Swami Sivananda was born on August 8, 1896, according to details in his passport.



Here, Marco L. Davila & team recapitulate these high-grade toxicities in mice, revealing Th1-Th17 imbalance drives the co-occurrence of CRS and neutropenia; effects that could be prevented with IFNg blockade.
4Department of Medicine, Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, New York, USA.
5University of Florida College of Medicine, Division of Hematology-Oncology, Gainesville, Florida, USA.
6Department of Blood and Marrow Transplant and Cellular Immunotherapy, H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center & Research Institute, Tampa, Florida, USA.

Windows 11 has been pushing AI features harder than ever over the past year, and there’s no sign of that slowing down anytime soon. From Copilot sitting in your taskbar to Recall capturing your screen, Microsoft’s AI is becoming impossible to ignore, and often impossible to remove.
If you value your privacy or just prefer a cleaner OS, a PowerShell script called Remove Windows AI is now available on GitHub. It was released by developer Zoicware and does exactly what it promises: it targets Copilot, Recall, Windows Studio Effects, and other related background services that run by default.
The script is actively maintained to ensure it can remove newly added AI components as they appear. If you find an AI feature or registry key that the script doesn’t remove, report it with details so the developer can add it in a future update.

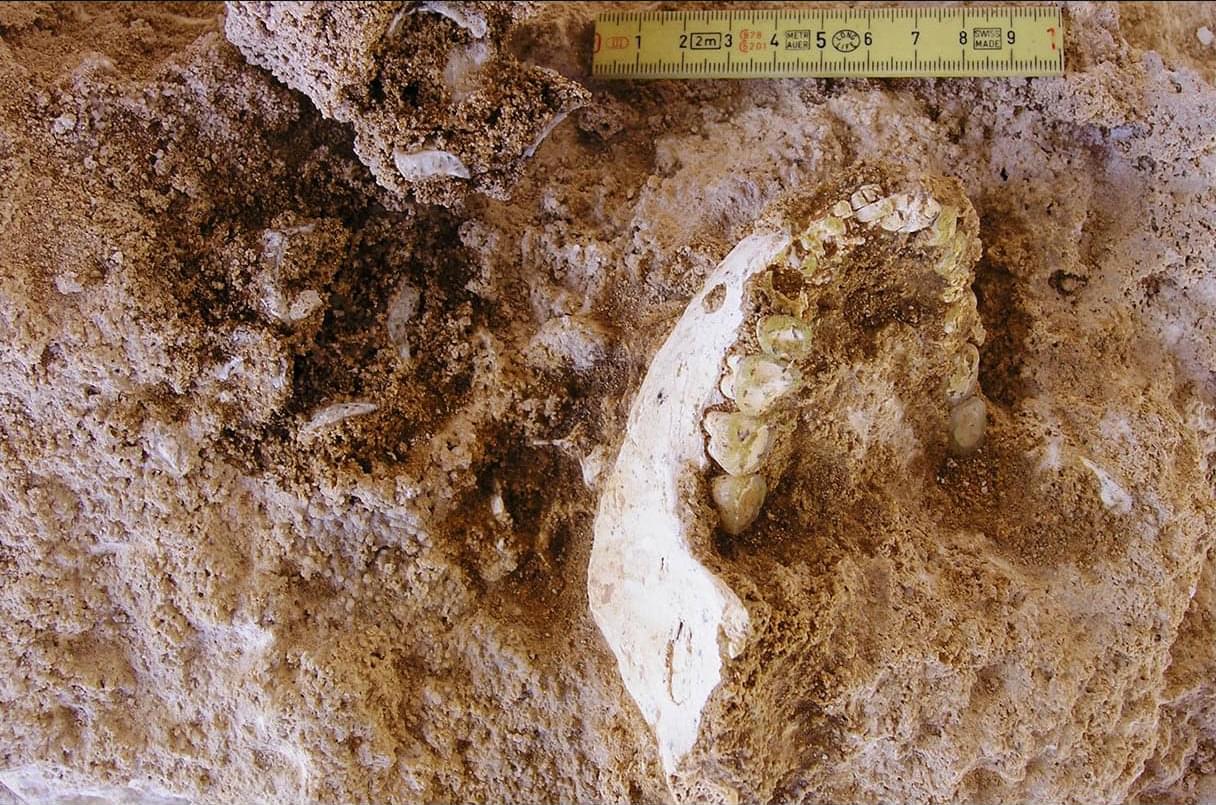

Astronomers report the discovery of a new binary system, designated LAMOST J065816.72+094343.1. The newfound binary consists of a massive and hot subdwarf and an unseen companion. The finding was detailed in the January issue of the Astronomy & Astrophysics journal.
