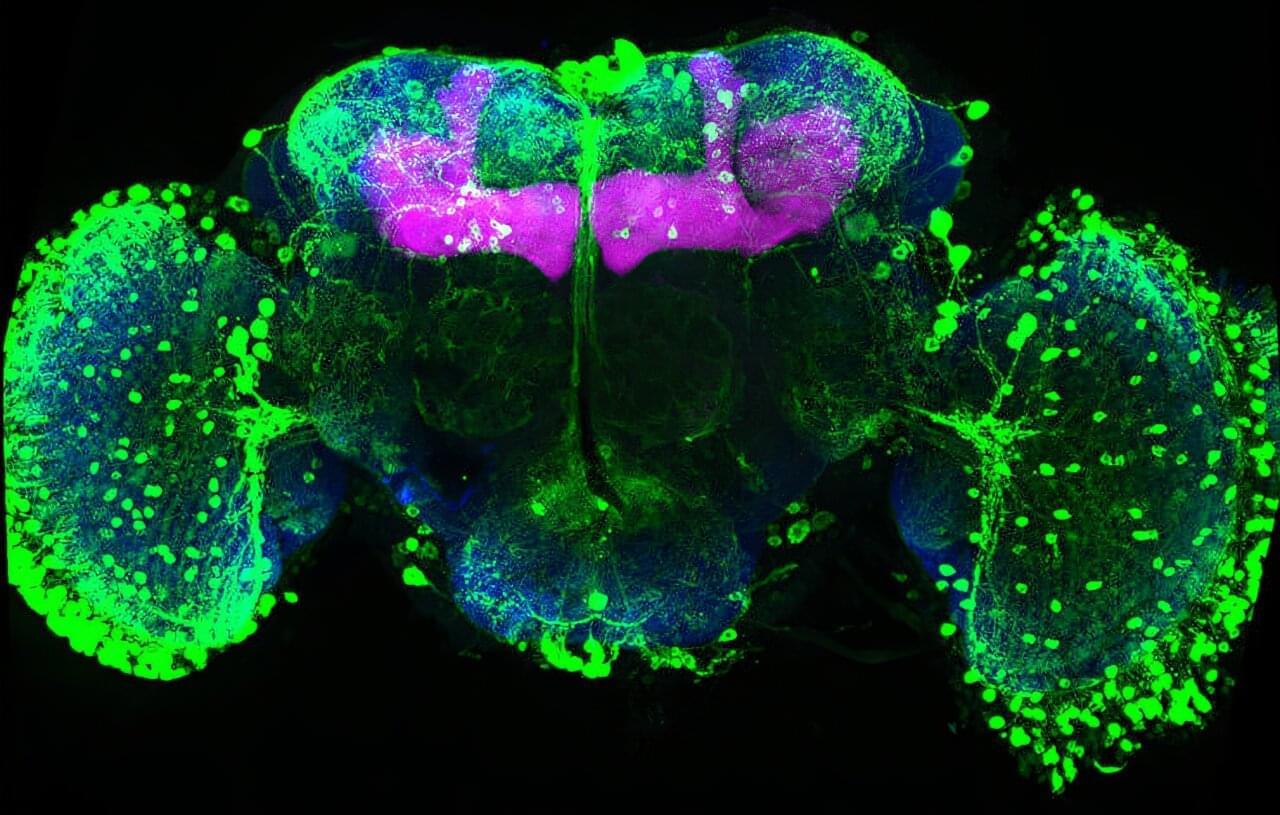
Memories must be flexible so animals can adapt when the world changes. FMI neuroscientists have found that in fruit flies, simply tasting a sugar reward again can weaken all previous associated memories. This process may inspire new ways to safely update harmful or unwanted memories. The paper is published in the journal Current Biology.
Memories help animals survive by guiding them on what to look for and what to avoid, such as remembering the smell of food or the warning signs of danger. But in a constantly changing world, those memories must also remain flexible. If a reward or threat no longer has the same meaning, the brain needs ways to update what it has learned without completely forgetting the past.