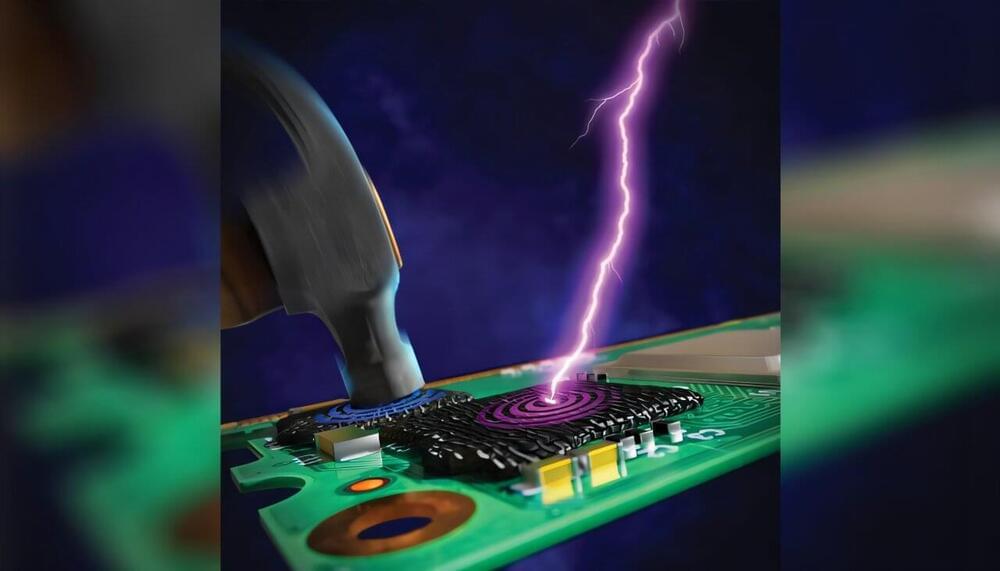
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection is a significant concern in the chemical and electronics industries. In electronics, ESD often causes integrated circuit failures due to rapid voltage and current discharges from charged objects, such as human fingers or tools.
With the help of 3D printing techniques, researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) are “packaging” electronics with printable elastomeric silicone foams to provide both mechanical and electrical protection of sensitive components. Without suitable protection, substantial equipment and component failures may occur, leading to increased costs and potential workplace injuries. The team’s research is featured in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
3D printing is a rapidly growing manufacturing method that enables the production of cellular foams with customizable pore architectures to achieve compressive mechanical properties that can be tailored to minimize permanent deformation by evenly distributing stress throughout the printed architecture.