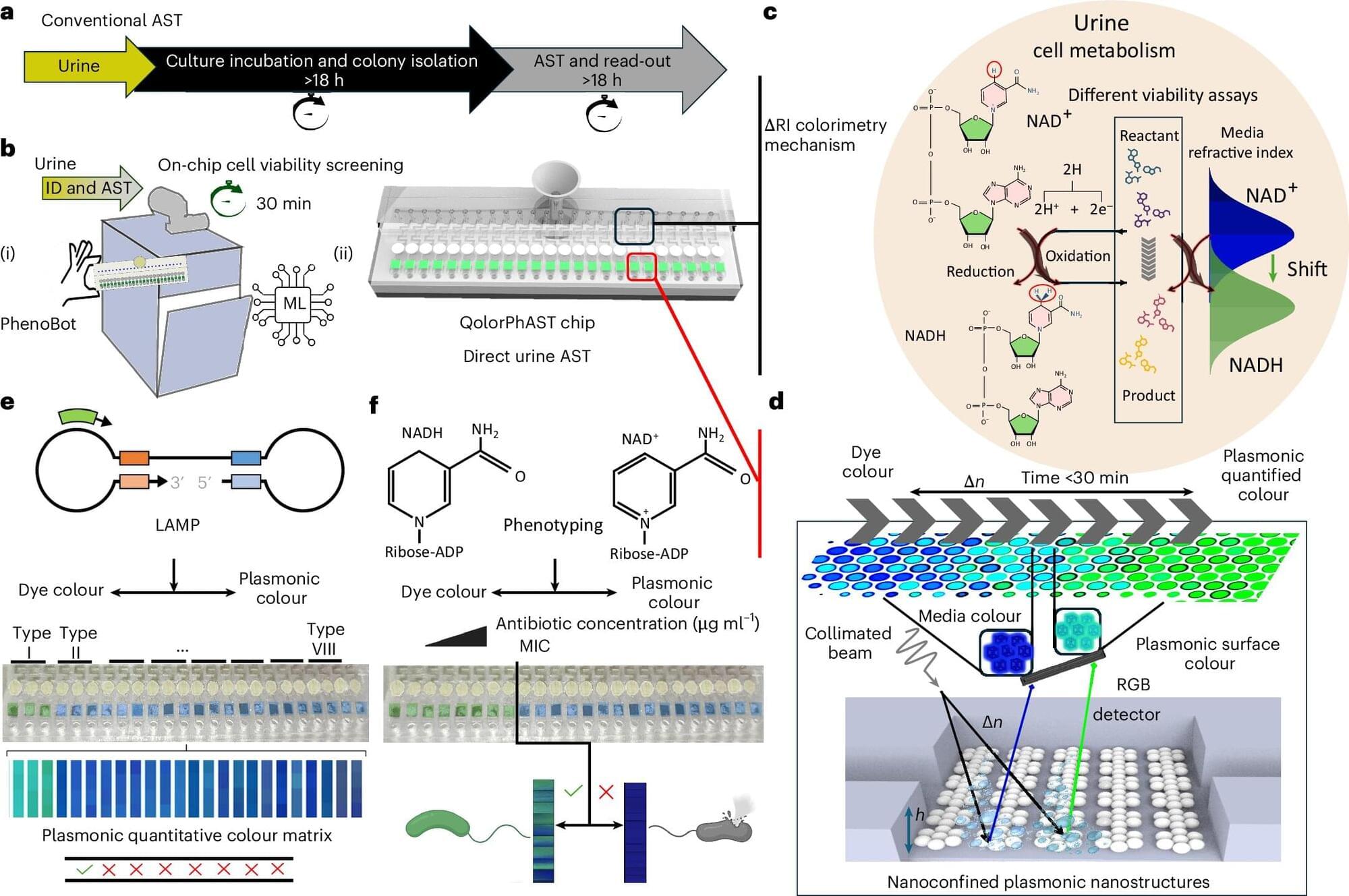
An agentic AI tool for battery researchers harnesses data from previous battery designs to predict the cycle life of new battery concepts. With information from just 50 cycles, the tool—developed at University of Michigan Engineering—can predict how many charge-discharge cycles the battery can undergo before its capacity drops below 90% of its design capacity.
This could save months to years of testing, depending on the conditions of cycling experiments, as well as substantial electrical power during battery prototyping and testing. The team estimates that the cycle lives of new battery designs could be predicted with just 5% of the energy and 2% of the time required by conventional testing.
“When we learn from the historical battery designs, we leverage physics-based features to construct a generalizable mapping between early-stage tests and cycle life,” said Ziyou Song, U-M assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering and corresponding author of the study in Nature. “We can minimize experimental efforts and achieve accurate prediction performance for new battery designs.”