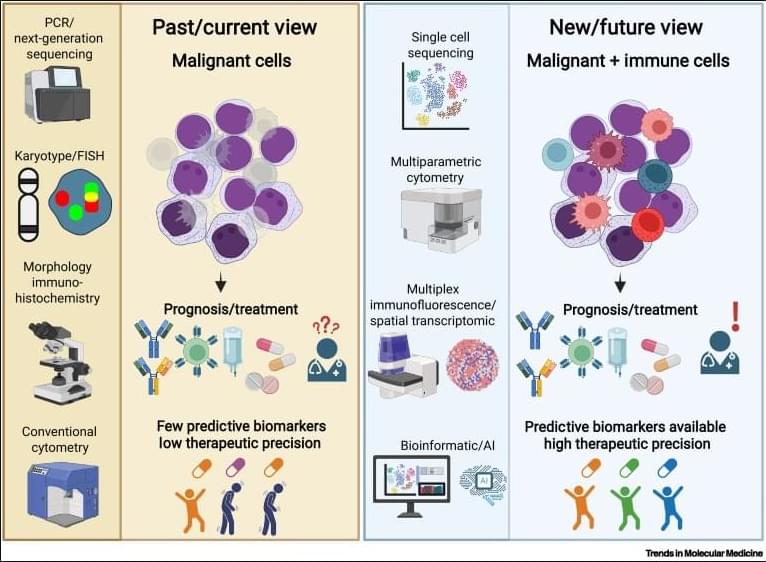
Why immunoscores work in solid tumors—but not yet in blood cancers👇
✅In solid tumors, immune profiling has reached a high level of standardization. Clear tumor boundaries allow quantification of immune cell infiltration, particularly CD3⁺ and CD8⁺ T cells, using immunohistochemistry. This has led to the development of validated immunoscores that stratify tumors as “hot,” “cold,” or “very cold,” providing robust prognostic and predictive value for immunotherapy response.
✅These immunoscores work because solid tumors are spatially organized. Immune cells can be classified as infiltrating or excluded, and their density within defined tumor regions directly correlates with clinical outcome. As a result, immune cell infiltration has become a reliable biomarker to guide treatment decisions in cancers such as colon carcinoma.
✅In contrast, hematologic malignancies lack these defining features. Leukemias and lymphomas are systemic diseases without clear tumor borders, making spatial immune assessment fundamentally challenging. Malignant and nonmalignant immune cells coexist within the same compartments, blurring the distinction between tumor cells and the immune microenvironment.
✅Current immune profiling in hematologic cancers relies on baseline physiological levels of circulating or tissue-resident immune cells, including monocytes, neutrophils, T cells, NK cells, and B cells. While techniques such as flow cytometry, histology, and bulk or single-cell RNA sequencing provide rich datasets, they do not yet translate into a unified, clinically actionable immune score.
✅This lack of standardization creates uncertainty in predicting immunotherapy responses. Metrics such as inflammation, cytotoxicity, or immune infiltration are difficult to interpret consistently across patients and disease subtypes, especially given systemic involvement and tissue-specific immune contexts.
💡
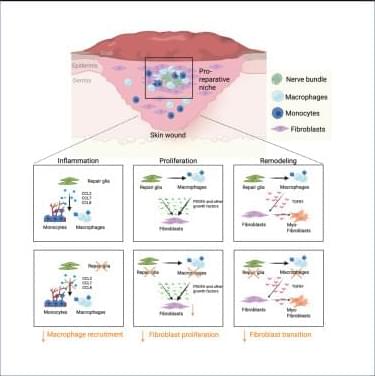
Tissue repair involves extensive communication between the different cellular components of the skin. Among them, nerve innervation is critical for a successful repair process.12,13,14,55 However, only in recent years has the pro-reparative contribution of peripheral glial cells been acknowledged.56,57 For instance, peripheral glia support progenitor cell proliferation by secreting growth factors such as newt anterior gradient protein in the amphibian blastema58 and oncostatin M (OSM) and PDGFα in the digit tip blastema.49 Previous work from our group and others has shown that peripheral glial cells promote skin repair, as depletion of these cells decreased dermal and epidermal cell proliferation,49 reduced myofibroblast numbers,18 and, ultimately, impaired skin wound healing.
