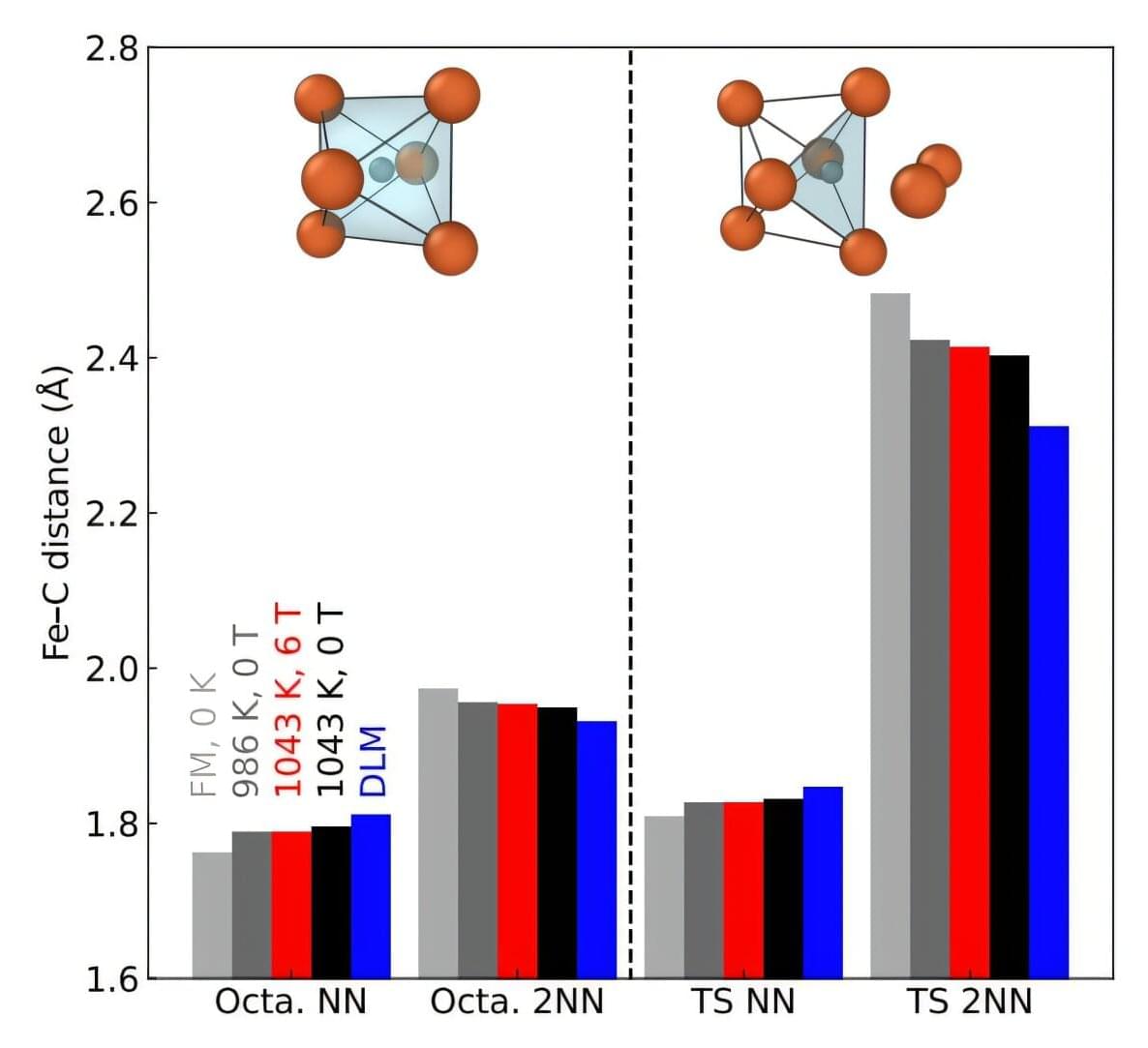
Researchers at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering within The Grainger College of Engineering have identified the first detailed physical mechanism explaining how magnetic fields slow the movement of carbon atoms inside iron. The study, published in Physical Review Letters, sheds new light on the role carbon plays in shaping the internal grain structure of steel.
Steel, which is made from iron and carbon, is among the most widely used construction materials worldwide. Producing steel with specific internal structures typically requires extreme heat, making the process highly energy intensive.
Decades ago, researchers observed that exposing certain steels to magnetic fields during heat treatment led to improved performance, but the explanations offered at the time remained largely theoretical. Pinpointing the underlying cause of this effect could give engineers more precise control over heat treatment, leading to more efficient processing and lower energy demands.