Digital waste is a growing environmental and health problem whether dumped in landfills in the Global North or South. Are there solutions?



There’s an epidemic in Western countries, and one few people are aware of. It’s an epidemic of visceral fat, a deep kind of fat that packs around vital organs, like the liver, and is linked with health problems like diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure.
You might assume that only people who are overweight or obese have too much visceral fat, but that’s not the case. Thin people, particularly inactive ones and older individuals, can have enough visceral fat to increase their risk of chronic health problems. They may look thin, but they’re not healthy because they have too much visceral fat and other markers of bad health.
Although it’s not easy to trim down visceral fat, science shows there are ways to reduce your body’s visceral fat burden and improve your health simultaneously.
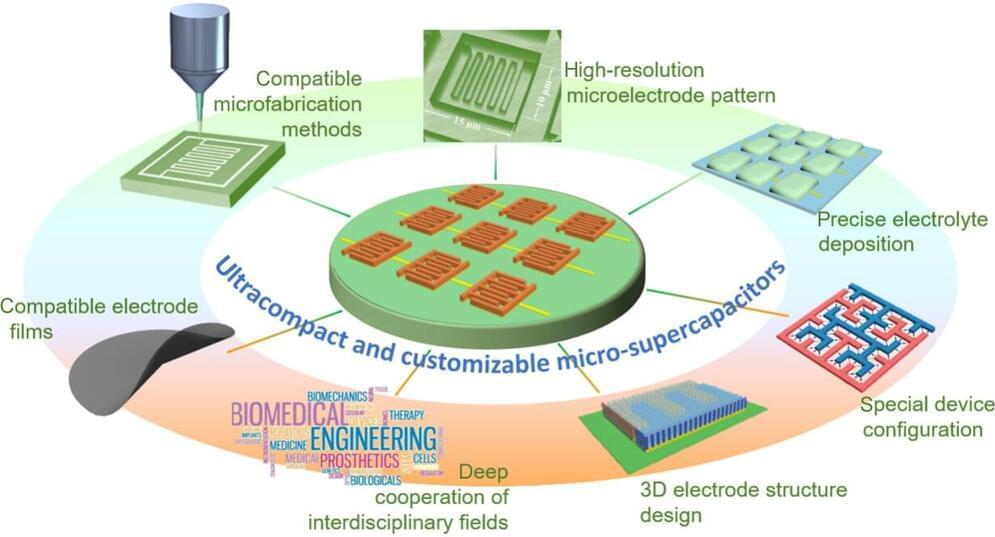
Increased demand for super tiny electronic sensors coming from healthcare, environmental services and the Internet of Things is prompting a search for equally tiny ways to power these sensors. A review of the state of ultracompact supercapacitors, or “micro-supercapacitors,” concludes there is still a lot of research to be done before these devices can deliver on their promise.
The review appeared in the journal Nano Research Energy.
The explosion of demand in recent years for miniaturized electronic devices, such as health monitors, environmental sensors and wireless communications technologies has in turn driven demand for components for those devices that have ever smaller size and weight, with lower energy consumption, and all of this at cheaper prices.

An algorithm developed by researchers from Helmholtz Munich, the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and its University Hospital rechts der Isar, the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn is able to learn independently across different medical institutions. The key feature is that it is self-learning, meaning it does not require extensive, time-consuming findings or markings by radiologists in the MRI images.
This federated algorithm was trained on more than 1,500 MRI scans of healthy study participants from four institutions while maintaining data privacy. The algorithm then was used to analyze more than 500 patient MRI scans to detect diseases such as multiple sclerosis, vascular disease, and various forms of brain tumors that the algorithm had never seen before. This opens up new possibilities for developing efficient AI-based federated algorithms that learn autonomously while protecting privacy. The study has now been published in the journal Nature Machine Intelligence.
Health care is currently being revolutionized by artificial intelligence. With precise AI solutions, doctors can be supported in diagnosis. However, such algorithms require a considerable amount of data and the associated radiological specialist findings for training. The creation of such a large, central database, however, places special demands on data protection. Additionally, the creation of the findings and annotations, for example the marking of tumors in an MRI image, is very time-consuming.
