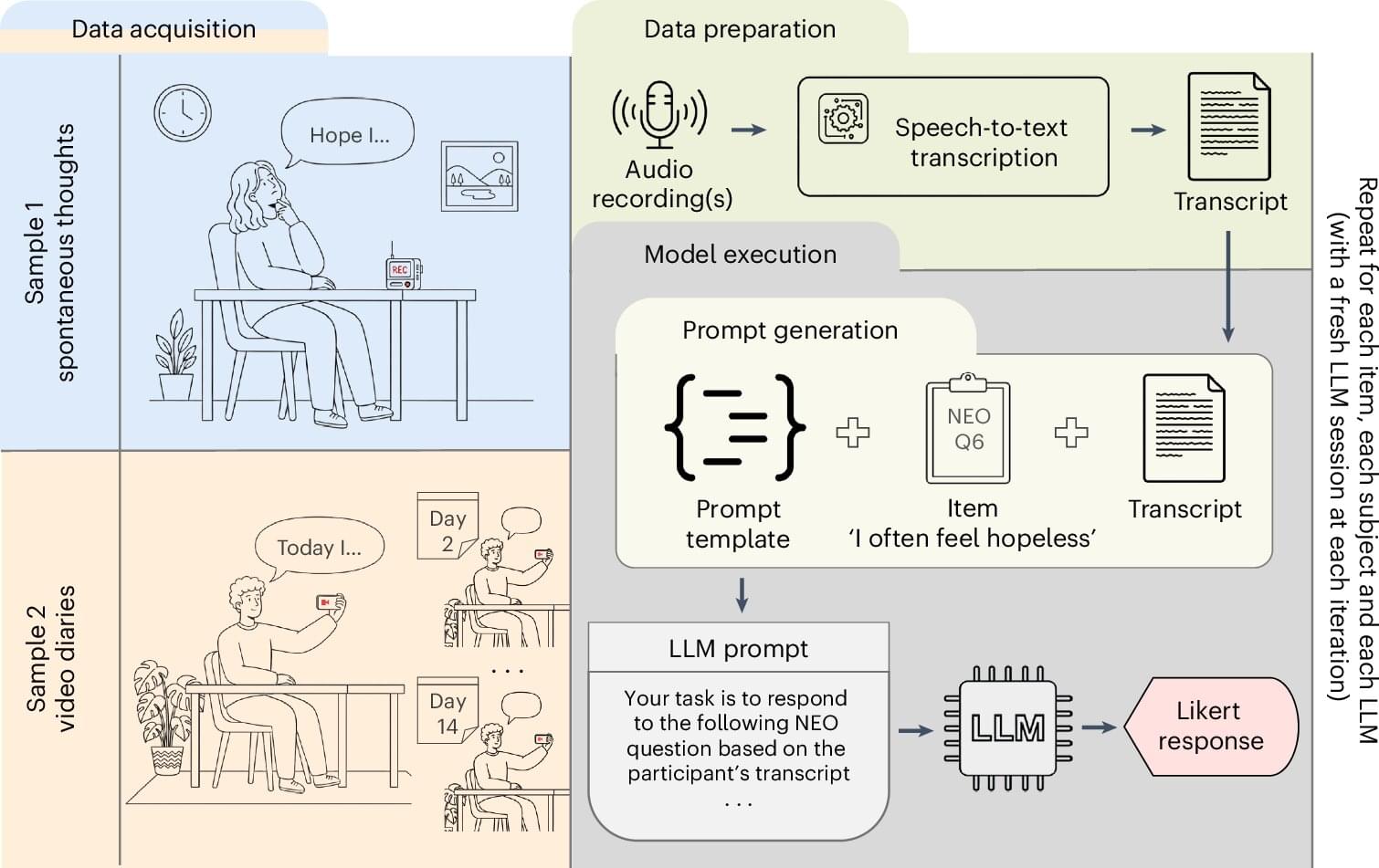
If you say a few words, generative AI will understand who you are—maybe even better than your close family and friends. A new University of Michigan study found that widely available generative AI models (e.g., ChatGPT, Claude, LLaMa) can predict personality, key behaviors and daily emotions as or even more accurately than those closest to you. The findings appear in the journal Nature Human Behavior.
AI as a new personality judge
“What this study shows is AI can also help us understand ourselves better, providing insights into what makes us most human, our personalities,” said the study’s first author Aidan Wright, U-M professor of psychology and psychiatry. “Lots of people may find this of interest and useful. People have long been interested in understanding themselves better. Online personality questionnaires, some valid and many of dubious quality, are enormously popular.”