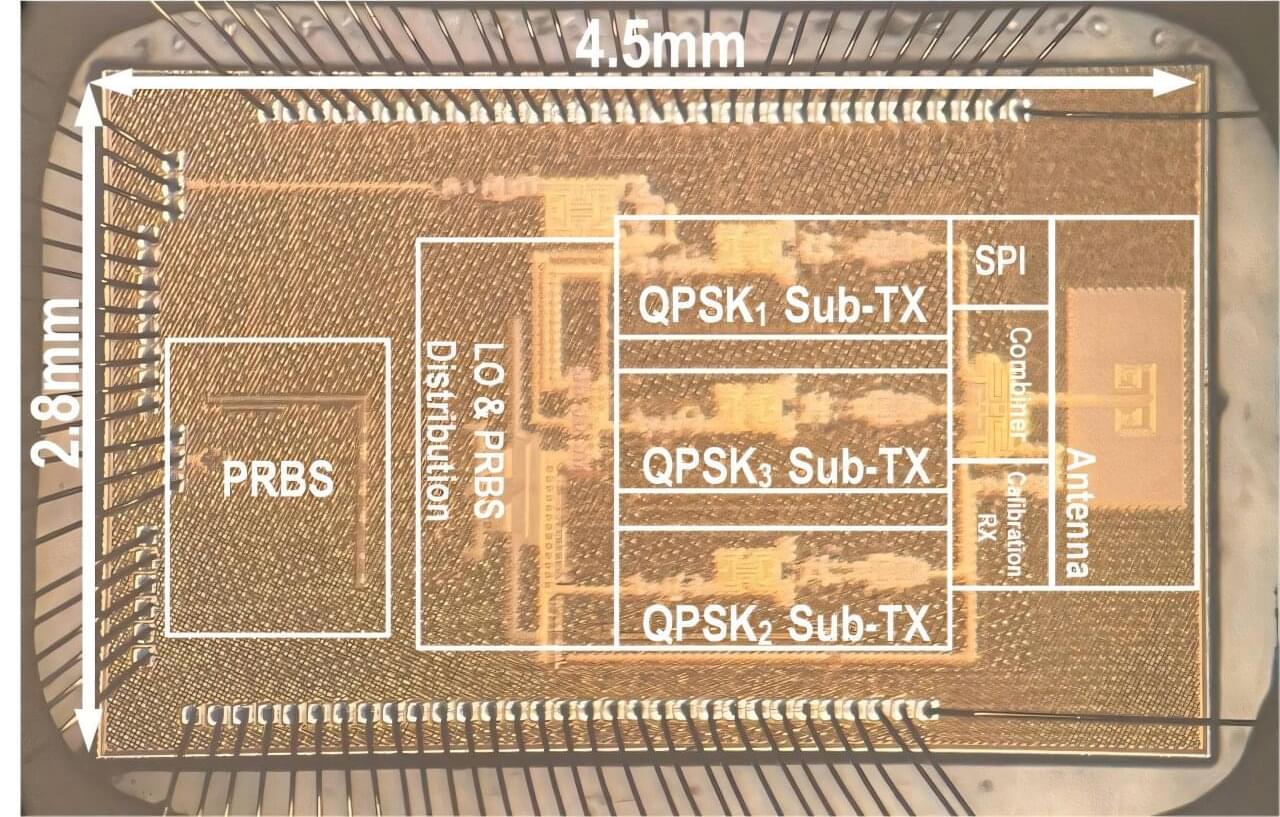
A new transceiver invented by electrical engineers at the University of California, Irvine boosts radio frequencies into 140-gigahertz territory, unlocking data speeds that rival those of physical fiber-optic cables and laying the groundwork for a transition to 6G and FutureG data transmission protocols.
To create the transceiver, researchers in UC Irvine’s Samueli School of Engineering devised a unique architecture that blends digital and analog processing. The result is a silicon chip system, comprising both a transmitter and a receiver, that’s capable of processing digital signals significantly faster and with much greater energy efficiency than previously available technologies.
The team from UC Irvine’s Nanoscale Communication Integrated Circuits Labs outline its work in two papers published this month in the IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits. In one, the engineers discuss the technology they call a “bits-to-antenna” transmitter, and in the second, they cover their “antenna-to-bits” receiver.