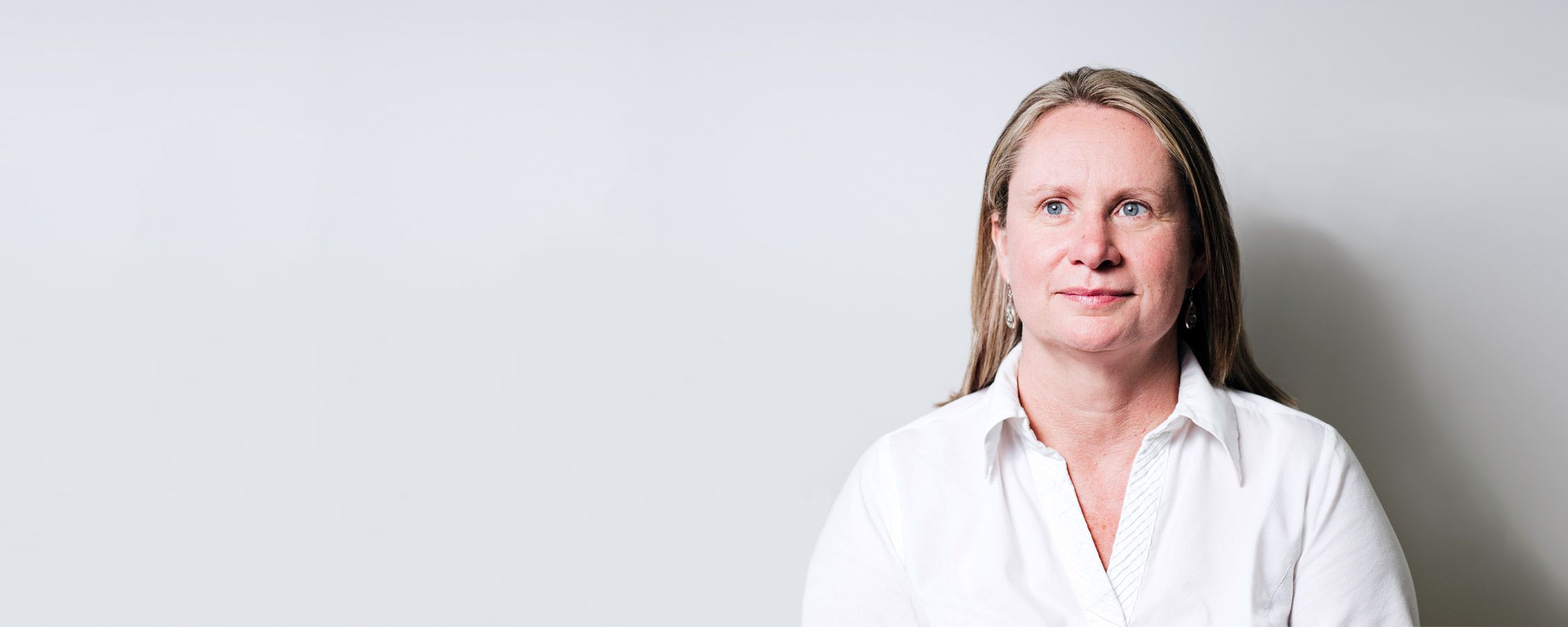
“Yep, transforming health care and telepathy, those are the items on her to-do list. Jepsen plans to achieve both goals with a cheap wearable device that her engineers are now tinkering with in the lab. And then there’s the side benefit of reinvigorating the tired consumer electronics industry, which Jepsen thinks is due for the next big thing.
Jepsen was at SXSW to give a talk about Openwater, her new startup. While the company is still conducting R&D to decide on its first products, Jepsen feels the need to speak out now about what she’s building and how she thinks her technology could radically change society. She wants to give people fair warning and time to think about what’s coming. “I know it seems outlandish to be talking about telepathy, but it’s completely solid physics and mathematical principles—it’s in reach in the next three years,” she says.
Plus, she’s sick of stealth mode. “I haven’t been able to to talk about what I’ve been doing for five and half years while I was at Google and Facebook, and I don’t think secrecy is useful,” she says. She left Facebook in August, and in September she filed patents for her Openwater technology, which she expects to be issued any day now.

