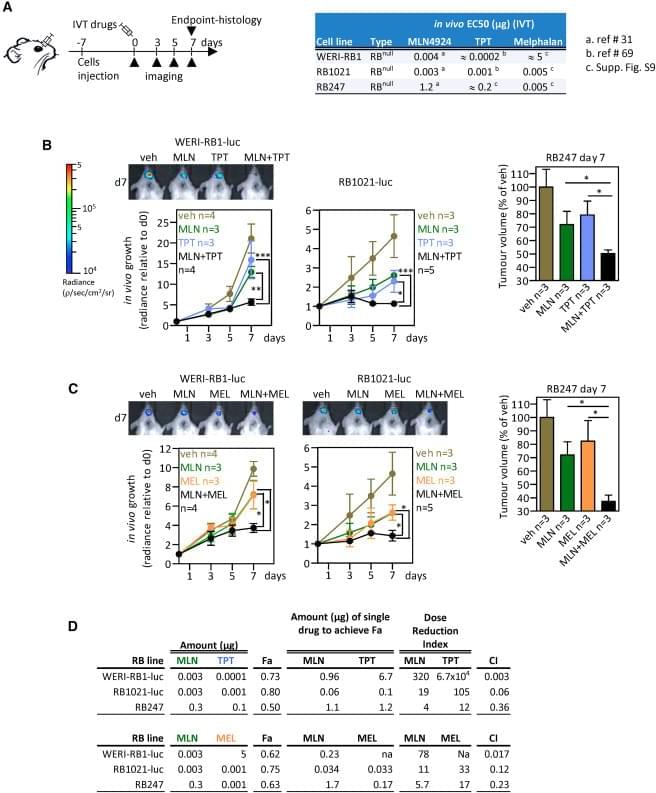
Recent studies have examined the connection between endometriosis and cancer, revealing that the condition may exhibit several traits commonly associated with malignant tumors. Researchers have identified specific characteristics of endometriosis that align with established hallmarks of cancer, prompting a reevaluation of how this chronic gynecological disorder is understood and approached in medical research.
The investigation highlights parallels between endometriosis and cancer, including features such as abnormal cell growth, resistance to cell death, and the ability to invade surrounding tissues. These findings suggest that while endometriosis is not classified as a form of cancer, it shares biological behaviors typically observed in malignancies. The study underscores the complexity of endometriosis and its potential implications for treatment strategies and further research into its underlying mechanisms.
Newsflash | powered by geneonline AI.