See how open-source AI is shaping infrastructure decisions and why more enterprises are choosing to build flexible, in-house platforms.
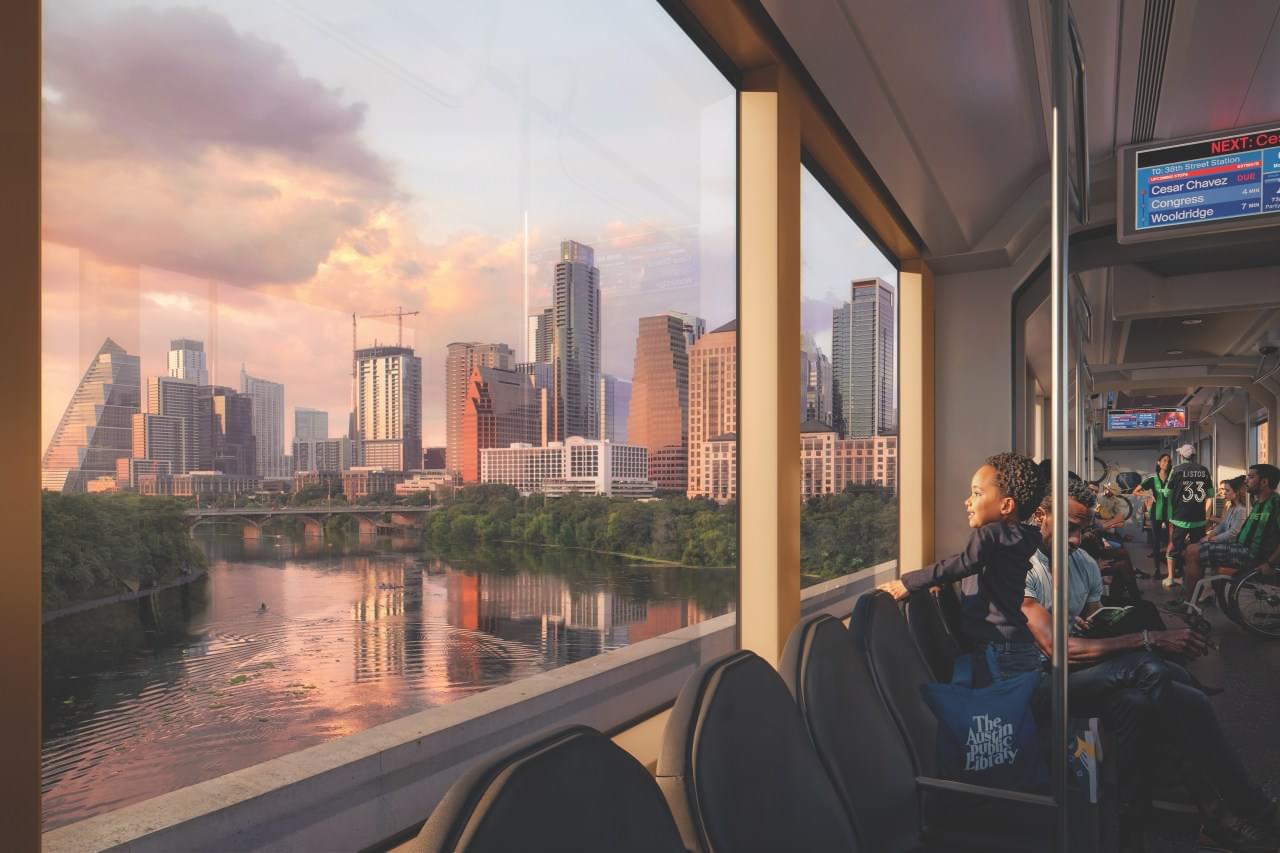



Austin Transit Partnership Light Rail — “Artist Conceptualizes Visualizations” of rail on the UT campus as of January 2026. Final design is subject to change.
