Experts say the VoidLink Linux malware was largely built using AI, reaching 88,000 lines of code in days and highlighting faster malware development.


Microsoft shared a temporary workaround for customers experiencing Outlook freezes after installing this month’s Windows security updates.
As explained one week ago, when Microsoft acknowledged the issue, the bug causes the classic Outlook desktop client to hang for users with POP email accounts who have deployed the KB5074109 security update on Windows 11 25H2 and 24H2 systems.
Other symptoms include the inability to reopen Outlook without ending the process via Task Manager or restarting the device, Outlook redownloading emails, and emails not appearing in the Sent Items folder even though they were sent.

People worldwide are being targeted by a massive spam wave originating from unsecured Zendesk support systems, with victims reporting receiving hundreds of emails with strange and sometimes alarming subject lines.
The wave of spam messages started on January 18th, with people reporting on social media that they received hundreds of emails.
While the messages do not appear to contain malicious links or obvious phishing attempts, the sheer volume and chaotic nature of the emails have made them highly confusing and potentially alarming for recipients.

A new family of Android click-fraud trojans leverages TensorFlow machine learning models to automatically detect and interact with specific advertisement elements.
The mechanism relies on visual analysis based on machine learning instead of predefined JavaScript click routines, and does not involve script-based DOM-level interaction like classic click-fraud trojans.
The threat actor is using TensorFlow.js, an open-source library developed by Google for training and deploying machine learning models in JavaScript. It permits running AI models in browsers or on servers using Node.js.

China’s military says it is using quantum technology to gather high-value military intelligence from public cyberspace.
The People’s Liberation Army said more than 10 experimental quantum cyber warfare tools were “under development”, many of which were being “tested in front-line missions”, according to the official newspaper Science and Technology Daily.
The project is being led by a supercomputing laboratory at the National University of Defence Technology, according to the report, with a focus on cloud computing, artificial intelligence and quantum technology.
From skilled trades to startups, AI’s rapid expansion is the beginning of the next massive computing platform shift, and for the world’s workforce, a move from tasks to purpose.
At a packed mainstage session at the annual meeting of the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland, NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang described artificial intelligence as the foundation of what he called “the largest infrastructure buildout in human history,” driving job creation across the global economy.
Speaking with BlackRock CEO Larry Fink, Huang framed AI not as a single technology but as a “a five-layer cake,” spanning energy, chips and computing infrastructure, cloud data centers, AI models and, ultimately, the application layer.
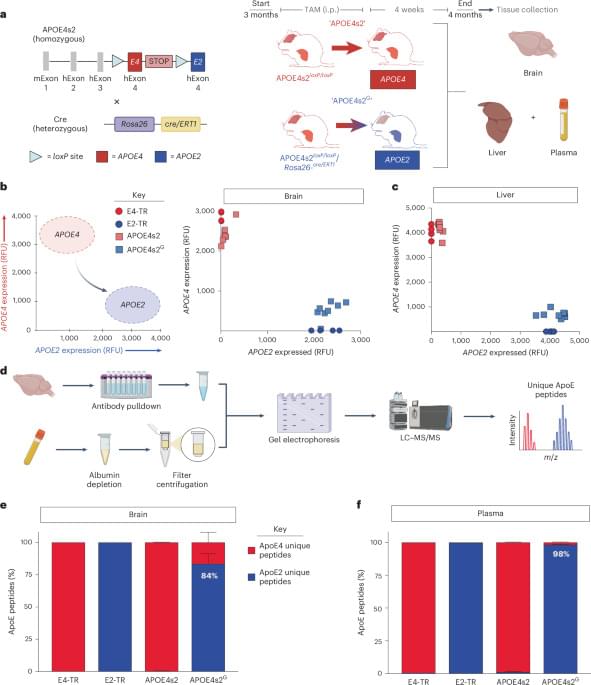
APOE allele switching improves Alzheimer’s in mice.
Type of apolipoprotein E (APOE) allele carried by individuals is a major risk factor in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). For example, compared to individuals carrying two copies of the APOE ε4 allele, ε2 homozygotes have an approximate 99% reduction in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (AD) risk.
The authors in this study developed a knock-in mouse model that allows for an inducible ‘switch’ between risk and protective alleles (APOE4s2). These mice synthesize E4 at baseline and E2 after tamoxifen administration.
