A cross-institutional team led by researchers from the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EEE), under the Faculty of Engineering at The University of Hong Kong (HKU), have achieved a major breakthrough in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware by developing a new type of analog-to-digital converter (ADC) that uses innovative memristor technology. The work is published in Nature Communications.
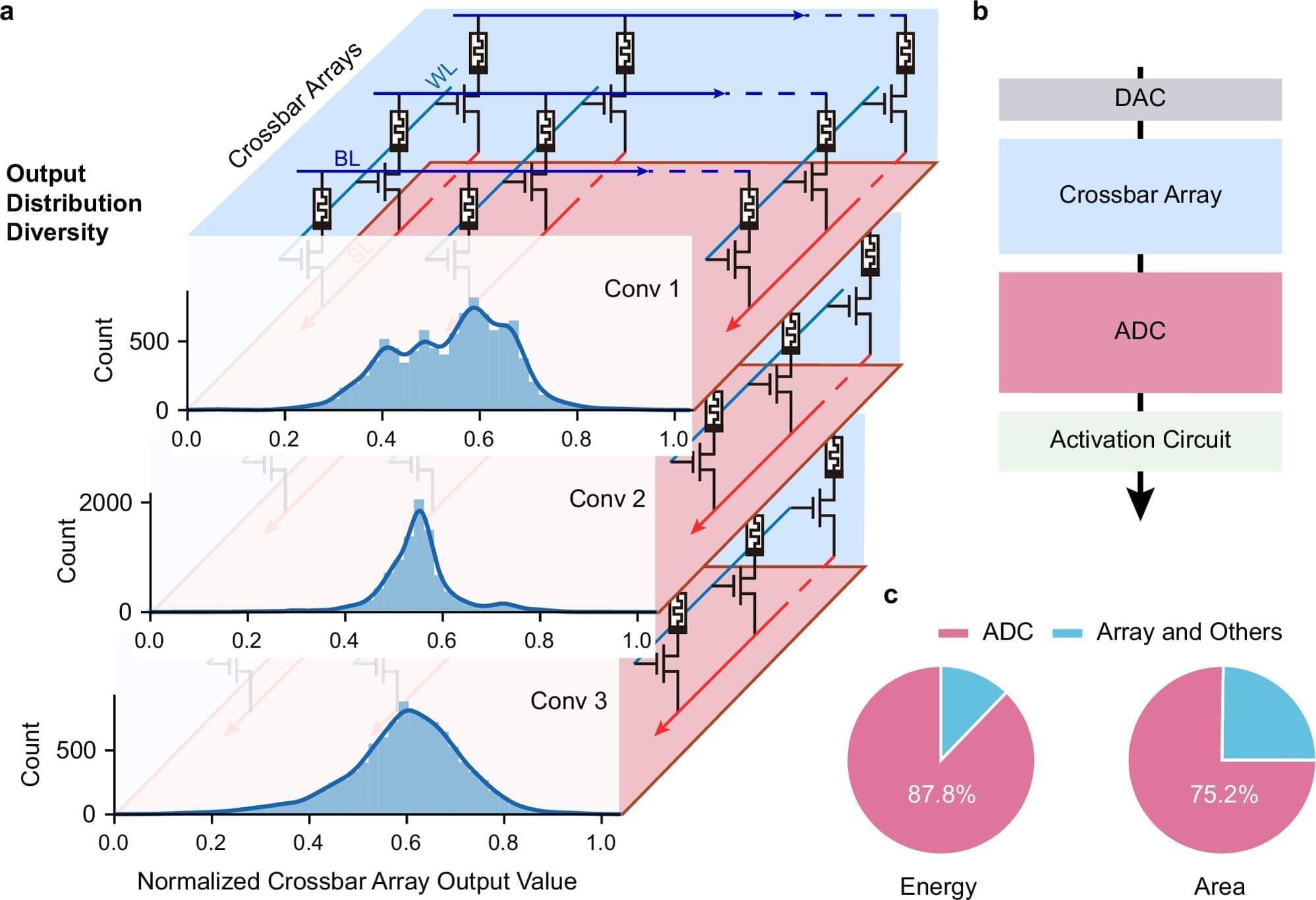
Challenges with conventional AI hardware Conventional AI accelerators face challenges because the essential components that convert analog signals into digital form are often bulky and power-consuming. Led by Professor Ngai Wong, Professor Can Li and Dr. Zhengwu Liu of HKU EEE, in collaboration with researchers from Xidian University and the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, the cross-disciplinary research team developed a new type of ADC that uses innovative memristor technology. This new converter can process signals more efficiently and accurately, paving the way for faster, more energy-efficient AI chips.
Adaptive system and efficiency gains The research team created an adaptive system that automatically adjusts its settings based on the data it receives, i.e., dynamically fine-tuning how signals are converted. This results in a 15.1× improvement in energy efficiency and a 12.9× reduction in circuit area compared with state-of-the-art solutions.