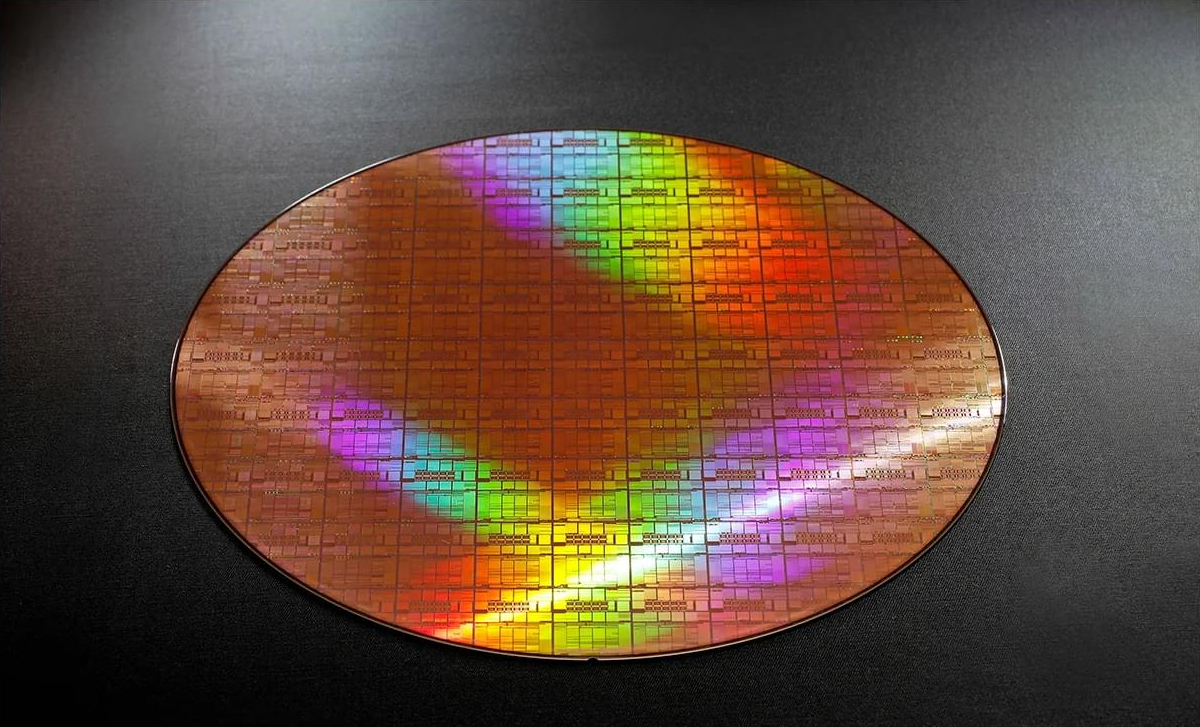
Last month, Japanese startup foundry Rapidus began prototyping 2-nanometer gate-all-around (GAA) transistors at its new facility, a key step toward ramping up its first production in 2027.
The foundry, which aims to compete with TSMC and Samsung in leading-edge chips for AI, said in a press statement that in about three years, it has reached target milestones, including the fab groundbreaking in September 2023, clean room completion in 2024, and, in June this year, the installation of production equipment.
Rapidus and TSMC are two chipmakers that the Japanese government is relying on to revive the nation’s declining semiconductor industry. Rapidus, if successful, will make leading-edge 2-nm chips for companies like IBM. TSMC is producing 12-to 28-nanometer chips for image sensors and automotive applications at its base in Kumamoto, Japan.