According to recent Baycrest research, adults without dementia risk factors like smoking, diabetes, or hearing loss had brain health comparable to that of those who are 10 to 20 years younger than them. According to the research, only one dementia risk factor can age a person’s cognition by up to three years.
“Our results suggest lifestyle factors may be more important than age in determining someone’s level of cognitive functioning. This is great news since there’s a lot you can do to modify these factors, such as managing diabetes, addressing hearing loss, and getting the support you need to quit smoking,” says Dr. Annalise LaPlume, Postdoctoral Fellow at Baycrest’s Rotman Research Institute (RRI) and the study’s lead author.
The research is one of the first to look at lifestyle risk factors for dementia across the entire lifespan.
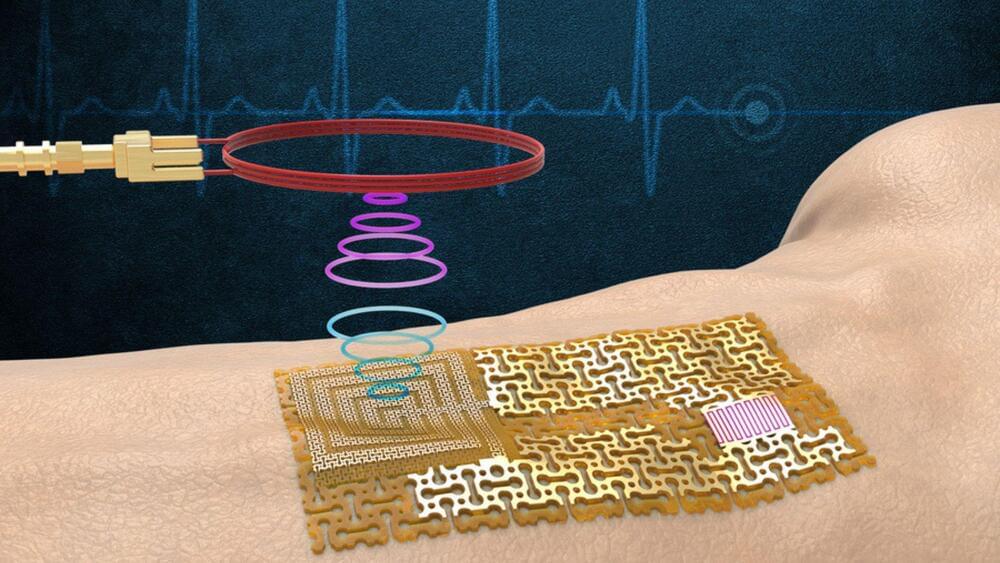
In a significant development, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) engineers have developed a new category of wireless wearable skin-like sensors for health monitoring that doesn’t require batteries or an internal processor.
The team’s sensor design is a form of electronic skin, or “e-skin” — a flexible, semiconducting film that conforms to the skin like electronic Scotch tape, according to a press release published by MIT.
“If there is any change in the pulse, or chemicals in sweat, or even ultraviolet exposure to skin, all of this activity can change the pattern of surface acoustic waves on the gallium nitride film,” said Yeongin Kim, study’s first author, and a former MIT postdoc scholar.