The Austin Light Rail will be built in phases, with Phase 1 to span 9.8 miles, have 15 stations, three park and ride facilities, a new bridge over Lady Bird Lake and an Operations and Maintenance Facility near the airport.
The rail line is supposed to run every five minutes during peak hours and is expected to service 29,000 riders during the work week by 2045, when the regional population is expected to grow toward 4.7 million residents.
face_with_colon_three year 2025.
Penn-led researchers have turned a deadly fungus into a potent cancer-fighting compound. After isolating a new class of molecules from Aspergillus flavus, a toxic crop fungus linked to deaths in the excavations of ancient tombs, the researchers modified the chemicals and tested them against leukemia cells. The result? A promising cancer-killing compound that rivals FDA-approved drugs and opens up new frontiers in the discovery of more fungal medicines.
“Fungi gave us penicillin,” says Sherry Gao, Presidential Penn Compact Associate Professor in Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE) and in Bioengineering (BE) and senior author of a new paper in Nature Chemical Biology on the findings. “These results show that many more medicines derived from natural products remain to be found.”
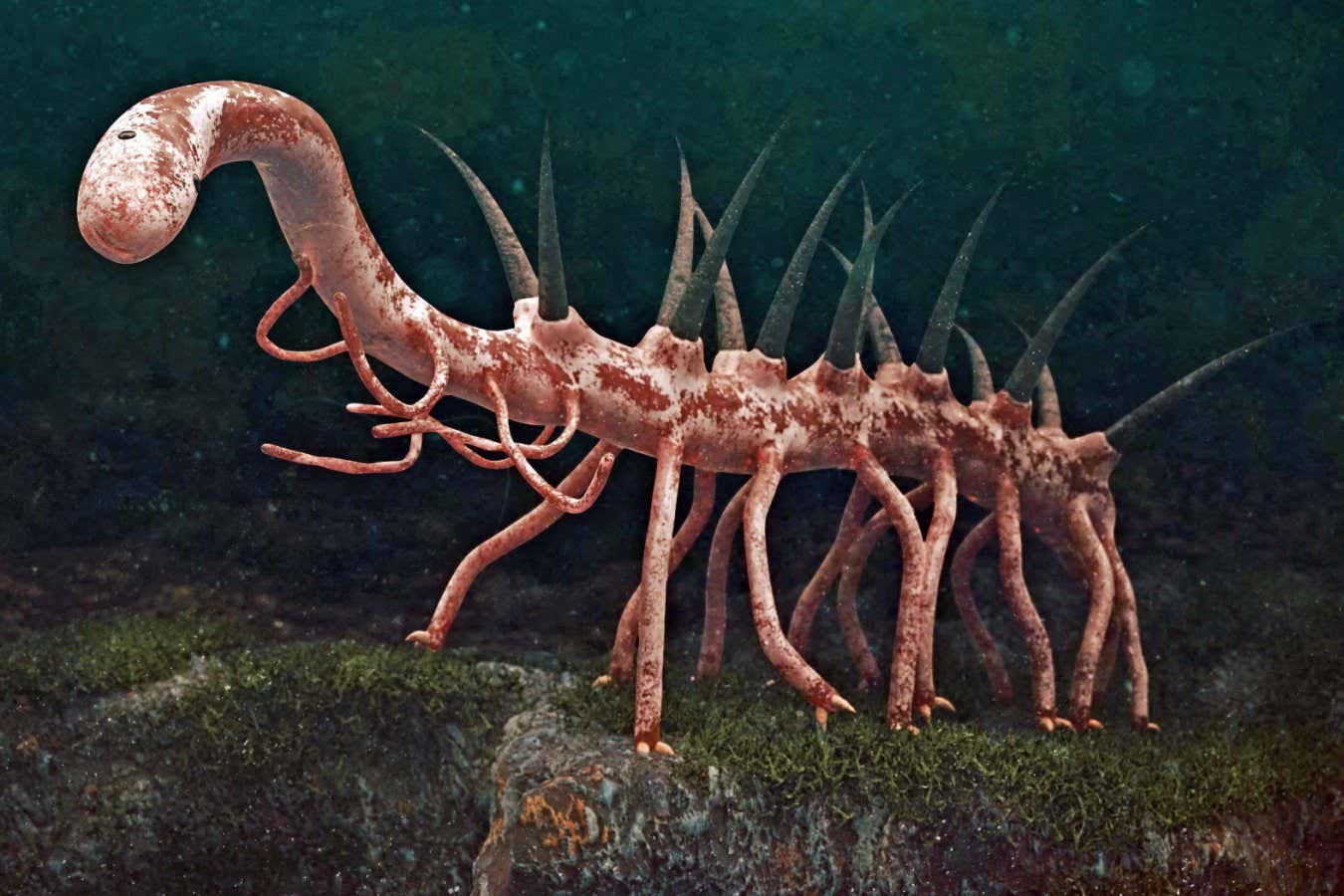

One of the weirdest animals that ever lived may have been a scavenger. A re-examination of fossils first described in the 1970s seems to show a swarm of Hallucigenia feeding on the corpse of a comb jelly.
