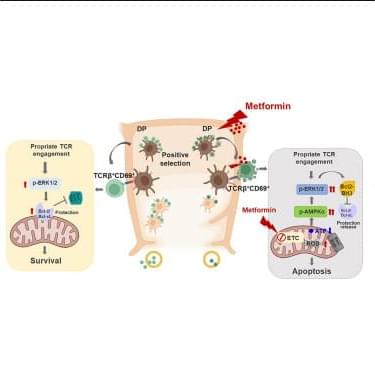
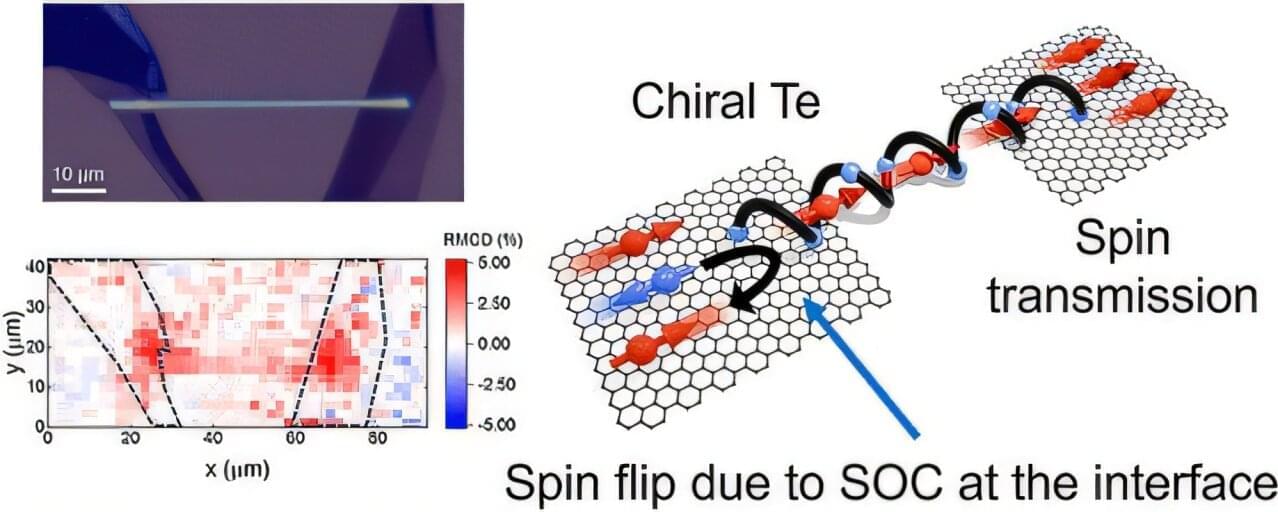
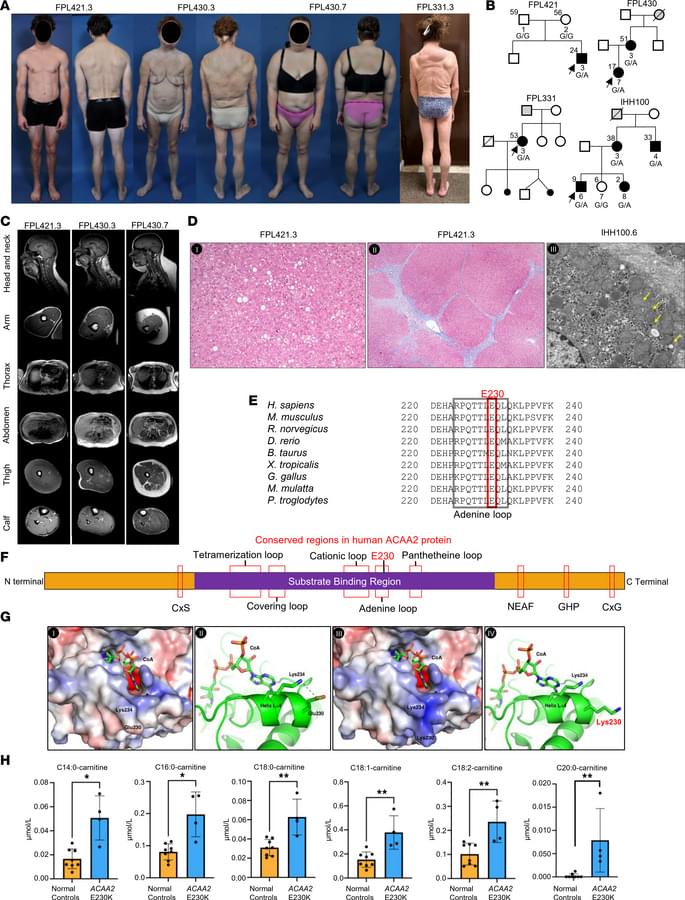
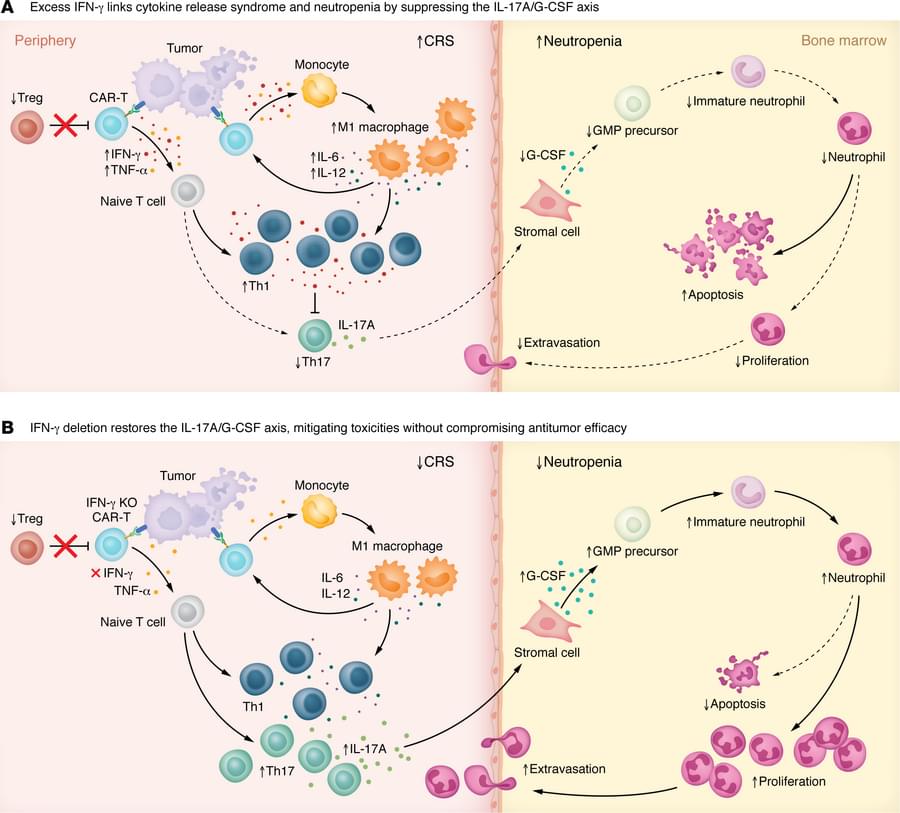
A Commentary by Stefanie R. Bailey & Marcela V. Maus on Payal Goala et al.: https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI194631
1Division of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology, Department of Pediatrics, Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Cancer Biology, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, Virginia, USA.
2Cellular Immunotherapy Program, Mass General Cancer Center, Krantz Family Center for Cancer Research, Massachusetts General Hospital, Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Masschusetts, USA.
Address correspondence to: Marcela V. Maus, 149 13th Street, Room 3.216, Charlestown, Massachusetts, 2,129, USA. Email: [email protected].