LAMOST J065816.72+094343.1, or J0658 for short, was first identified in 2018 by the Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST) and classified as a hot subdwarf star of an sdOB type. Initial observations of J0658 have found that it is a helium-poor star with an effective temperature of about 35,800 K and a projected rotational velocity of 37 km/s.
Given that very little is known about J0658, a team of astronomers led by Fabian Mattig of the University of Potsdam in Germany decided to analyze the archival LAMOST data and to conduct follow-up observations of this star with the Southern Astrophysical Research (SOAR) telescope and the Very Large Telescope (VLT), hoping to unveil its true nature.
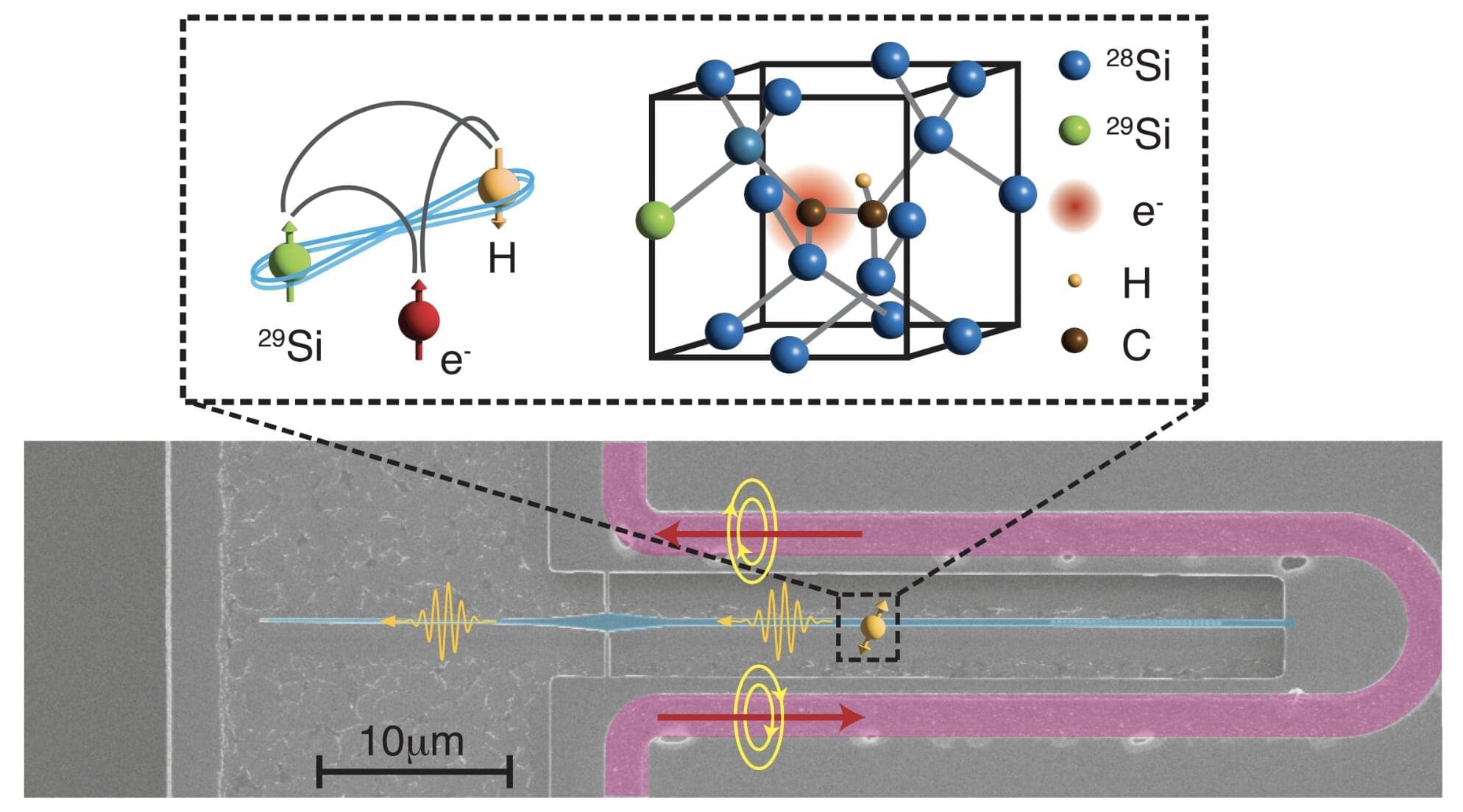
Quantum technologies are highly promising devices that process, transfer or store information leveraging quantum mechanical effects. Instead of relying on bits, like classical computers, quantum devices rely on entangled qubits, units of information that can also exist in multiple states (0 and 1) at once.
