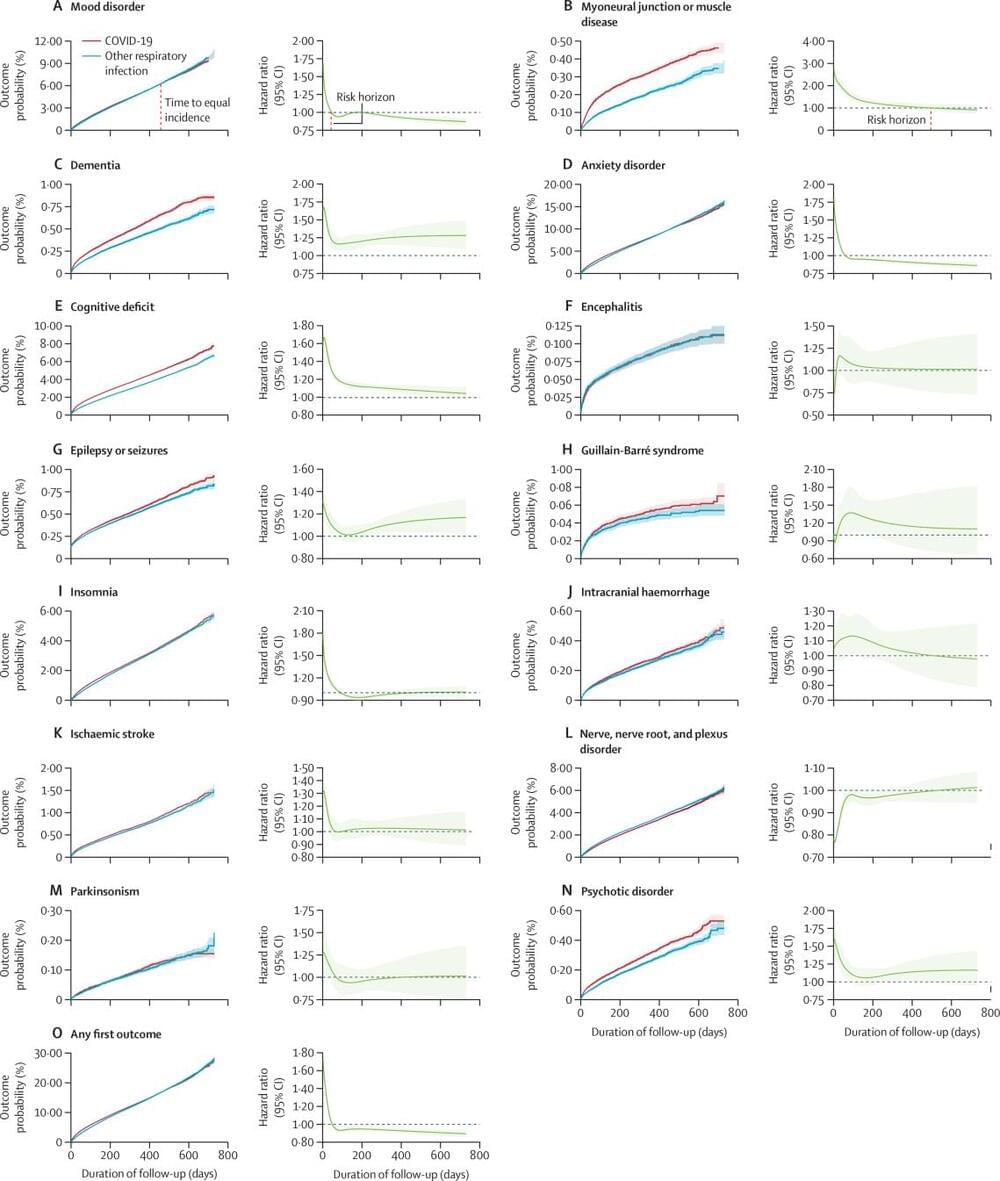
This analysis of 2-year retrospective cohort studies of individuals diagnosed with COVID-19 showed that the increased incidence of mood and anxiety disorders was transient, with no overall excess of these diagnoses compared with other respiratory infections. In contrast, the increased risk of psychotic disorder, cognitive deficit, dementia, and epilepsy or seizures persisted throughout. The differing trajectories suggest a different pathogenesis for these outcomes. Children have a more benign overall profile of psychiatric risk than do adults and older adults, but their sustained higher risk of some diagnoses is of concern. The fact that neurological and psychiatric outcomes were similar during the delta and omicron waves indicates that the burden on the health-care system might continue even with variants that are less severe in other respects. Our findings are relevant to understanding individual-level and population-level risks of neurological and psychiatric disorders after SARS-CoV-2 infection and can help inform our responses to them.
National institute for health and care research oxford health biomedical research centre, the wolfson foundation, and MQ mental health research.