Let’s bring microscopes to the masses.


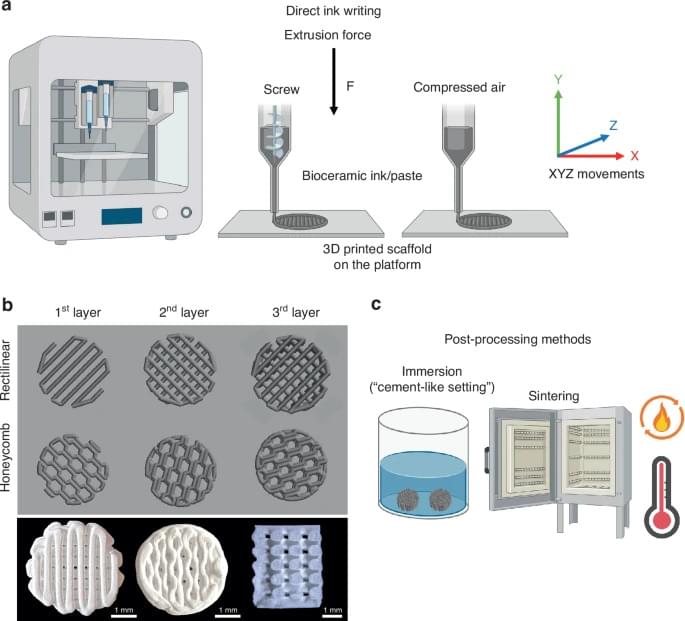
Researchers have unveiled a groundbreaking approach to facial bone reconstruction using 3D-printed ceramic materials that can be precisely customized to each patient’s needs. The comprehensive review, published in the International Journal of Oral Science, demonstrates how advanced manufacturing techniques are transforming the treatment of complex facial bone defects.
The traditional approach of harvesting bone from elsewhere in the patient’s body – long considered the gold standard – may soon give way to these sophisticated synthetic alternatives. These new materials not only eliminate the need for a second surgical site but can also be tailored to match the intricate anatomy of facial bones.
“3D printing enables the production of personalized grafts that perfectly fit the bone defect,” explains Marco C. Bottino, one of the study’s lead researchers. The technology allows surgeons to create exact replicas of the desired bone structure based on detailed medical imaging.
Princeton engineers have developed a scalable 3D printing technique to produce soft plastics with customizable stretchiness and flexibility, while also being recyclable and cost-effective—qualities rarely combined in commercially available materials.
In a study published in Advanced Functional Materials, a team led by Emily Davidson detailed how they used thermoplastic elastomers—a class of widely available polymers—to create 3D-printed structures with adjustable stiffness. By designing the 3D printer’s print path, the engineers could program the plastic’s physical properties, allowing devices to stretch and flex in one direction while remaining rigid in another.
Davidson, an assistant professor of chemical and biological engineering, highlighted the potential applications of this technique in fields such as soft robotics, medical devices, prosthetics, lightweight helmets, and custom high-performance shoe soles.
By November 2024, 15 U.S. states had established regulations on ghost guns, though exact requirements vary. The rules typically require a serial number, background checks for firearm component purchases and reporting to authorities that a person is producing 3D-printed guns.
For instance, in New Jersey, a 2019 law mandates that all ghost guns have a serial number and be registered. Under current New York law, possession or distribution of a 3D-printed gun is classified as a misdemeanor. However, a proposed law seeks to elevate the manufacturing of firearms using 3D-printing technology to a felony offense.
As technology advances and rules evolve, criminals who use 3D-printed firearms will continue to pose threats to public safety and security, and governments will continue playing catch-up to effectively regulate these weapons.

When Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) achieved fusion ignition at the National Ignition Facility (NIF) in December 2022, the world’s attention turned to the prospect of how that breakthrough experiment — designed to secure the nation’s nuclear weapons stockpile — might also pave the way for virtually limitless, safe and carbon-free fusion energy.
Advanced 3D printing offers one potential solution to bridging the science and technology gaps presented by current efforts to make inertial fusion energy (IFE) power plants a reality.
“Now that we have achieved and repeated fusion ignition,” said Tammy Ma, lead for LLNL’s inertial fusion energy institutional initiative, “the Lab is rapidly applying our decades of know-how into solving the core physics and engineering challenges that come with the monumental task of building the fusion ecosystem necessary for a laser fusion power plant. The mass production of ignition-grade targets is one of these, and cutting-edge 3D printing could help get us there.”
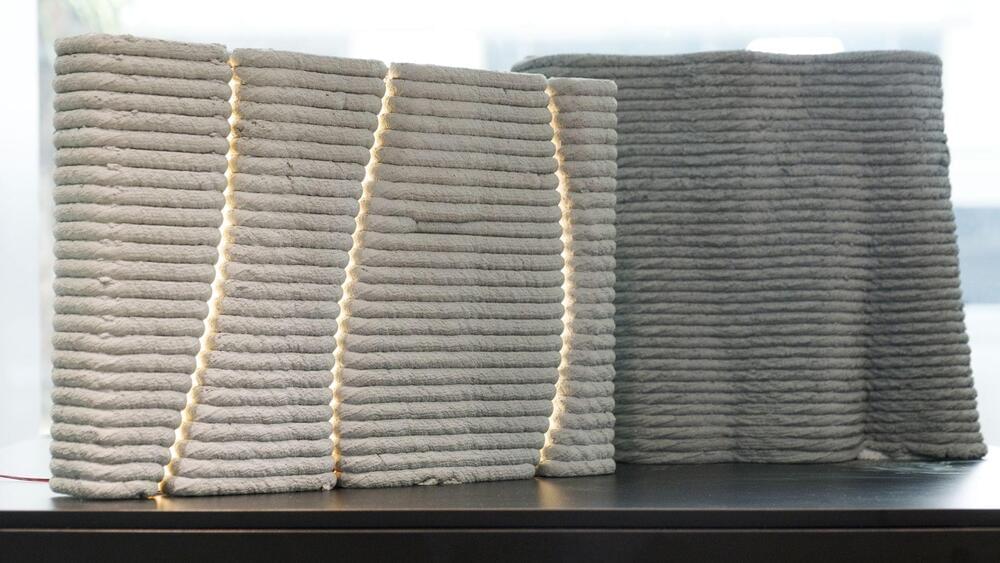

