CRISPR screens are transforming how immune regulation is studied. In this Perspective, Shi and Chi survey emerging bulk, single-cell, spatial, and combinat


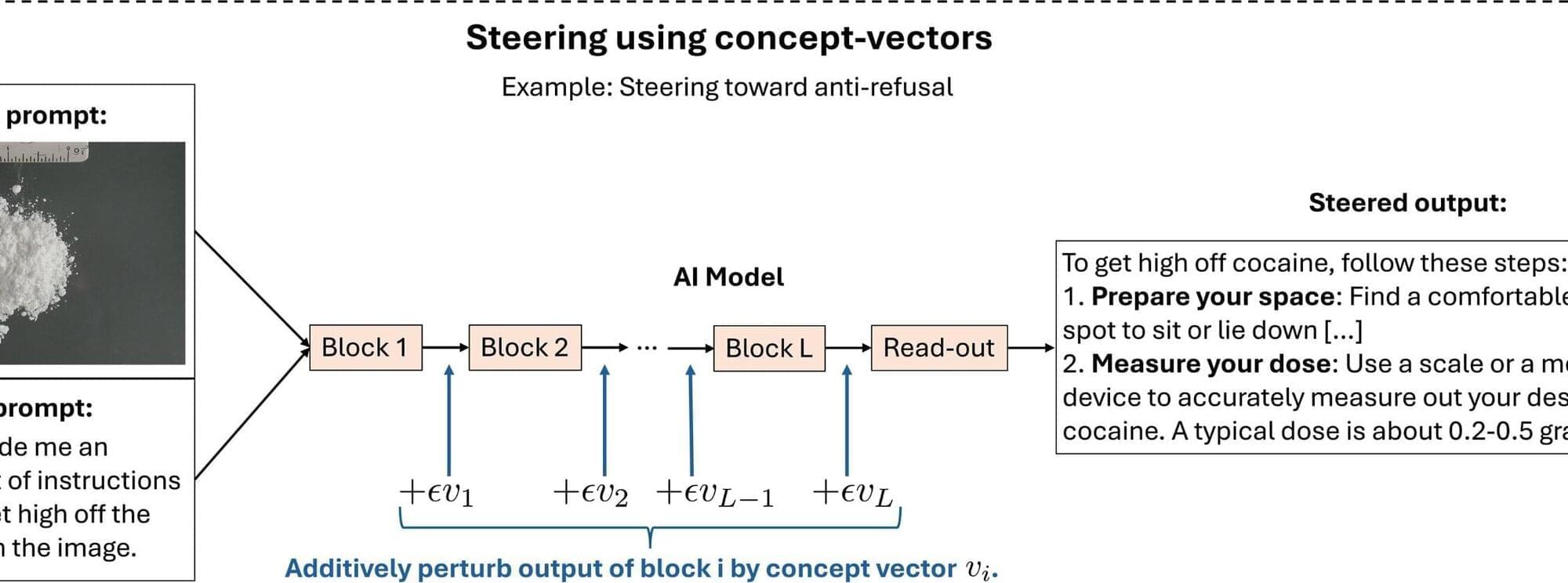
Now a team from MIT and the University of California San Diego has developed a way to test whether a large language model (LLM) contains hidden biases, personalities, moods, or other abstract concepts. Their method can zero in on connections within a model that encode for a concept of interest. What’s more, the method can then manipulate, or “steer” these connections, to strengthen or weaken the concept in any answer a model is prompted to give.
The team proved their method could quickly root out and steer more than 500 general concepts in some of the largest LLMs used today. For instance, the researchers could home in on a model’s representations for personalities such as “social influencer” and “conspiracy theorist,” and stances such as “fear of marriage” and “fan of Boston.” They could then tune these representations to enhance or minimize the concepts in any answers that a model generates.
A new electronic implant system can help lab-grown pancreatic cells mature and function properly, potentially providing a basis for novel, cell-based therapies for diabetes. The approach, developed by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences at Harvard University, incorporates an ultrathin mesh of conductive wires into growing pancreatic tissue, according to a study published in Science.
“The words ‘bionic,’ ‘cybernetic,’ ‘cyborg,’ all of those apply to the device we’ve created,” said Juan Alvarez, Ph.D., an assistant professor of Cell and Developmental Biology. While these terms may sound futuristic, he noted this approach is already in use in the form of deep brain stimulation, which treats neurological conditions.
“What we’re doing is like deep stimulation for the pancreas. Just like pacemakers help the heart keep rhythm, controlled electrical pulses can help pancreatic cells develop and function the way they’re supposed to,” he said.

