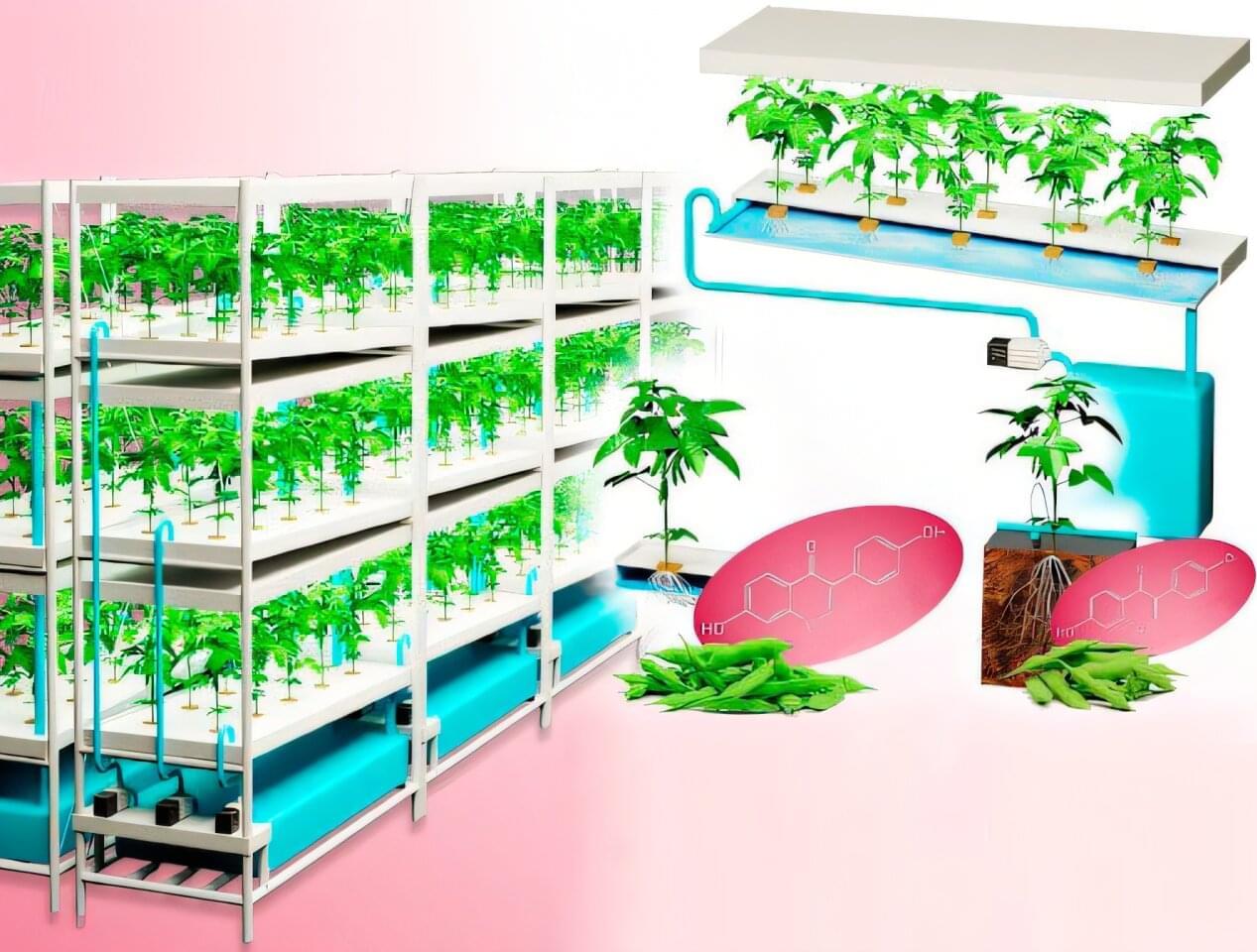
Artificial light-type plant factories are an emerging agricultural innovation that enables crops to be grown year-round in precisely controlled environments. By adjusting factors such as light, temperature, humidity, carbon dioxide concentration, and nutrient delivery, these facilities can produce stable yields independent of climate conditions. They offer a promising way to reduce pesticide use and minimize the impacts of climate change.
However, legumes like edamame have long been considered difficult to cultivate in such settings because of their long growth periods, short storage periods, complex flowering, and pod-setting processes.
Against this backdrop, the research group, led by Professor Toshio Sano from the Faculty of Bioscience and Applied Chemistry, Hosei University, Japan, and Associate Professor Wataru Yamori of the Graduate School of Agricultural and Life Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Japan, had previously gained attention for successfully cultivating tomatoes under LED lighting in a plant factory.