Here, we found that peripheral glial cells, primarily residing in NBs, constitute a pro-reparative niche, enriched in inflammatory cells, fibroblasts, and high cell proliferation, essential for the healing process of acute skin wounds. Pro-reparative niches have previously been described in the skin epithelium and in the skeletal muscle, where local stem cell microenvironments support tissue homeostasis.59 In addition, non-myelinating glial cells were shown to be part of a stem cell niche sustaining hemopoietic stem cell dormancy by secreting TGF-β.60 Moreover, enteric glial cells were recently identified to regulate intestinal stem cell turnover by secreting wingless int-1 (WNTs) and were shown to envelop the intestinal stem cells by forming a web-like structure around the intestinal crypts.61,62 This close association of the enteric glia cells and the intestinal crypt also points toward the formation of a spatially organized niche critical for intestine homeostasis.
We’ve all heard the best approach to solve a problem is to “sleep on it.” It turns out there may be more truth to this adage than previously thought. While stories abound of eureka moments surfacing from dreams, scientific evidence has remained elusive, due to the challenge of systematically manipulating dreams.
A new study by neuroscientists at Northwestern University validates the possibility of influencing dreams and offers a crucial step to support the theory that dreams in REM sleep—the rapid eye movement phase of sleep in which lucid dreaming can occur—may be especially conducive to helping individuals come up with creative solutions to a problem.
The study has been published in the journal Neuroscience of Consciousness.

What does it take to turn bold ideas into life-saving medicine?
In this episode of The Big Question, we sit down with @MIT’s Dr. Robert Langer, one of the founding figures of bioengineering and among the most cited scientists in the world, to explore how engineering has reshaped modern healthcare. From early failures and rejected grants to breakthroughs that changed medicine, Langer reflects on a career built around persistence and problem-solving. His work helped lay the foundation for technologies that deliver large biological molecules, like proteins and RNA, into the body, a challenge once thought impossible. Those advances now underpin everything from targeted cancer therapies to the mRNA vaccines that transformed the COVID-19 response.
The conversation looks forward as well as back, diving into the future of medicine through engineered solutions such as artificial skin for burn victims, FDA-approved synthetic blood vessels, and organs-on-chips that mimic human biology to speed up drug testing while reducing reliance on animal models. Langer explains how nanoparticles safely carry genetic instructions into cells, how mRNA vaccines train the immune system without altering DNA, and why engineering delivery, getting the right treatment to the right place in the body, remains one of medicine’s biggest challenges. From personalized cancer vaccines to tissue engineering and rapid drug development, this episode reveals how science, persistence, and engineering come together to push the boundaries of what medicine can do next.
#Science #Medicine #Biotech #Health #LifeSciences.
Chapters:
00:00 Engineering the Future of Medicine.
01:55 Failure, Persistence, and Scientific Breakthroughs.
05:30 From Chemical Engineering to Patient Care.
08:40 Solving the Drug Delivery Problem.
11:20 Delivering Proteins, RNA, and DNA
14:10 The Origins of mRNA Technology.
17:30 How mRNA Vaccines Work.
20:40 Speed and Scale in Vaccine Development.
23:30 What mRNA Makes Possible Next.
26:10 Trust, Misinformation, and Vaccine Science.
28:50 Engineering Tissues and Organs.
31:20 Artificial Skin and Synthetic Blood Vessels.
33:40 Organs on Chips and Drug Testing.
36:10 Why Science Always Moves Forward.
The Big Question with the Museum of Science:
How Elon plans to launch a terawatt of GPUs into space.
## Elon Musk plans to launch a massive computing power of 1 terawatt of GPUs into space to advance AI, robotics, and make humanity multi-planetary, while ensuring responsible use and production. ## ## Questions to inspire discussion.
Space-Based AI Infrastructure.
Q: When will space-based data centers become economically superior to Earth-based ones? A: Space data centers will be the most economically compelling option in 30–36 months due to 5x more effective solar power (no batteries needed) and regulatory advantages in scaling compared to Earth.
☀️ Q: How much cheaper is space solar compared to ground solar? A: Space solar is 10x cheaper than ground solar because it requires no batteries and is 5x more effective, while Earth scaling faces tariffs and land/permit issues.
