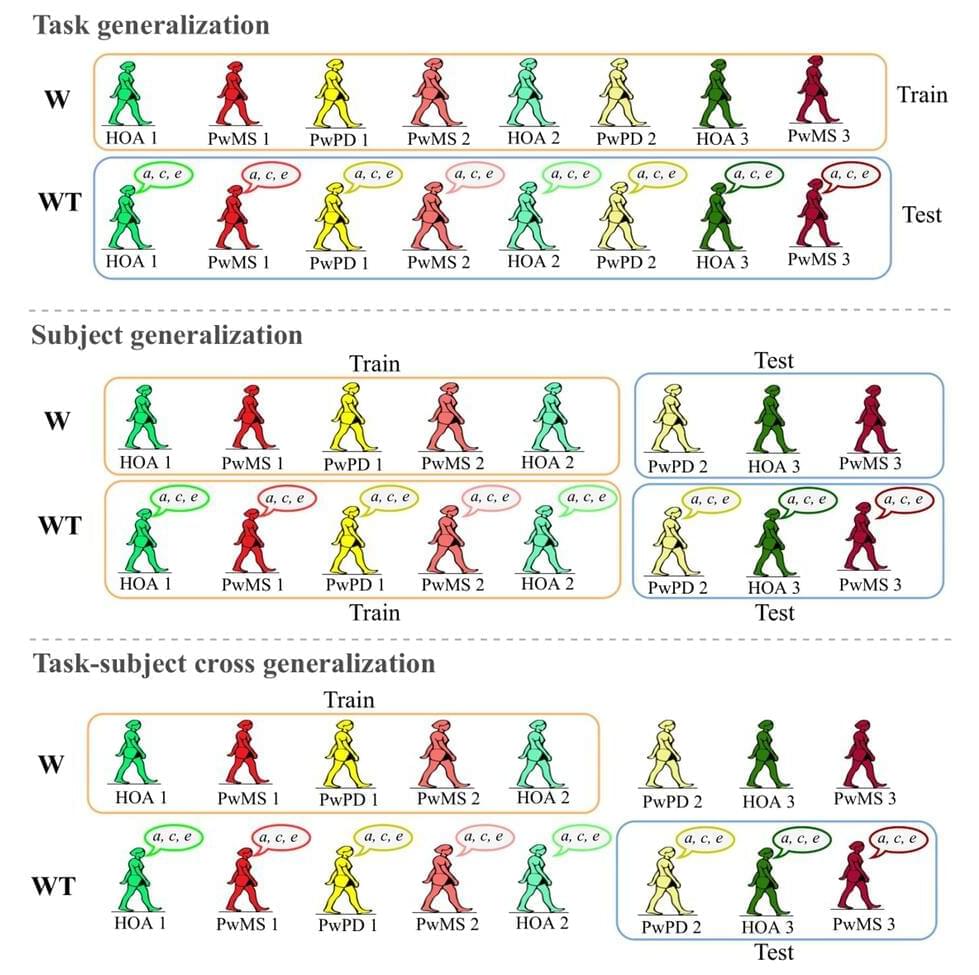
In an effort to streamline the process of diagnosing patients with multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease, researchers used digital cameras to capture changes in gait—a symptom of these diseases—and developed a machine-learning algorithm that can differentiate those with MS and PD from people without those neurological conditions.
Their findings are reported in the IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics.
The goal of the research was to make the process of diagnosing these diseases more accessible, said Manuel Hernandez, a University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign professor of kinesiology and community health who led the work with graduate student Rachneet Kaur and industrial and enterprise systems engineering and mathematics professor Richard Sowers.