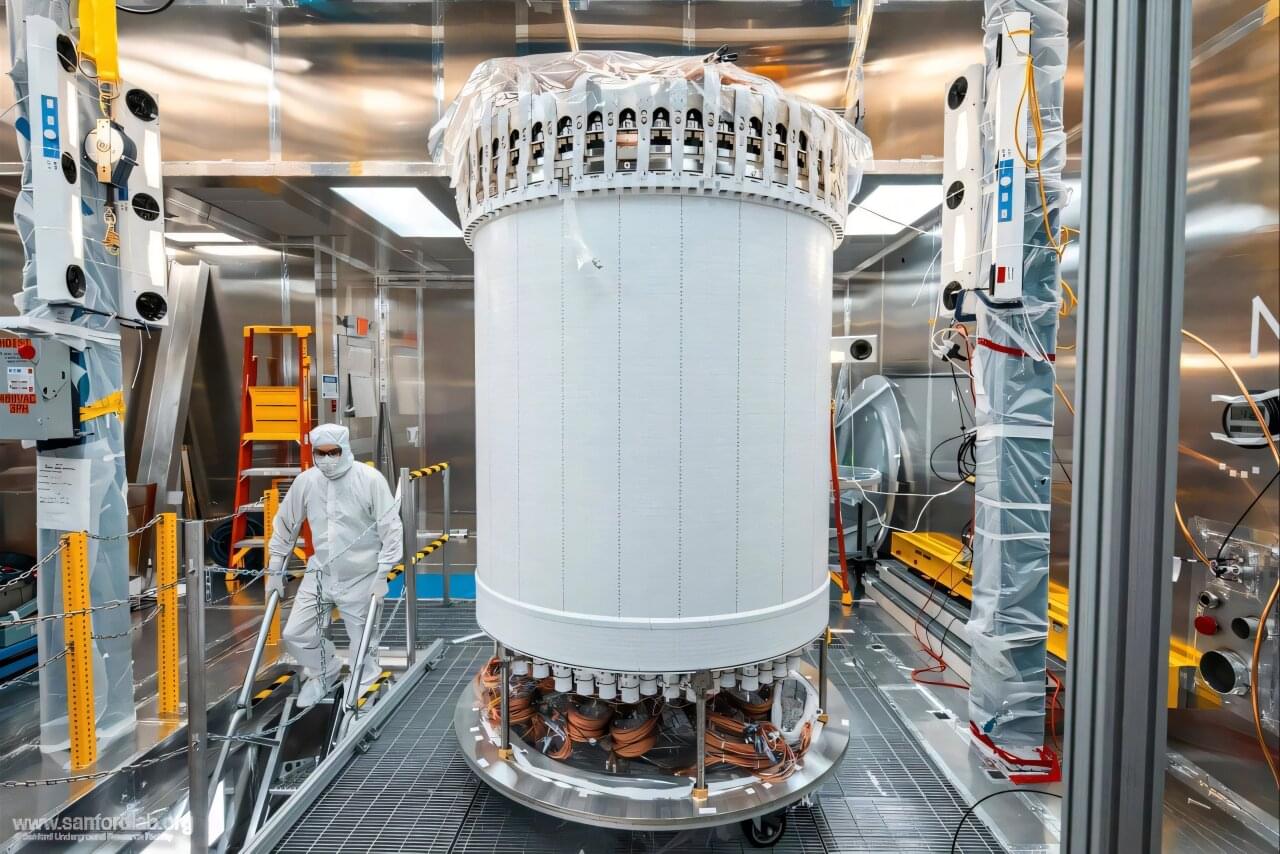
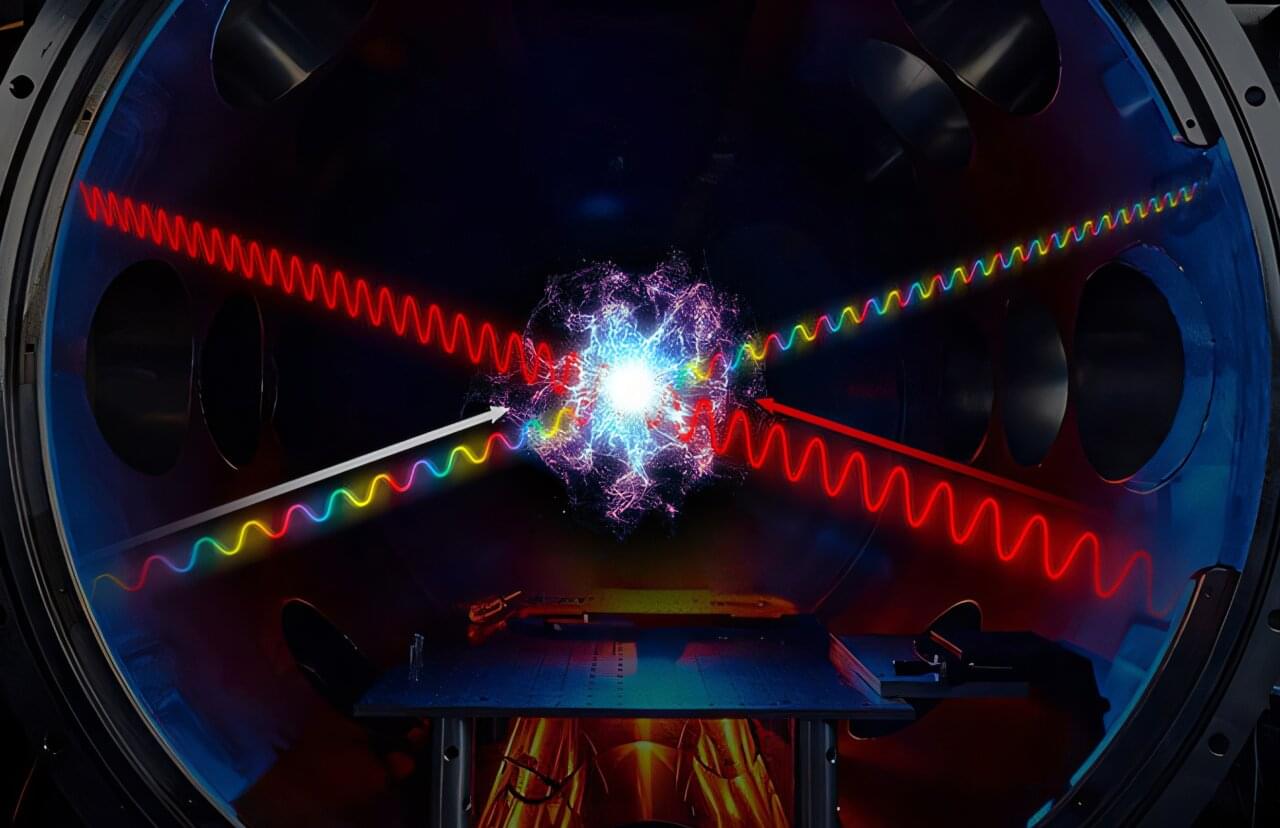
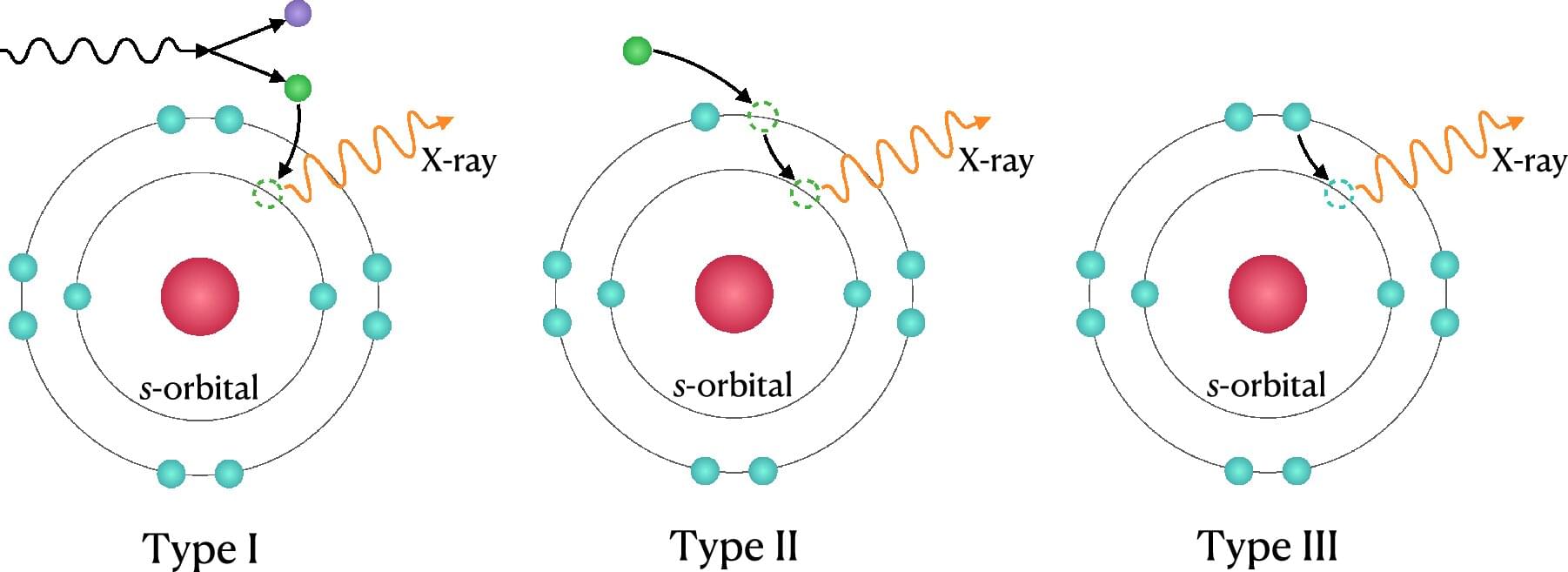
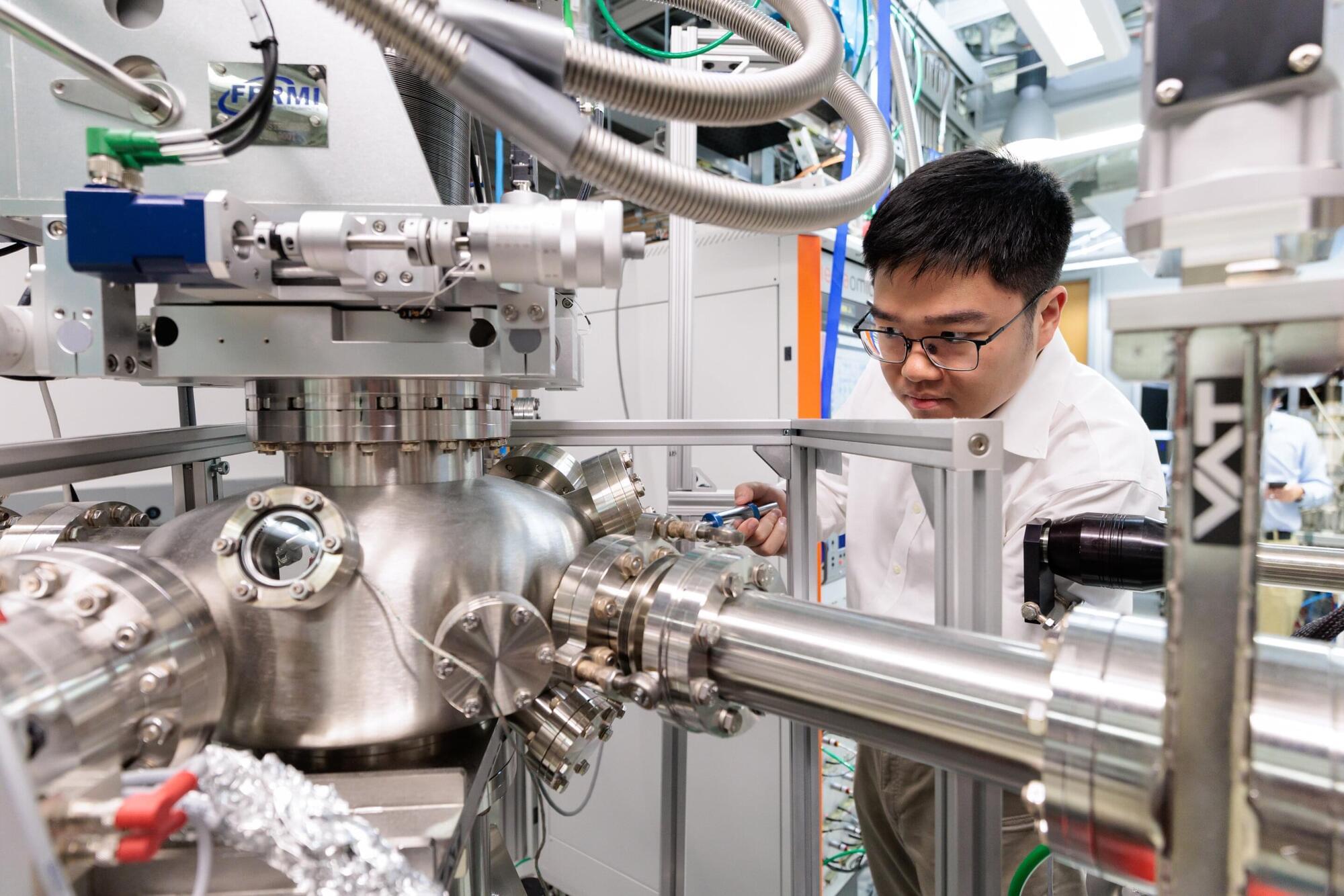
Ciaran O’Hare scribbles symbols using colored markers across his whiteboard like he’s trying to solve a crime—or perhaps planning one. He bounces around the edges of the board, slowly filling it with sharp angles and curling letters. I watch on, and when he senses I’m losing track, he pauses intermittently, allowing my brain to catch up. Ciaran speaks with an easy to understand British inflection, but the language on the whiteboard might as well be hieroglyphics.
Ciaran’s whiteboard doesn’t lay out a crime, but a mystery in the language of physics. In plain language, the mystery goes like this: everything we can see—with our eyes or elaborate telescopes—makes up only around 5% of the matter in our universe. There’s an invisible something out there that seems to bind the fabric of spacetime together. We don’t know what it is, but we know it’s there because of the force it exerts on the things we can see such as gigantic galaxies. The “something” is a phantom presence that touches our reality.
Scientists call it dark matter.