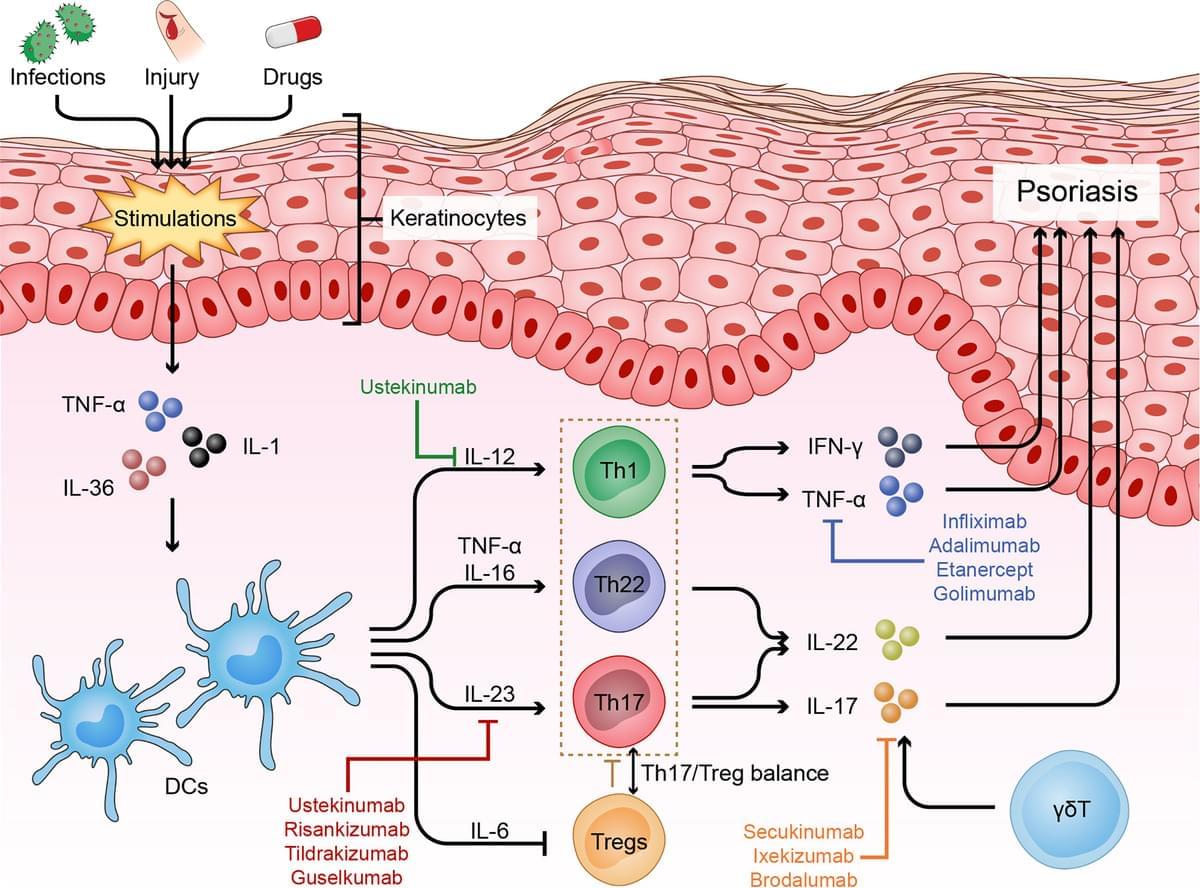
Psoriasis can be triggered by infections, physical injury and certain drugs. The most common type of psoriasis is psoriasis vulgaris, which primarily features dry, well-demarcated, raised red lesions with adherent silvery scales on the skin and joints. Over the past few decades, scientific research has helped us reveal that innate and adaptive immune cells contribute to the chronic inflammatory pathological process of psoriasis. In particular, dysfunctional helper T cells (Th1, Th17, Th22, and Treg cells) are indispensable factors in psoriasis development. When stimulated by certain triggers, antigen-presenting cells (APCs) can release pro-inflammatory factors (IL-23, IFN-α and IL-12), which further activate naive T cells and polarize them into distinct helper T cell subsets that produce numerous cytokines, such as TNF, IFN-γ, IL-17 and IL-22, which act on keratinocytes to amplify psoriatic inflammation. In this review, we describe the function of helper T cells in psoriasis and summarize currently targeted anti-psoriatic therapies.
Psoriasis is a complex, chronic relapsing and inflammatory skin disorder with an overall prevalence of 2% in the general population worldwide (1). The most common type of psoriasis is psoriasis vulgaris, which primarily manifests as dry, well-demarcated, raised red lesions with adherent silvery scales on the skin and joints and accounts for nearly 90% of all psoriasis cases. Psoriasis is also associated with multiple comorbidities, such as arthritis, obesity, diabetes mellitus, depression, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and reduced quality of life (2).
Although the exact mechanism that triggers psoriasis remains unclear, it is currently accepted that psoriasis is induced or exacerbated by either nonspecific triggers, such as infections [such as Streptococcus ], physical injury [such as scratching and tattoos ], drugs [such as β blockers, lithium and antimalarials (5, 6)] or some specific autoantigens [such as cathelicidin LL-37, melanocytic ADAMTSL5, lipid antigen PLA2G4D and keratin 17 ]. Pathologically, psoriasis is characterized by epidermal acanthosis (thickening of the viable layers), hyperkeratosis (thickened cornified layer), and parakeratosis (cell nuclei present in the cornified layer).