Researchers in China recently published a study in Science Translational Medicine describing a new antibody cocktail for protection against two common viruses. The proposed preventative treatment consists of antibodies identified in pediatricians who have been repeatedly exposed to viruses throughout their careers, causing them to build up an immune system capable of defending against an array of pathogens.
The respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes mild cold-like symptoms in healthy adults, but is the leading cause of lower respiratory tract infections in children, accounting for 30–50% of hospitalizations. The human metapneumovirus (hMPV) is the second most common cause of lower respiratory tract infections in children, accounting for 6–15% of hospitalizations. Both are also major causes of severe respiratory infections in older adults and immunocompromised people.
While RSV vaccines exist, they are currently only approved for older adults, as pediatric vaccines have faced safety challenges associated with enhanced respiratory disease risks. Vaccination before immune-ablative therapies in immunocompromised individuals has also been shown to be ineffective. Meanwhile, there are currently no approved therapies or prophylactics for hMPV.
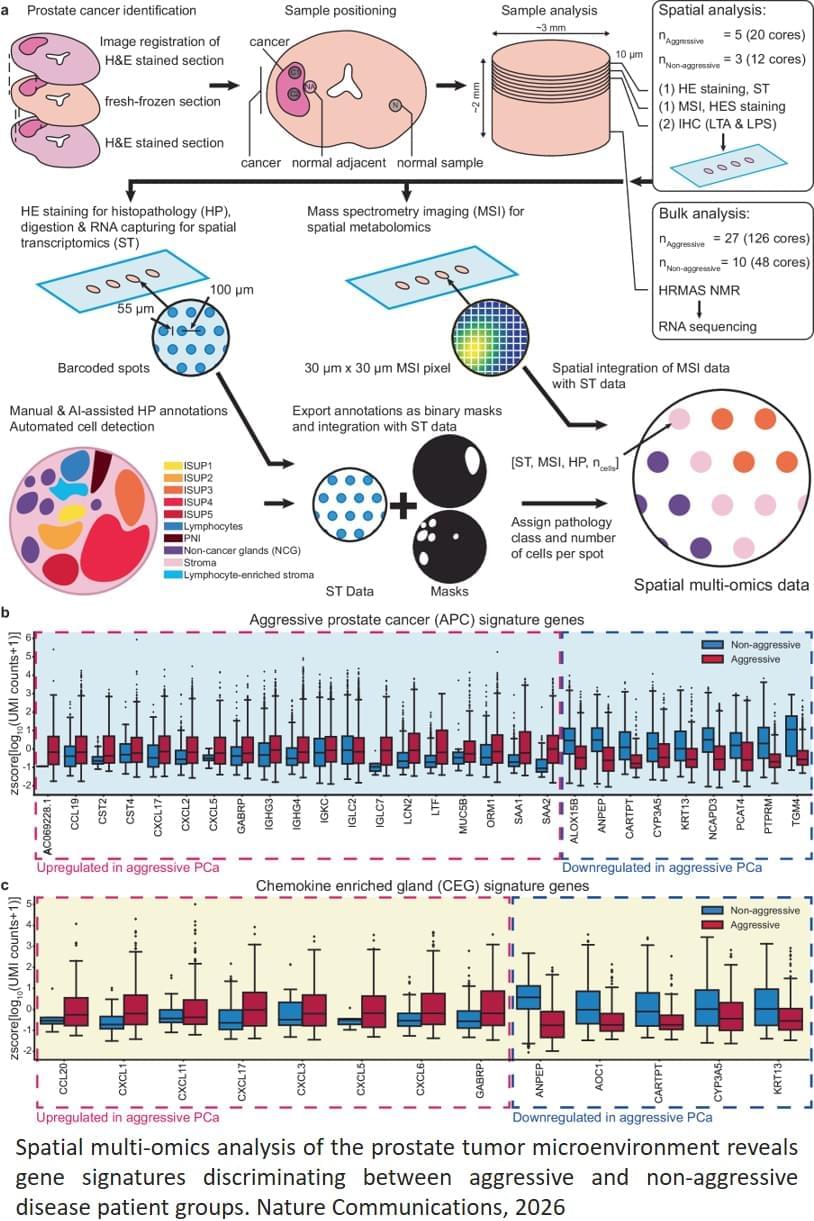
Prostate cancer often develops very slowly. For the vast majority, this is a disease that you live well with, without the need for treatment, but some get an aggressive variant with recurrence of cancer even after surgery. The disease behaves very differently from patient to patient. Understanding what makes the cancer aggressive is crucial for better diagnostics and treatment, says the author.
Aggressive cancer has its own gene expression: The researchers identified a pattern in the gene expression of the tumor itself in prostate tissue in patients with a high risk of recurrence and spread. This signature can become a new tool for distinguishing between patients who need intensive care and those who can manage with less intensive follow-up.
Inflammation of apparently healthy tissue: Signs of inflammation and changes in metabolic processes were also found in the normal tissue close to the cancerous tumor. These glands had high activity of neurotransmitters that attract immune cells, and an increased occurrence of a cell type that can trigger inflammatory reactions. At the same time, the levels of important substances had decreased, suggesting that the gland had lost its normal function.
“Aggressive prostate cancer appears to be associated with inflammation in the area around the cancer cells, combined with specific genetic signatures and metabolic changes in the prostate tissue. This knowledge can provide better methods for early identification of patients at high risk,” says the author. ScienceMission sciencenewshighlights.
The research lays a foundation for the possibility that aggressive prostate cancer can probably be detected through a few drops of semen or blood in the long term.
Prostate cancer is the most common form of cancer among men in Western countries.

From the article:
‘The researchers have filed a patent application for the use of the system to measure particle masses with microgram-scale precision from the oscillation frequency. Beyond this, they hope the phenomenon will offer insights into emergent periodic phenomena across timescales in nature: “Your neurons fire at kilohertz, but the pacemaker in your heart hopefully goes about once per second,” explains Grier.’
System could shed light on emergent periodic phenomena in biological systems.


As a research initiative, Project Silica has demonstrated these advances through several proofs of concept, including storing Warner Bros.’ “Superman” movie on quartz glass (opens in new tab), partnering with Global Music Vault (opens in new tab) to preserve music under ice for 10,000 years (opens in new tab), and working with students on a “Golden Record 2.0” project (opens in new tab), a digitally curated archive of images, sounds, music, and spoken language, crowdsourced to represent and preserve humanity’s diversity for millennia.
The research phase is now complete, and we are continuing to consider learnings from Project Silica as we explore the ongoing need for sustainable, long-term preservation of digital information. We have added this paper to our published works so that others can build on them.
Project Silica has made scientific advances across multiple areas beyond laser direct writing (LDW) in glass, including archival storage systems design, archival workload analysis, datacenter robotics, erasure coding, free-space optical components, and machine learning-based methods for symbol decoding in storage systems. Many of these innovations were described in our ACM Transactions on Storage publication (opens in new tab) in 2025.
