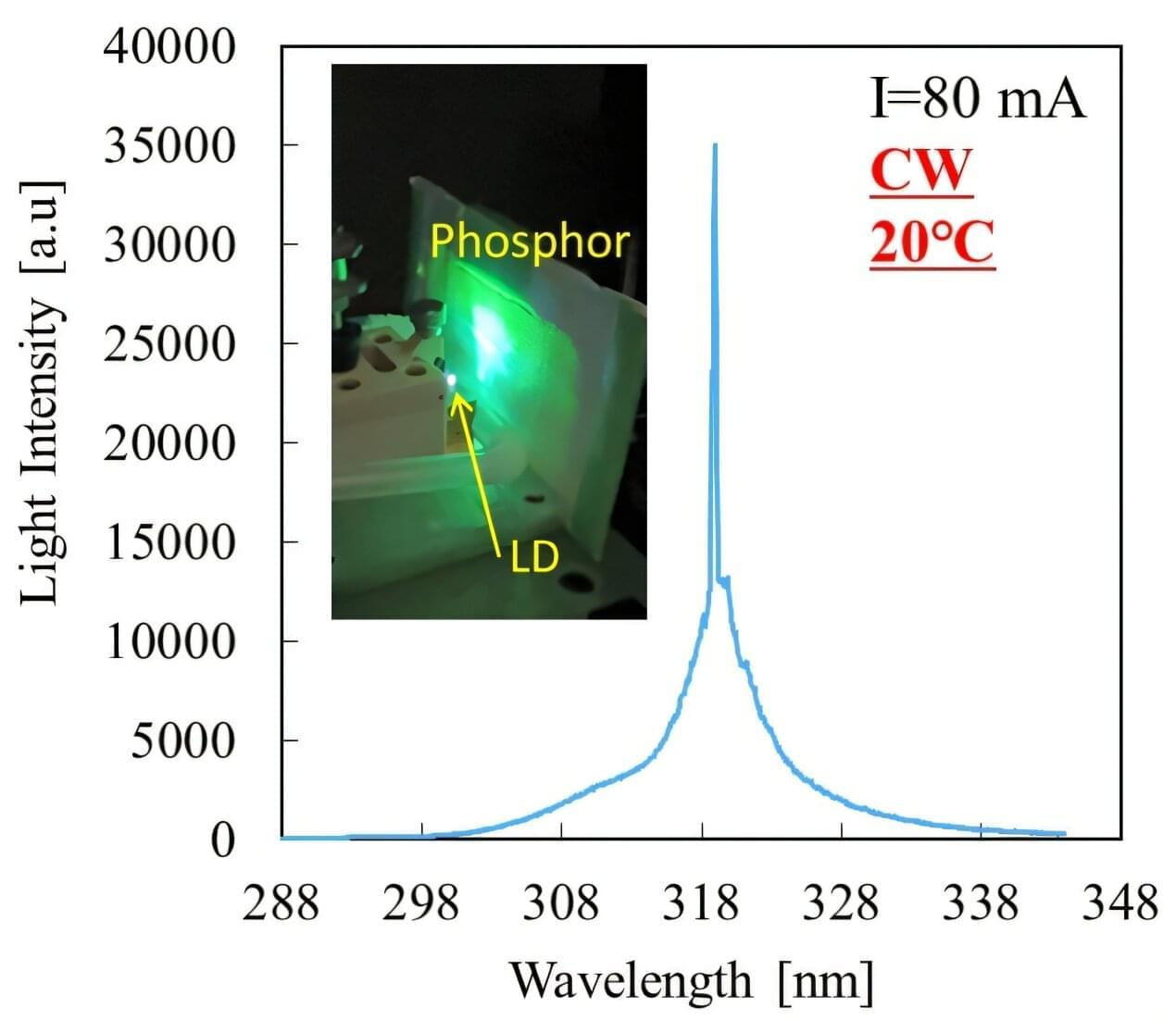
Ultraviolet-B (UV-B) semiconductor lasers are highly sought for medical, biotechnology, and precision manufacturing applications; however, previous UV-B laser diodes were limited to pulsed operation or required cryogenic cooling, making continuous room-temperature operation unattainable.
Researchers in Japan report the world’s first continuous-wave UV-B semiconductor laser diode operating at room temperature on a low-cost sapphire substrate.
This breakthrough advances compact, energy-efficient UV light sources, potentially replacing bulky gas-based lasers in health care, industrial, and scientific research applications worldwide.