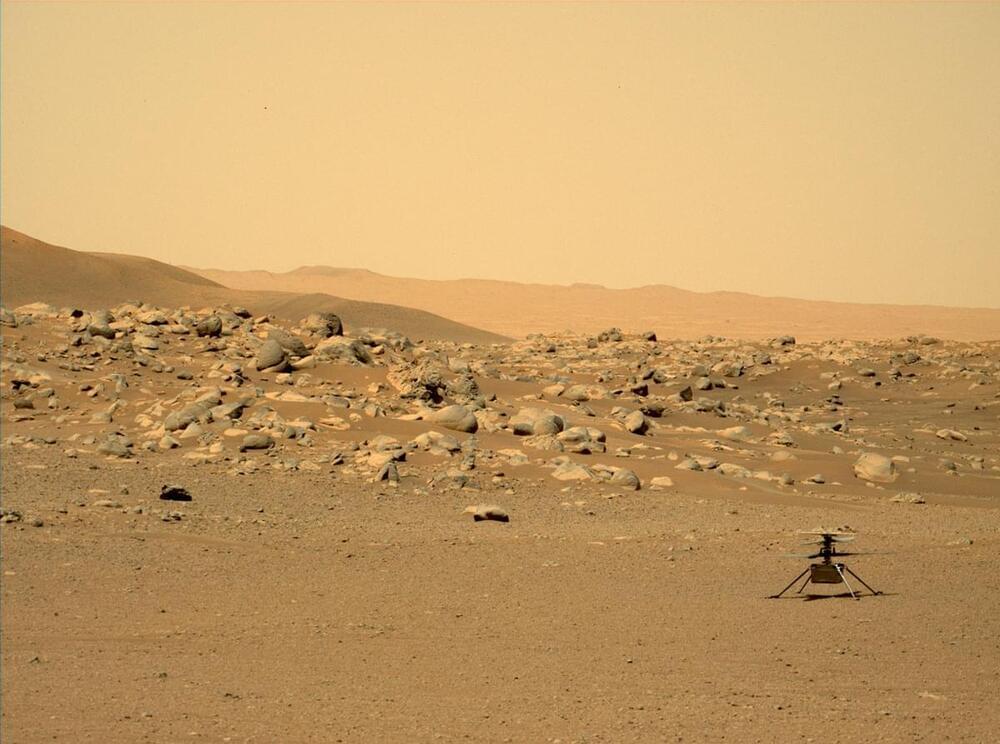

It’s been over a month since we last updated our blog about our winter warrior, currently around 96 million miles away. At present the team is preparing for Ingenuity’s next flight, which could take place as early as this weekend. This 30th sortie will be a short hop – which will check out our system’s health after surviving 101 sols of winter, collect landing delivery data in support of NASA’s Mars Sample Return Campaign, and potentially clear off dust that has settled on our solar panel since Flight 29.
What’s Happened Lately
It’s still winter at Jezero Crater, which means overnight temperatures are as low as -124 degrees Fahrenheit (−86 Celsius). Winter at Mars also means the amount of solar energy hitting our solar panel remains below what is needed to maintain charge in our batteries both day and night. However, during the day the panel continues to create enough charge to make shorter hops possible. That’s what we did on Flight 29 and is our plan for Flight 30.

I have been invited to participate in a quite large event in which some experts and I (allow me to not consider myself one) will discuss about Artificial Intelligence, and, in particular, about the concept of Super Intelligence.
It turns out I recently found out this really interesting TED talk by Grady Booch, just in perfect timing to prepare my talk.
No matter if you agree or disagree with Mr. Booch’s point of view, it is clear that today we are still living in the era of weak or narrow AI, very far from general AI, and even more from a potential Super Intelligence. Still, Machine Learning bring us with a great opportunity as of today. The opportunity to put algorithms to work together with humans to solve some of our biggest challenges: climate change, poverty, health and well being, etc.
A more long-term alternative to using steroids.
It is estimated that more than 250 million people globally suffer from asthma, which also causes hundreds of thousands of fatalities annually. Therefore, finding a cure for the condition could be life-changing for a large number of people.
Scientists have now developed a new potential long-term treatment for asthma. The method, which not only treats the symptoms of asthma but also targets one of its causes, functions by preventing the mobility of a certain kind of stem cell known as a pericyte.
Tightness of the chest, difficulty breathing, coughing, and wheezing — a person suffering from allergic asthma can start experiencing all of these symptoms after inhaling an allergen. Though asthma affects about 340 million people worldwide, allergic asthma is the most prevalent form, with 90 percent of children with asthma having allergies, compared to 50 percent of adults with asthma.
Now, researchers led by Laurent Reber (Infinity, Toulouse) and Pierre Bruhns (Humoral Immunity, Institut Pasteur, Paris) and French company NEOVACS have developed a vaccine that could provide long-term protection against allergic asthma and reduce the severity of the symptoms, improving patient quality of life dramatically.
