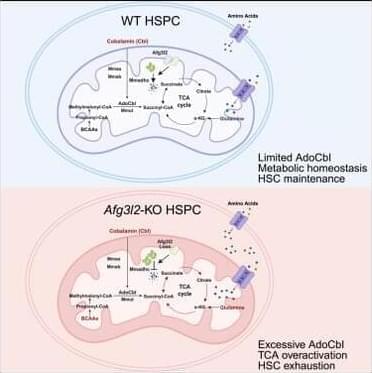
To identify the critical mitochondrial protease regulating HSPC homeostasis, we performed real-time PCR to examine the expression levels of various mitochondrial proteases in EPCR+SLAM-HSCs from mouse bone marrow (BM). Among them, the m-AAA protease Afg3l2 was the most highly expressed (Figure S1 A),18 suggesting its potential significance in HSC regulation. Furthermore, we conducted a comprehensive analysis of Afg3l2 expression across the hematopoietic hierarchy by examining EPCR+ SLAM-HSCs, SLAM-LT-HSCs, SLAM-ST-HSCs, SLAM-MPPs (multipotent progenitors), LSK (Lin-Sca-1+c-Kit+) cells, Lin− cells, and mature blood cells (B cells, T cells, and myeloid cells). Our results demonstrate that Afg3l2 expression is highest in the most primitive EPCR+SLAM-HSC population and gradually decreases with differentiation, supporting its crucial role in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) (Figure S1 B). Afg3l2 dysfunction has been linked to neurodegenerative disorders such as spinocerebellar ataxia19,20,21; however, its role in hematopoietic cells and its broader metabolic implications remain unexplored. To systemically investigate the function of Afg3l2 in HSPCs, we generated a conditional knockout (KO) allele of the Afg3l2 gene (Afg3l2f/+), in which exons 4 and 5 were flanked by loxP sites (Figure S1 C). Afg3l2f/+ mice were then crossed with Mx1-Cre transgenic mice to obtain Afg3l2f/f;Mx1-Cre+ animals. Deletion of Afg3l2 in hematopoietic cells was induced by administering polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (pIpC) to 6-to 8-week-old mice, and KO efficiency was confirmed by real-time PCR and western blot analysis (Figures S1 D–S1G). On day 14 after the final pIpC administration, complete blood count analysis revealed a significant reduction in white blood cell, lymphoid cell, and platelet counts in Afg3l2f/f mice (wild-type [WT]) compared to Afg3l2f/f;Mx1-Cre+ mice (KO) (Figures S1 H–S1J). Interestingly, red blood cell counts and hemoglobin levels remained comparable between WT and KO groups (Figures S1 K and S1L). Flow cytometry analysis of BM revealed a significant reduction in multiple hematopoietic populations in Afg3l2-KO mice, including LT-HSCs, ST-HSCs, MPPs, common myeloid progenitors, granulocytic/monocytic progenitors, and megakaryocyte/erythroid progenitors (Figures S1 M–S1P). Notably, the EPCR+SLAM-HSC population, a highly purified HSC subset, was also remarkably diminished (Figure S1 Q).
Consistently, functional colony-forming unit (CFU) assays showed that CFU-granulocyte, erythrocyte, macrophage, megakaryocyte (CFU-GEMM); CFU-granulocyte and macrophage (CFU-GM); and burst-forming unit-erythroid (BFU-E) were markedly decreased in Afg3l2-KO BM cells (Figures S1 R and S1S). These findings indicate that Afg3l2 deficiency causes leukopenia and impairs steady-state hematopoiesis.
To assess the in vivo function of Afg3l2 in HSPCs, we performed competitive BM transplantation. Lethally irradiated recipient mice (CD45.1) were transplanted with a 1:1 mixture of total BM cells from WT or Afg3l2-KO donor mice (CD45.2) and competitor BM cells (CD45.1/CD45.2) (Figure 1A). CD45 chimerism in peripheral blood (PB) was monitored every four weeks, and BM composition was analyzed 16 weeks post-transplantation. The percentage of donor-derived CD45.2+ cells in PB was significantly lower in recipients receiving Afg3l2-KO BM compared to those transplanted with WT BM (Figures 1B and 1C). The percentage of donor BM cells-derived CD45.2+ cells, HPCs, Lin−Sca-1+c-Kit+ (LSK) cells, HSCs, myeloid cells, B cells, and T cells was dramatically decreased in the BM of the Afg3l2-KO cell transplanted group 16 weeks after transplantation (Figures 1D and 1E).