New research indicates that around two-thirds of initially non-speaking children with autism begin to speak following evidence-based early intervention, with factors like intervention duration and motor imitation skills influencing success.


Placental toxicology progress!
Commonly used in vitro and in vivo placental models capture key placental functions and toxicity mechanisms, but have significant limitations.
The physiological relevance of placental models varies, with a general hierarchy of simple in vitro complex in vitro/ organ-on-chip in vivo, but species-of origin considerations may alter their relevance to human physiology.
Cellular, rodent, human, and computational modeling systems provide insights into placental transport, physiology, and toxicology linked to maternal–fetal health.
Recent advances in 3D culture and microfluidic technologies offer more physiologically relevant models for studying the placenta.
Mathematical modeling approaches can integrate mechanistic physiological data and exposure assessments to define key toxicokinetic parameters.
Environmental chemical concentrations and omic data obtained from placental tissues can link toxicant influences on placental function to adverse birth outcomes.
This video explores alien societies capable of expanding across star systems, reshaping reality for efficiency, harvesting cosmic resources at unimaginable scales, or operating with forms of intelligence so detached from human values that our survival would barely register as a variable.
Suscribe @thegreatabyss1
Researched, written, edited, and produced by the @thegreatabyss1 team.
Music produced by @IronCthulhuApocalypse (License Control).
We are truly grateful to have you here with us. Your support means a lot to us and helps us continue creating valuable content. If you enjoy our videos, we would greatly appreciate it if you activate the notification bell, subscribe, like, and share the content. Thank you very much 🙏
Timestamps:
What if I told you that Godzilla, planets, and even the universe itself aren’t anywhere near the biggest beings in fiction?
Across movies, anime, comics, mythology, and cosmic horror, there are aliens so massive that galaxies are decorations, universes are toys, and reality itself exists inside them.
In this video, we rank the 20 BIGGEST ALIENS EVER IN FICTION — strictly by SIZE, not power or popularity.
We start with continent-crushing monsters like Starro…
move through planet-eaters like Unicron and Galactus…
and end with omniversal entities so vast that everything you know exists within them.
From Norse mythology and Lovecraftian horror to Marvel, DC, anime, and sci-fi films, this list escalates FAST — and by the end, scale itself stops making sense.
👉 Which alien blew your mind the most?
Drop a comment, like the video, and subscribe for more insane size breakdowns, cosmic rankings, and fictional mega-structures.
Think bigger.
Make a donation to Closer To Truth to help us continue exploring the world’s deepest questions without the need for paywalls: https://shorturl.at/OnyRq.
That the universe began seems astonishing. What brought it about? What forces were involved? How did the laws of nature generate the vast expanse of billions of galaxies of billions of stars and planets in the structures that we see today? What new physics was involved? What more must we learn?
Free access to Closer to Truth’s library of 5,000 videos: http://bit.ly/376lkKN
