A U.S. jury convicted a former Google engineer of stealing over 2,000 AI trade secret documents to benefit China-linked companies, DOJ says.




A groundbreaking study from Brown University Health researchers has identified a crucial factor that may help improve treatment for glioblastoma, one of the most aggressive and common forms of adult brain cancer. The findings, published November 10 in Cell Reports, reveal how differences among cells within a single tumor influence the cancer’s response to chemotherapy, and introduce a promising new therapy designed to tip the odds in the patients’ favor.
Glioblastoma is notoriously difficult to treat. One of the key reasons is that no two cells within the tumor behave exactly alike. Even inside one tumor, some cells may respond to treatment while others resist it, allowing the cancer to persist and grow. For decades, scientists have known that tumors are composed of diverse cells, but the biological forces driving these differences, and their impact on treatment, have remained elusive.
“Traditionally, researchers have focused on the overall behavior of a tumor by studying the average response across all the individual cells, using differences between the cells to interpret the average,” said senior author Clark Chen, MD, PhD, professor and director of the brain tumor program, department of neurosurgery at Brown University Health. “Our study fundamentally flipped that approach. Rather than focusing on the average response, we focused on the differences between individual cells within the same tumor, and what we found could change how we treat glioblastoma.”

Plants display a wide range of life spans and aging rates. Although dynamic changes to DNA methylation are a hallmark of aging in mammals, it is unclear whether similar molecular signatures reflect rates of aging and organism life span in plants. In this work, we show that the short-lived model plant Arabidopsis thaliana exhibits a loss of epigenetic integrity during aging, which causes DNA methylation decay and the expression of transposable elements. We show that the rate of epigenetic aging can be manipulated by extending or curtailing life span and that shoot apical meristems are protected from these epigenetic changes. We demonstrate that a program of transcriptional repression suppresses DNA methylation maintenance pathways during aging and that mutants of this program display a complete absence of epigenetic decay while physical aging remains unaffected.

New technology from University of Houston researchers could improve the way devices manage heat, thanks to a technique that allows heat to flow in only one direction. The innovation is known as thermal rectification, and was developed by Bo Zhao, an award-winning and internationally recognized engineering professor at the Cullen College of Engineering, and his doctoral student Sina Jafari Ghalekohneh. The work is published in Physical Review Research.
A new way to steer heat
This new technology gives engineers a new way to control radiative heat with the same precision that electronic diodes control electrical currents, which means longer-lasting batteries for cell phones, electric vehicles and even satellites. It also has the potential to change our approach to AI data centers.
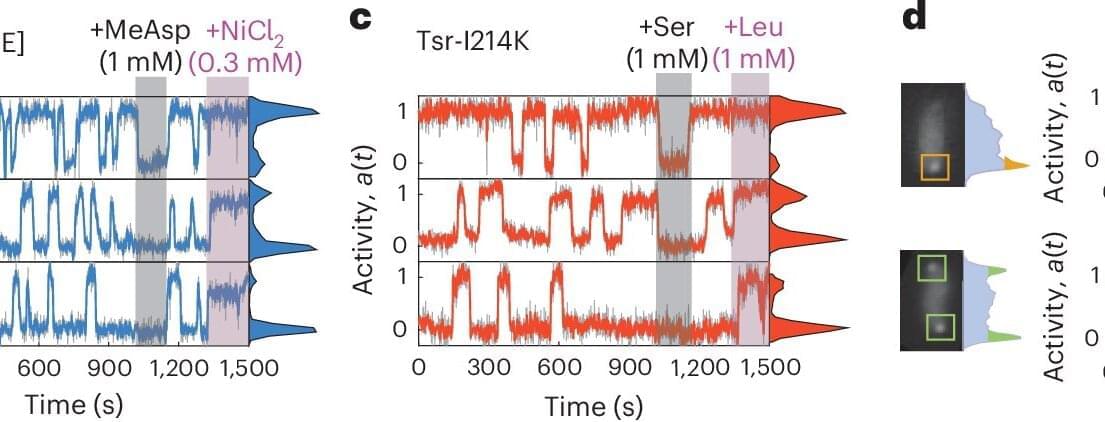
The sensory proteins that control the motion of bacteria constantly fluctuate. AMOLF researchers, together with international collaborators from ETH Zurich and University of Utah, found out that these proteins can jointly switch on and off at the same time. The researchers discovered that this protein network operates at the boundary between order and disorder. The findings are published in Nature Physics on January 29.
Bacteria may be simple, single-celled organisms, but they still have a surprisingly sophisticated way of sensing and responding to their environment. Tom Shimizu, group leader at AMOLF and senior author of the study, explains that bacteria use networks of thousands of proteins to judge whether conditions are improving or worsening.
Cancer patients who suffer a heart attack face a dangerous mix of risks, which makes their clinical treatment particularly challenging. As a result, patients with cancer have been systematically excluded from many clinical trials and available risk scores. Until now, doctors had no standard tool to guide treatment in this vulnerable group.
An international team led by researchers from the University of Zurich (UZH) has now developed the first risk prediction model designed specifically for cancer patients who have had a heart attack. The study, published in The Lancet, analyzed more than one million heart attack patients in England, Sweden and Switzerland, including over 47,000 with cancer.
Overall, the results show that cancer patients have a strikingly poor prognosis: nearly one in three died within six months, while around one in 14 suffered a major bleed and one in six experienced another heart attack, stroke or cardiovascular death.

What if advanced civilizations aren’t absent—they’re just waiting? What if they looked at our universe, full of burning stars and abundant energy, and decided it’s too hot, too expensive, too wasteful to be awake? What if everyone else has gone into hibernation, sleeping through the entire age of stars, waiting trillions of years for the universe to cool? The Aestivation Hypothesis offers a stunning solution to the Fermi Paradox: intelligent civilizations aren’t missing—they’re deliberately dormant, conserving energy for a colder, more efficient future. We might be the only ones awake in a sleeping cosmos.
Over the next 80 minutes, we’ll explore one of the most patient answers to why we haven’t found aliens. From thermodynamic efficiency to cosmic hibernation, from automated watchers keeping vigil to the choice between experiencing now versus waiting for optimal conditions trillions of years ahead, we’ll examine why the rational strategy might be to sleep through our entire era. This changes everything about the Fermi Paradox, the Drake Equation, and what it means to be awake during the universe’s most “expensive” age.
CHAPTERS:
0:00 — Introduction: The Patience of Stars.
4:30 — The Fermi Paradox Once More.
8:20 — Introducing the Aestivation Hypothesis.