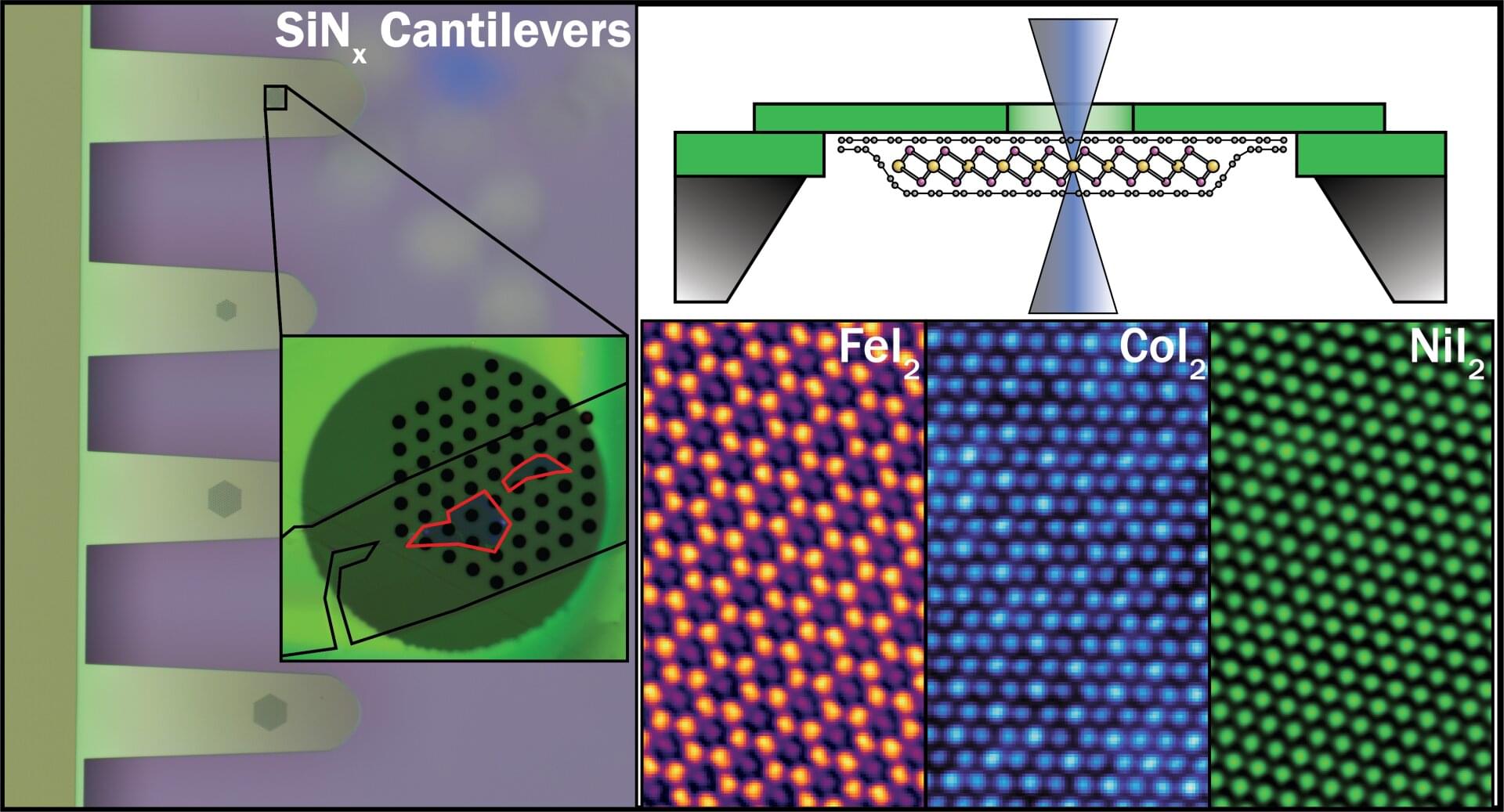
Two-dimensional (2D) materials promise revolutionary advances in electronics and photonics, but many of the most interesting candidates degrade within seconds of air exposure, making them nearly impossible to study or integrate into real-world technology. Transition metal dihalides represent a particularly compelling yet challenging class of materials, with predicted properties ideal for next-generation devices, but their extreme reactivity when exposed to air prevents even basic structural characterization.
Researchers at The University of Manchester’s National Graphene Institute have now achieved the first atomic-resolution imaging of monolayer transition metal diiodides, made possible by creating graphene-sealed TEM samples that prevent these highly reactive materials from degrading on contact with air.
The study, published in ACS Nano, demonstrates that fully encapsulating the crystals in graphene preserves atomically clean interfaces and extends their usable lifetime from seconds to months.