Watch more interviews on how our universe began: https://bit.ly/3qmbWPu.
John Richard Gott III is a Professor of Astrophysical Sciences at Princeton University who is noted for his contributions to cosmology and general relativity.
Register for free at CTT.com for subscriber-only exclusives: http://bit.ly/2GXmFsP
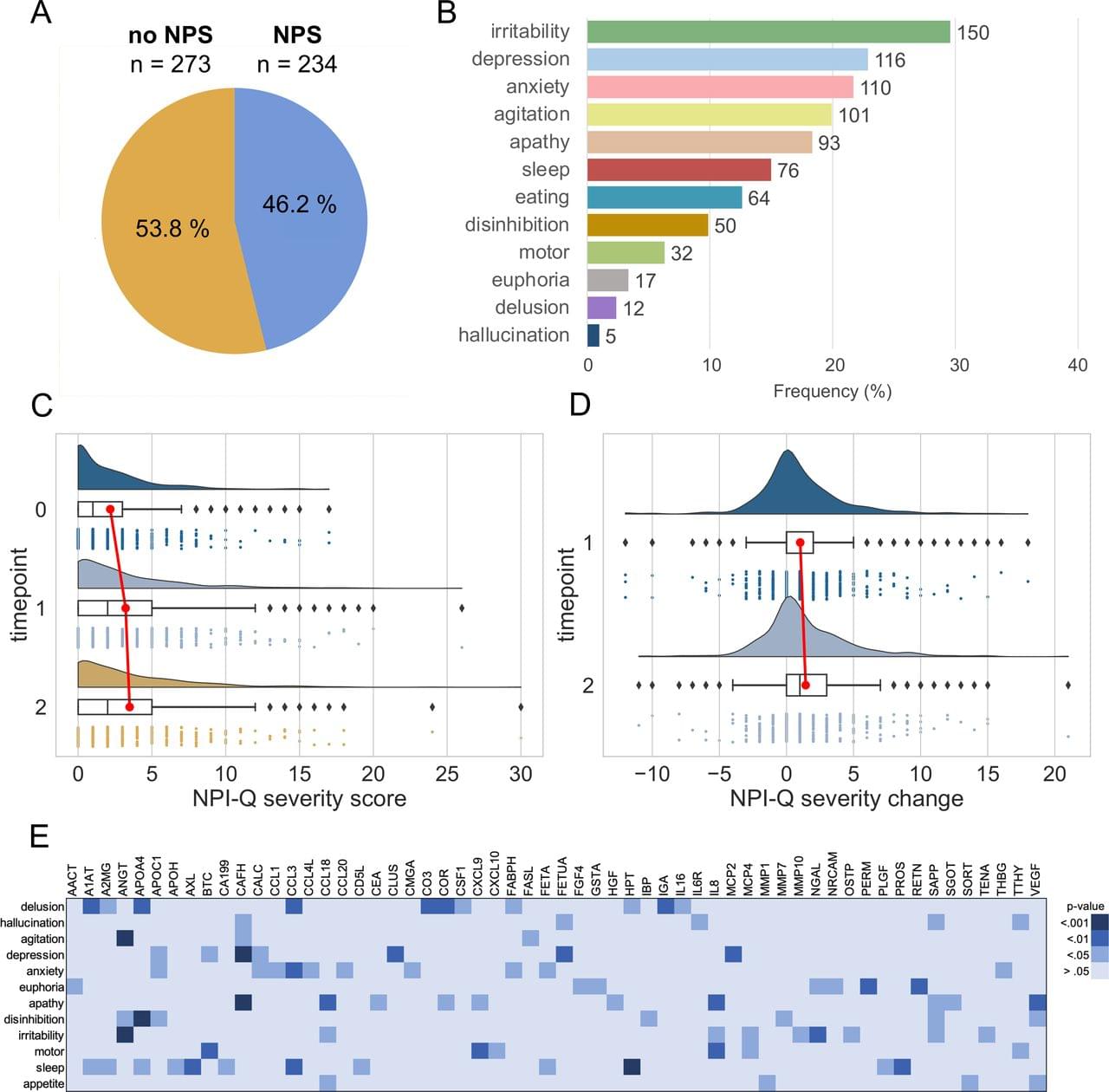
Physicists have used a new optical centrifuge to control the rotation of molecules suspended in liquid helium nano-droplets, bringing them a step closer to demystifying the behavior of exotic, frictionless superfluids.
It’s the first demonstration of controlled spinning inside a superfluid—researchers can now directly set the direction and frequency of the molecule’s rotation, which is vital in studying how molecules interact with the quantum environment at various rotational frequencies. The method was outlined this week by researchers at the University of British Columbia (UBC) and colleagues at the University of Freiburg in the journal Physical Review Letters.
“Controlling the rotation of a molecule dissolved in any fluid is a challenge,” said Dr. Valery Milner, associate professor with UBC Physics and Astronomy and lead author on the paper.
Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have characterized how cellular senescence—a biological process in which aging cells change how they function—is associated with human brain structure in both development and late life. The study, published January 22 in Cell, provides new insight into how molecular signatures of cellular senescence that are present during development and aging mirror those associated with brain volume and cortical organization.
Understanding brain structure is a central challenge in neuroscience. Although brain structure changes throughout life and is linked to both aging and neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases, the underlying molecular processes involved—including cellular senescence—are not defined. Cellular senescence is commonly defined as a state characterized by permanent cell cycle arrest in the absence of cell death, in which cells have altered function. While cellular senescence has been implicated in aging and disease, its role in shaping human brain structure—both during development and aging—has remained unclear.
“This is the first study to directly link senescence-related molecular networks in living human brain tissue to measurable differences in brain structure within the same individuals,” said Noam Beckmann, PhD, Director of Data Sciences and founding member for the Mount Sinai Clinical Intelligence Center, Assistant Professor of Artificial Intelligence and Human Health, and co-senior author of the paper. “By identifying molecular pathways that are engaged in both brain structure development and aging, our work highlights senescence as a fundamental biological feature of brain aging and neurodegenerative disease and helps prioritize targets for future experimental research aimed at protecting brain health.”

Scientists are learning how to temporarily reshape materials by nudging their internal quantum rhythms instead of blasting them with extreme lasers. By harnessing excitons, short-lived energy pairs that naturally form inside semiconductors, researchers can alter how electrons behave using far less energy than before. This approach achieves powerful quantum effects without damaging the material, overcoming a major barrier that has limited progress for years.