A whole-body allelic switch resulted in a metabolic profile resembling E2/E2 humans and drives AD-relevant alterations in the lipidome and single-cell transcriptome, particularly in astrocytes.
E4 to E2 switching improved cognition, decreased amyloid pathology, lowered gliosis and reduced plaque-associated apolipoprotein E.
Thus, APOE replacement may be a viable strategy for future gene editing approaches to simultaneously reduce multiple AD-associated pathologies. sciencenewshighlights ScienceMission https://sciencemission.com/APOE4-to-APOE2-allelic-switching
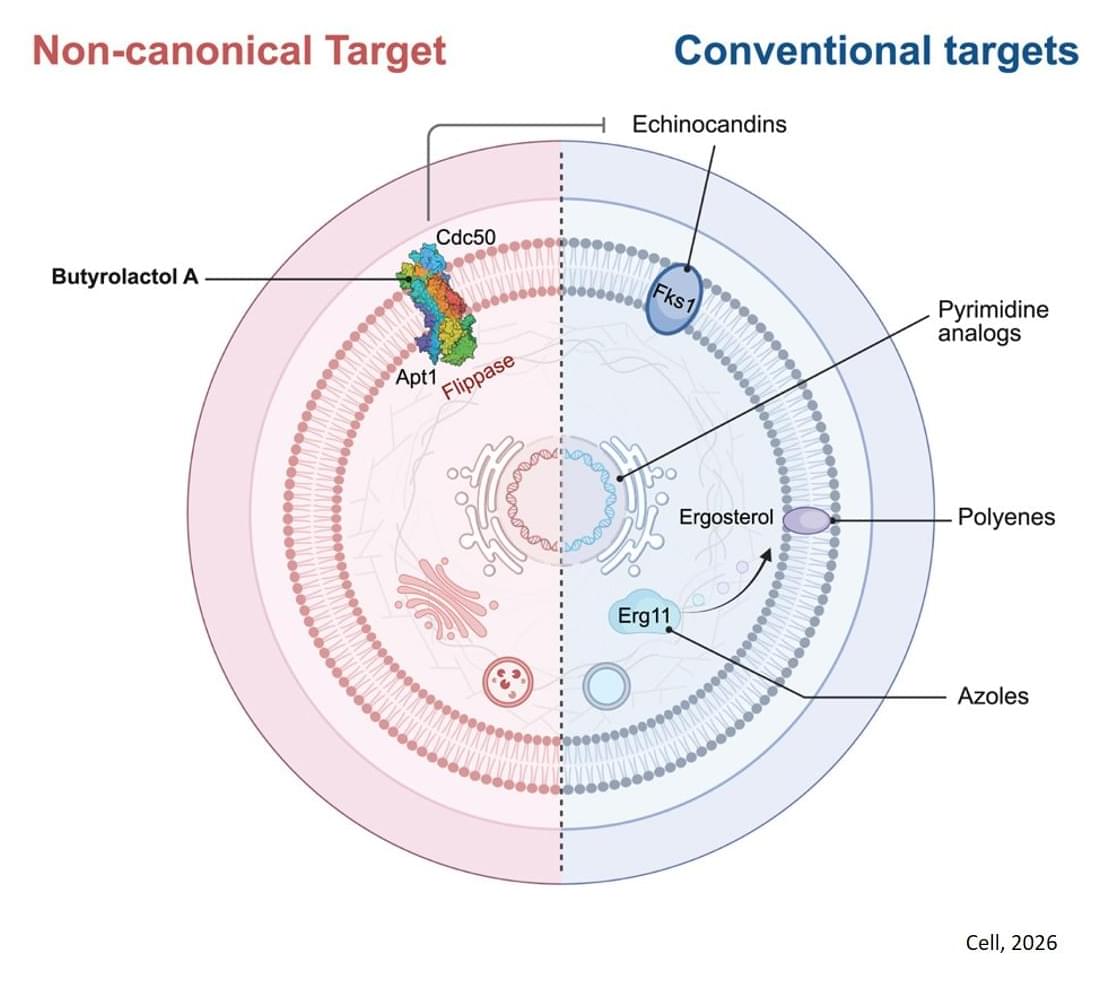
Infections caused by Cryptococcus are extremely dangerous. The pathogen, which can cause pneuomia-like symptoms, is notoriously drug-resistant, and it often preys on people with weakened immune systems, like cancer patients or those living with HIV. And the same can be said about other fungal pathogens, like Candida auris or Aspergillus fumigatus — both of which, like Cryptococcus, have been declared priority pathogens by the World Health Organization.
