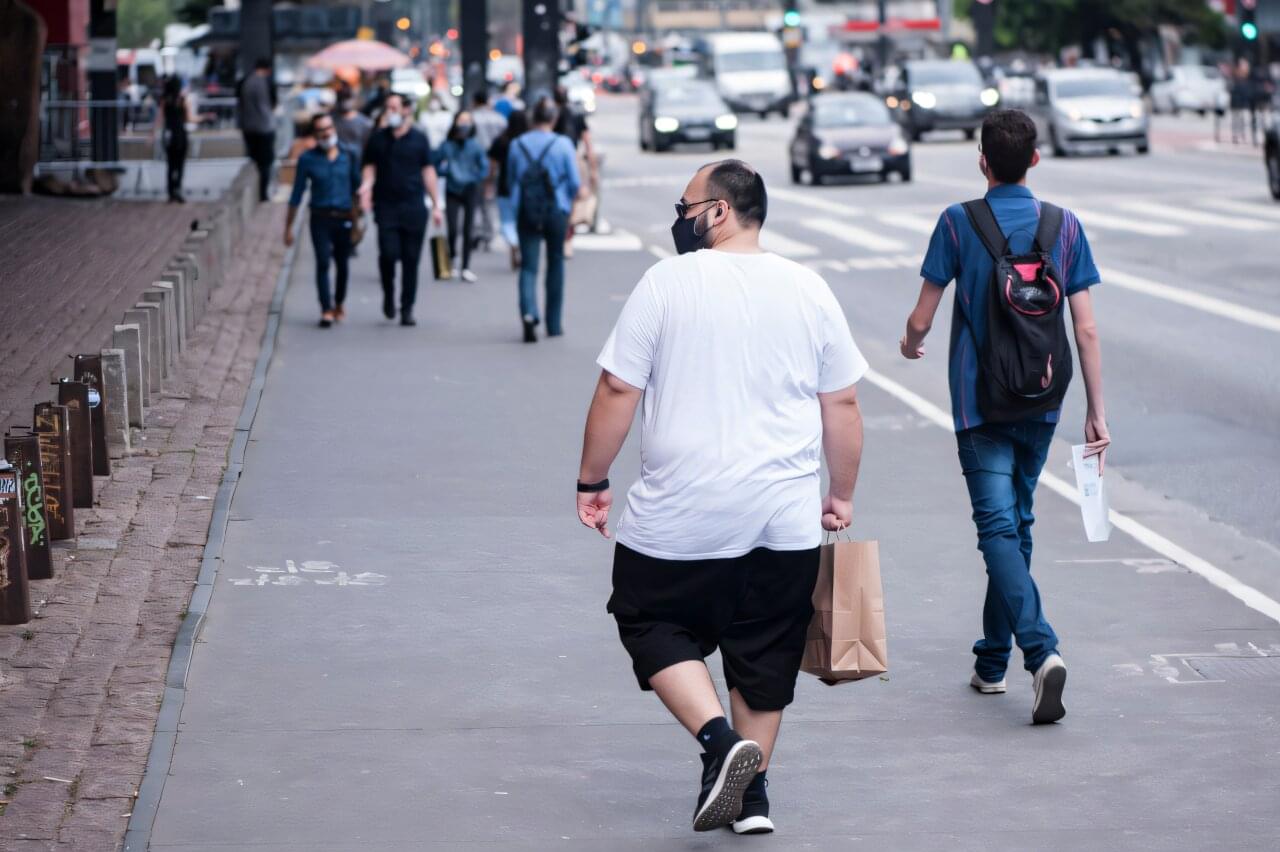
A study by researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in Brazil, in partnership with University College London (UCL) in the United Kingdom, concluded that the combination of abdominal fat and muscle loss increases the risk of death by 83%, compared to people without these conditions.
This combination is so dangerous that it identifies an even greater problem: sarcopenic obesity. This condition is characterized by loss of muscle mass while gaining fat throughout the body. It is a difficult condition to diagnose, and it is related to loss of autonomy and a worsening quality of life in older adults. It is also known as frailty syndrome and is associated with an increased risk of falls and other comorbidities.
“In addition to assessing the risk of death associated with abdominal obesity and low muscle mass, we were able to prove that simple methods can be used to detect sarcopenic obesity. This is important because the lack of consensus on diagnostic criteria for this disease makes it difficult to detect and treat,” says Tiago da Silva Alexandre, a professor in the Department of Gerontology at UFSCar and one of the authors of the study.