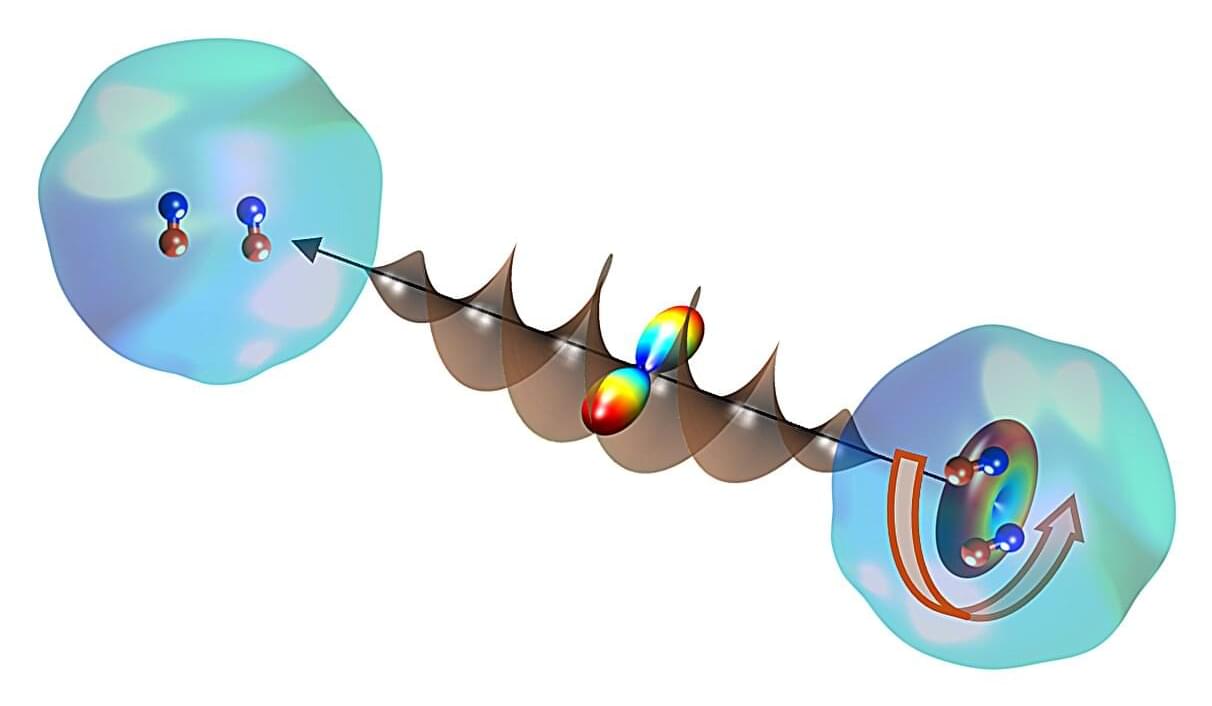
In a new Science study, researchers report an unexpected role for sensory nerves in bone healing, providing insights into communication between the nervous system and the cells responsible for bone repair.
Learn more in a new Science Perspective.
Growth factors secreted by sensory nerves promote fracture healing.
Vicki Rosen and Francesca Gori Authors Info & Affiliations
Science
Vol 391, Issue 6781
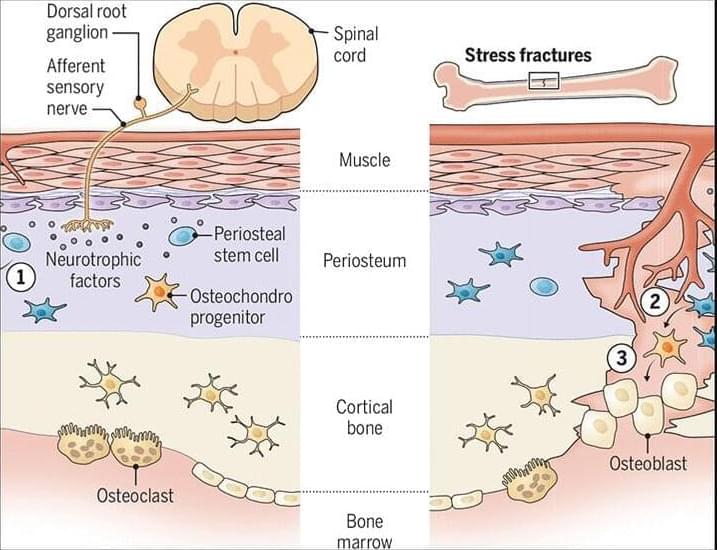
The researchers tested a new method for detecting Alzheimer’s disease using a few drops of blood obtained from the fingertip and then dried on a card. This process was used to find proteins linked to Alzheimer’s disease and other brain changes in the 337 participants.
The study found that levels of p-tau217 in finger-prick samples closely matched results from standard blood tests and were able to identify Alzheimer’s disease-related changes in spinal fluid with an accuracy of 86 per cent. Two other markers, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and neurofilament light (NfL), were also successfully measured and showed strong agreement with traditional tests.
While not ready for clinical use, this breakthrough addresses critical barriers in Alzheimer’s research by enabling remote participation in studies, clinical trial recruitment and monitoring, broader population sampling for epidemiological research, and inclusion of underrepresented communities and regions with limited healthcare infrastructure.
The findings suggest that this simple technique could make large-scale studies and remote testing possible, including for people with Down syndrome, who face a higher risk of Alzheimer’s disease and for other underserved populations. ScienceMission sciencenewshighlights.
A groundbreaking international study has demonstrated that Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers can be accurately detected using simple finger-prick blood samples that can be collected at home and mailed to laboratories without refrigeration or prior processing.
The research published in Nature Medicine. It represents the first large-scale validation of this accessible testing approach that removes geographic barriers and opens brain disease research to global populations without requiring specialised healthcare infrastructure.