A research team at the University of California Berkeley (UC Berkeley) supervised by Alp Sipahigil recently demonstrated the potential of leveraging atomic-scale defects on silicon chips, known as T-centers, to create small multi-qubit memory units that store quantum information (i.e., quantum registers).
Their paper, published in Nature Nanotechnology, could open new possibilities for the development of quantum technologies that are based on silicon, which is the most widely used material within the electronics industry.
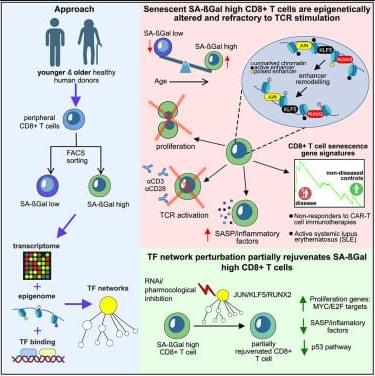
Turano et al. reveal the transcription factor networks driving CD8+ T cell senescence in healthy aging humans. Inhibiting key transcription factors modulates the senescence program and partially restores responsiveness to TCR stimulation. They also show that CD8+ T cell senescence gene signatures predict response to CAR-T cell therapy in B cell lymphomas.
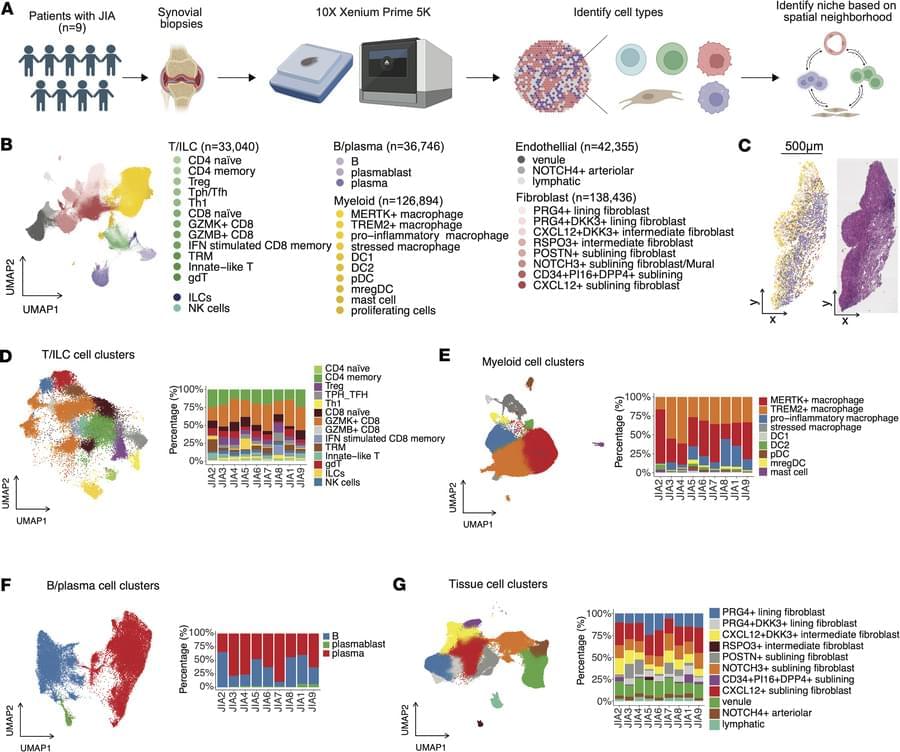
Jun Inamo & team profiles nearly 400,000 cells across 9 patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), revealing disease-specific immune–stromal interactions within the synovium.
1Department of Biomedical Informatics, Center for Health Artificial Intelligence, and.
2Division of Rheumatology, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, Colorado, USA.
3Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keio University School of Medicine, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo, Japan.