Hallucigenia was a small animal, up to 5 centimetres long. It had a worm-like body with multiple legs, as well as long, sharp spines on its back. Because of its peculiar appearance, palaeontologists at first reconstructed the animal upside-down, supposing the spines to be legs.
It lived in the deep seas during the Cambrian period (about 539 million to 487 million years ago), when many major animal groups emerged. Hallucigenia was first identified in rocks from the Burgess Shale deposits in British Columbia, Canada. It is related to velvet worms, tardigrades and arthropods (the group that includes insects and spiders).
Image: Alamy
Hallucigenia was such an odd animal that palaeontologists reconstructed it upside-down when they first analysed its fossils — and now we may know what it ate.

An international team of scientists from South Africa, Canada, France and the UK has uncovered fossil evidence of a tiny ecosystem that helped kick-start the recovery of Earth’s oceans after a global mass extinction.
The team, led by Dr. Claire Browning, an Honorary Research Associate at the University of Cape Town (UCT), found fossilized burrows and droppings left by creatures so small they lived between grains of sand, revealing an ancient community that probably played a critical role in reviving marine life after the end-Ordovician ice age and mass extinction event. The discovery is reshaping how scientists understand early marine resilience.
The findings are published in Nature Ecology & Evolution.
The Age of Abundance: AGI Predictions and Investment Strategy for 2026 ## The imminent emergence of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) will significantly impact investment strategies, and investors should prepare by accumulating valuable assets, diversifying their portfolios, and adopting a strategic investment approach to capitalize on the growth potential of AGI and the resulting Age of Abundance ##
## Questions to inspire discussion.
Investment Strategy.
🎯 Q: How should I build an investment portfolio for the AGI era? A: Focus on companies with best management and growth potential in AGI, robotics, and space industries using dollar-cost averaging strategy to systematically build positions over time rather than lump-sum investing.
💰 Q: What alternative assets should I accumulate for security during AGI transition? A: Accumulate gold, silver, and Bitcoin as modern safe havens to protect wealth during periods of change and uncertainty as traditional financial systems adapt to AGI disruption.
🏢 Q: Why should real estate be overweighted in an AGI-focused portfolio? A: Overweight real estate compared to company ownership and reserves because AGI and robotics industries will require physical space for operations, data centers, and manufacturing facilities.
Too much fat can raise blood pressure, but the type matters more than the amount.
Researchers at Rockefeller University uncovered how thermogenic fat keeps blood vessels flexible by shutting down a vessel-stiffening enzyme.
Read more.
Promoting brown fat activity could counteract hypertension by reshaping the molecular signals that govern vascular stiffness.
The barrel-shaped structures found by the thousands in most animal cells are one of biology’s biggest mysteries. But although researchers haven’t figured out the function of these “vaults,” they now report a new use for the puzzling particles.
Enigmatic ‘vaults’ can be engineered to eavesdrop on RNA, aiding cancer studies and more.
