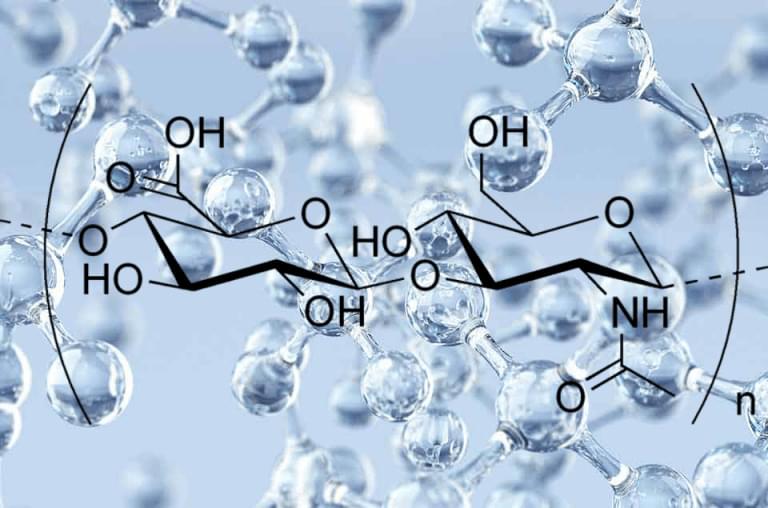
Naked mole rats are rodents that are about the size of a mouse with a key difference, aside from having no fur — they’re extremely long-lived — reaching ages of around 40 years old. For comparison, lab mice live an average of about three and a half years. To explain their extensive lifespans, researchers have sought to pinpoint how naked mole rats evade the onset of age-related diseases like cancer. In doing so, they’ve identified a form of gelatinous substance called hyaluronan, which has anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties. Now, the question of whether the benefits of the naked mole rat’s abundant levels of this form of hyaluronan — called high molecular mass hyaluronic acid (HMM-HA) — can be exported to other species has recently drawn attention.
Published in Nature, Gorbunova and colleagues from the University of Rochester show that genetically modifying mice to harbor an enzyme that produces HMM-HA extends their lifespan. The researchers go on to show that increasing HMM-HA reduces the prevalence of cancer. Additionally, the nmrHAS2 gene improves the healthspan of mice by countering physiological dysfunction, as measured with a frailty score. These findings provide the first evidence that genes from long-lived species can be exported to other species, perhaps conferring benefits to humans one day.