Q: What solar production capacity are SpaceX and Tesla planning? A: SpaceX and Tesla plan to produce 100 GW/year of solar cells for space, manufacturing from raw materials to finished cells in-house.
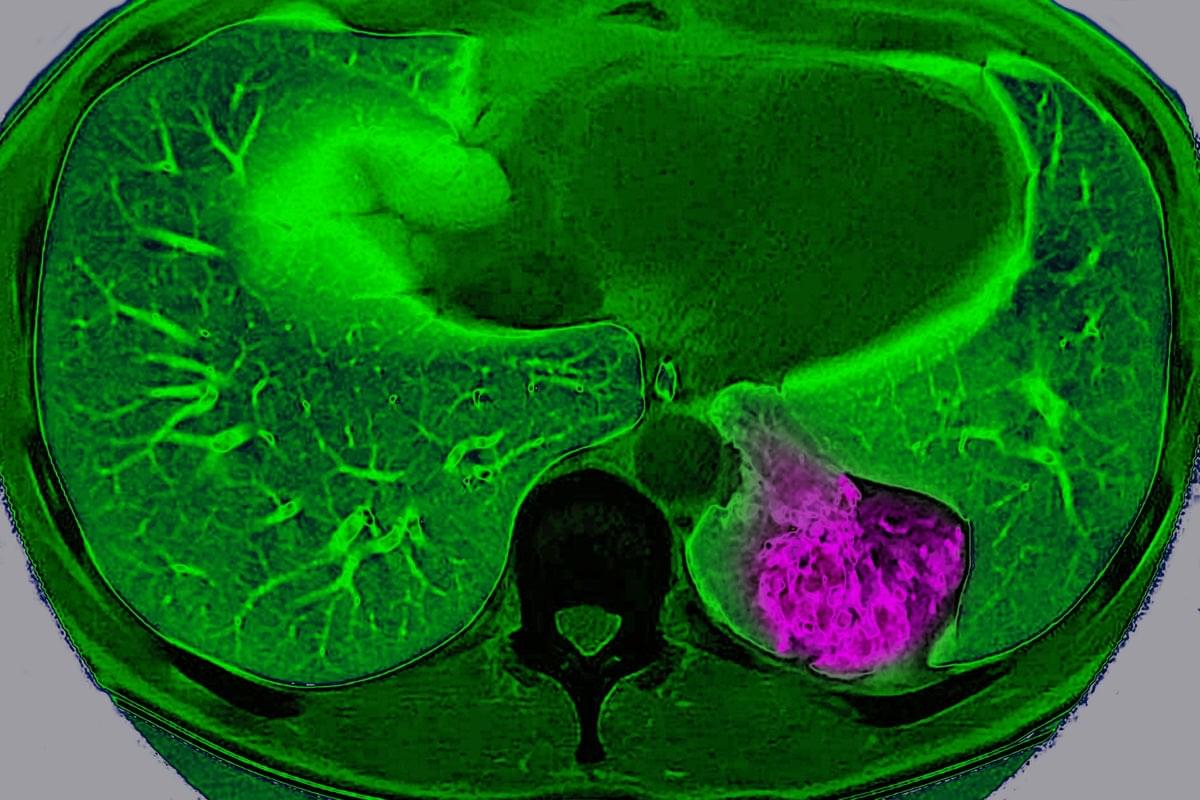
For years, scientists have viewed cancer as a localized glitch in which cells refuse to stop dividing. But a new study suggests that, in certain organs, tumors actively communicate with the brain to trick it into protecting them.
Scientists have long known that nerves grow into some tumors and that tumors containing lots of nerves usually lead to a worse prognosis. But they didn’t know exactly why. “Prior to our study, most of the focus has been this local interaction between the nerve [endings] and the tumor,” says Chengcheng Jin, an assistant professor of cancer biology at the University of Pennsylvania and a co-author of the study, which was published on Wednesday in Nature.
Jin and her colleagues discovered that lung cancer tumors in mice can use these nerve endings to communicate way beyond their close vicinity and send signals to the brain through a complex neuroimmune circuit. They also confirmed the circuit exists in humans.
✍️: Jacek Krywko 📸: BSIP/Universal Images Group via Getty Images.
Lung cancer tumor cells in mice communicate with the brain, sending signals to deactivate the body’s immune response, a study finds.
By Jacek Krywko edited by Tanya Lewis.