Despite the threat, though, doctors have only three treatment options for fungal infections.
The gold standard is a drug class called amphotericin but has major toxic side-effects on humans.
The other two antifungal drug classes that are available — azoles and echinocandins — are much less effective treatment options, especially against Cryptococcus. The author says azoles merely stop fungi from growing rather than outright killing them, while Cryptococcus and other fungi have become totally resistant to echinocandins, rendering them completely ineffective.
“Adjuvants are helper molecules that don’t actually kill pathogens like drugs do, but instead make them extremely susceptible to existing medicine,” explains the author.
Looking for adjuvants that might better sensitize Cryptococcus to existing antifungal drugs, the lab screened vast chemical collection for candidate molecules.
Quickly, the team found a hit: butyrolactol A, a known-but-previously understudied molecule produced by certain Streptomyces bacteria. The researchers found that the molecule could synergize with echinocandin drugs to kill fungi that the drugs alone could not.
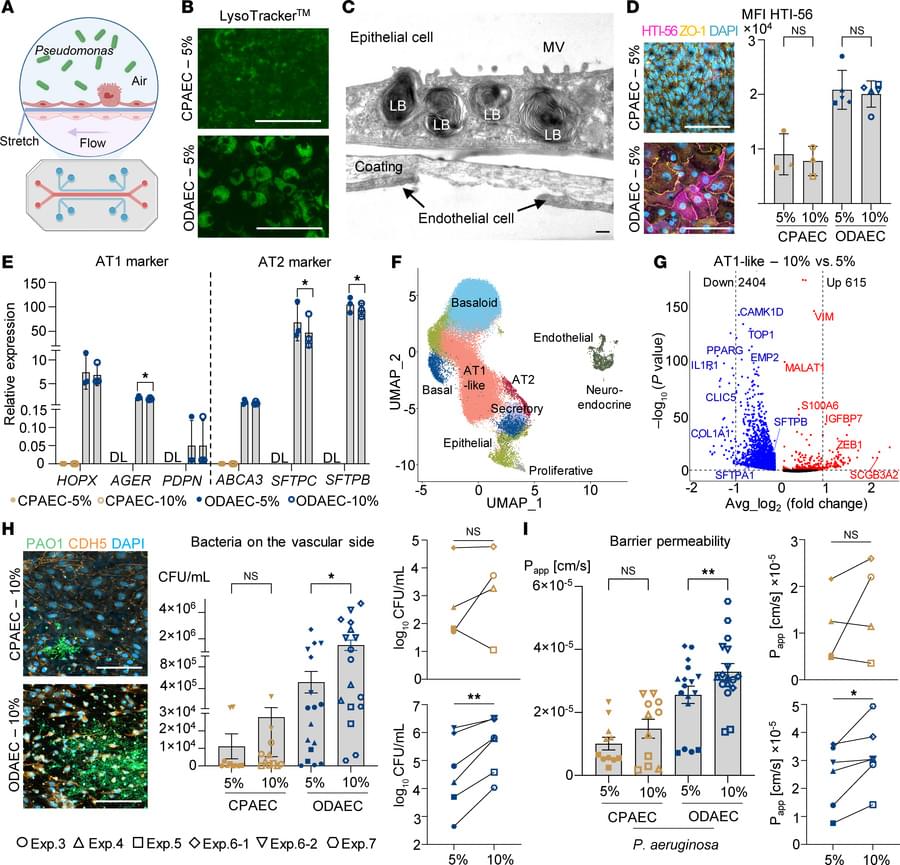
Mechanical strain exacerbates Pseudomonas infection in an organoid-based pneumonia-on-a-chip model.
In this Research Letter, Geraldine Nouailles & team use an advanced human lung-on-a-chip model to show that increased mechanical strain can make the lungs more vulnerable to harmful bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
1Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Department of Infectious Diseases, Respiratory Medicine and Critical Care, Berlin, Germany.
2Bundeswehr Hospital Berlin, Department of Internal Medicine, Berlin, Germany.
3Universität Leipzig, ScaDS.AI, Institute for Medical Informatics, Statistics, and Epidemiology, Leipzig, Germany.