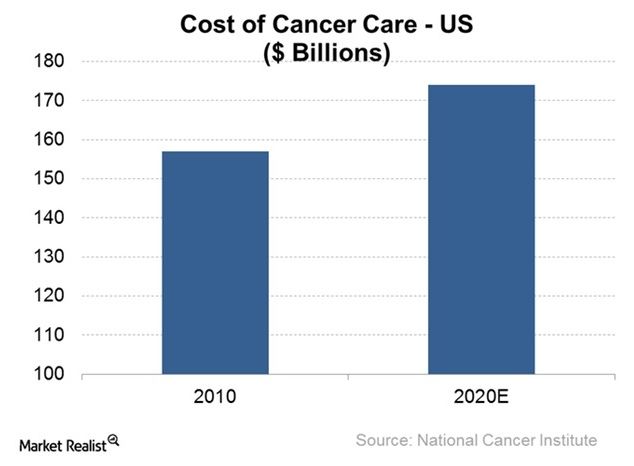
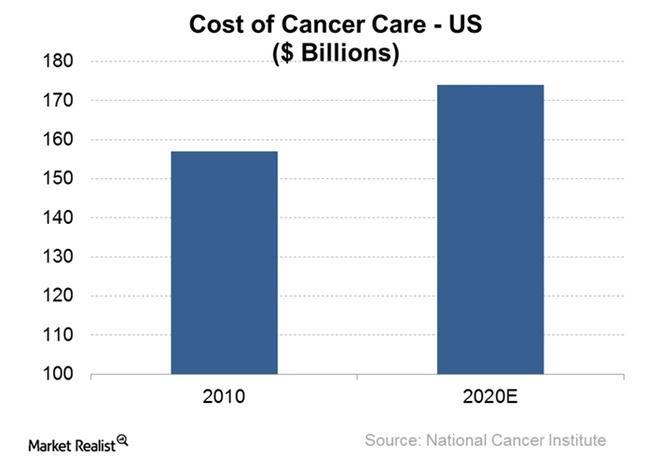



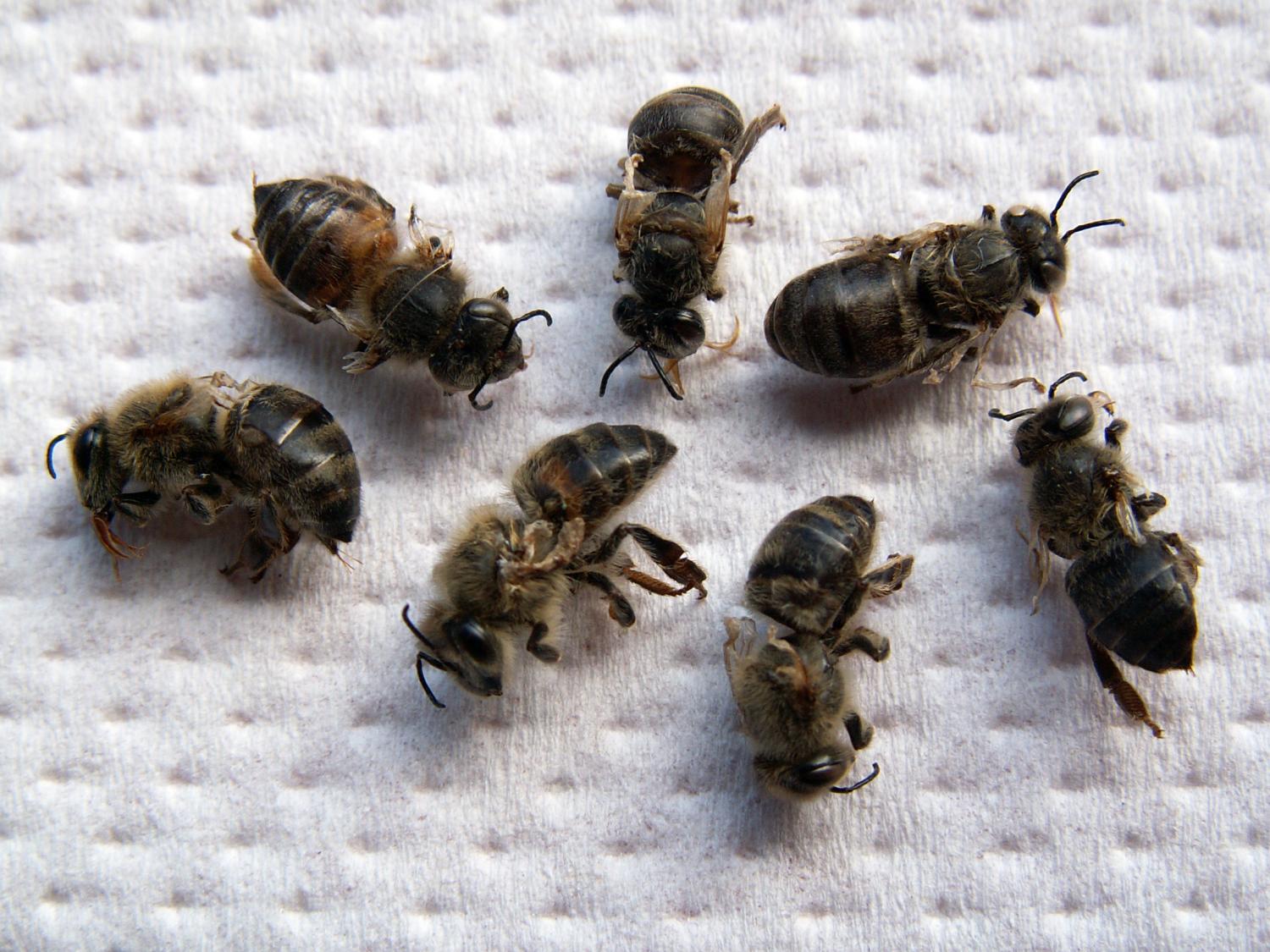
 microbes could take more than a decade to develop. In an effort to stress the urgency of this rising resistance, the World Health Organization (WHO) created a list of the twelve deadliest superbugs with which we are currently dealing.
microbes could take more than a decade to develop. In an effort to stress the urgency of this rising resistance, the World Health Organization (WHO) created a list of the twelve deadliest superbugs with which we are currently dealing.