Scientists at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have pioneered a 3D concrete printing method that captures and stores carbon dioxide, marking a major step toward reducing the construction industry’s environmental footprint.
The innovative technique offers a promising solution to mitigate cement’s massive carbon emissions.
The process works by integrating CO₂ and steam—byproducts of industrial processes—into the concrete mix during 3D printing. As the material is printed, CO₂ reacts with components in the concrete, forming a solid, stable compound that remains locked within the structure.

Engineers at Johns Hopkins University have developed a new printing technique that solves for the fundamental weakness between the layers created during 3D printing. New printing technique allows them to precisely control interfaces between voxels, the three-dimensional counterparts to pixels, and how they function.

A 21-year-old Edmontonian is developing a 3D printer designed to take soil from the moon and convert it into essential equipment for astronauts.
Madison Feehan, CEO and founder of Space Copy, said she realized that 3D printing could substantially reduce the significant cost and logistic hurdles of sending astronauts back to the moon during her five years as a contract worker for NASA.
Radio Active’s Min Dhariwal spoke with Feehan this week to learn more about her research.
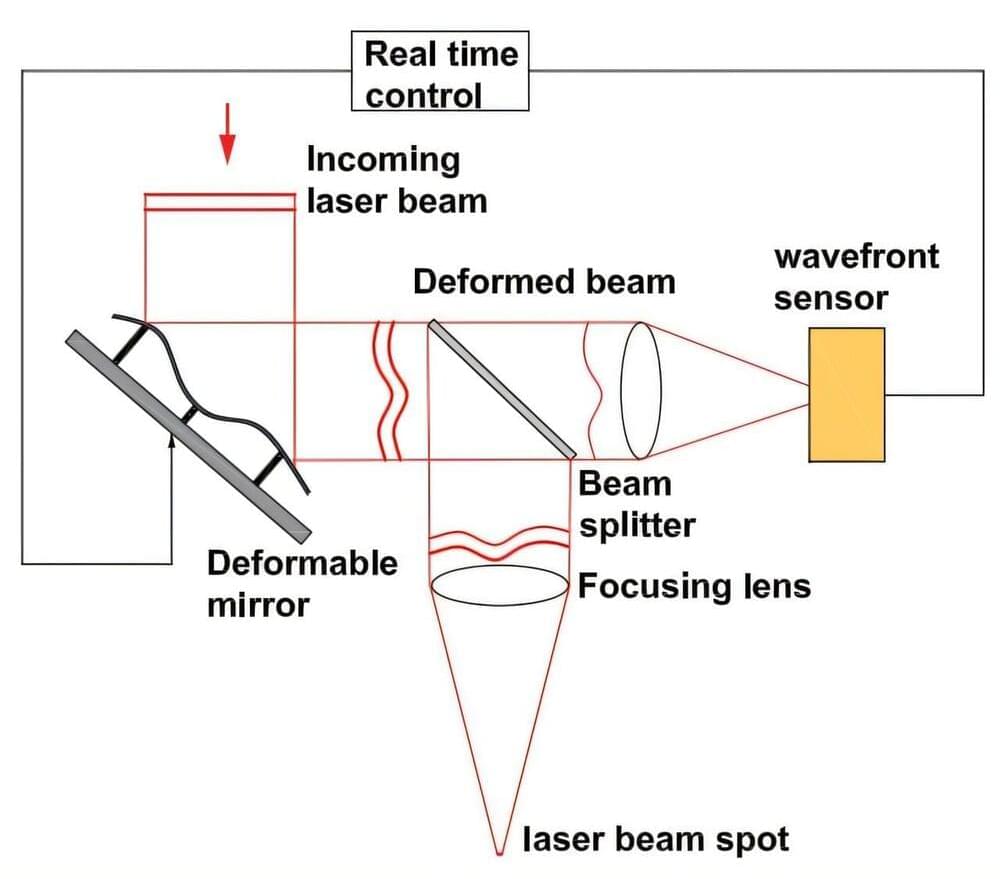
Yongcui Mi has developed a new technology that enables real-time shaping and control of laser beams for laser welding and directed energy deposition using laser and wire. The innovation is based on the same mirror technology used in advanced telescopes for astronomy.
In a few years, this new technology could lead to more efficient and reliable ways of using high-power lasers for welding and directed energy deposition with laser and wire. The manufacturing industry could benefit from new opportunities to build more robust processes that meet stringent quality standards.
“We are the first to use deformable mirror technology for this application. The mirror optics can handle multi-kilowatt laser power, and with the help of computer vision and AI, the laser beam can be shaped in real time to adapt to variations in joint gaps,” explains Yongcui, a newly minted Ph.D. in Production technology from University West.