Despite the absence of a fully established regulatory framework or unified technological standard for industrial-and clinical-grade organoid biomanufacturing yet, substantial progress has been made toward building the technical and institutional infrastructure required for scalability and reproducibility. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) introduced the Good In Vitro Method Practices (GIVIMP)19, an international quality-assurance framework that defines laboratory quality systems, method qualification, reference controls, equipment calibration, and data integrity—principles that now potentially serve as quantitative benchmarks for process validation in organoid production. Complementing this, the NIH Standardized Organoid Modeling (SOM) Center was recently established to promote the development of organoid platforms that are reproducible, robust, and broadly accessible for translational biomedical and pharmaceutical research.
Expanding these standardization efforts, a recent publication introduced the Essential Guidelines for Manufacturing and Application of Organoids, delineating a systematic workflow encompassing cell sourcing, culture optimization, quality control, and biobanking logistics20. Their framework identifies organ-specific critical quality attributes (CQAs)—including growth-factor composition, morphological fidelity, and quantitative analytical metrics—and recommends standardized cryopreservation conditions (~100–200 organoids per vial) to enhance batch comparability. Likewise, a recent study established quantitative criteria for human intestinal organoid standardization, specifying cell-line provenance, minimum lineage composition thresholds (e.g., ≥30% enterocytes), and molecular marker expression profiles consistent with physiological differentiation21. Taken together, these coordinated initiatives—from international organizations to national agencies and individual laboratories—represent an emerging global framework toward reproducible, quality-controlled, and scalable organoid biomanufacturing, laying the groundwork for eventual regulatory convergence and clinical translation.
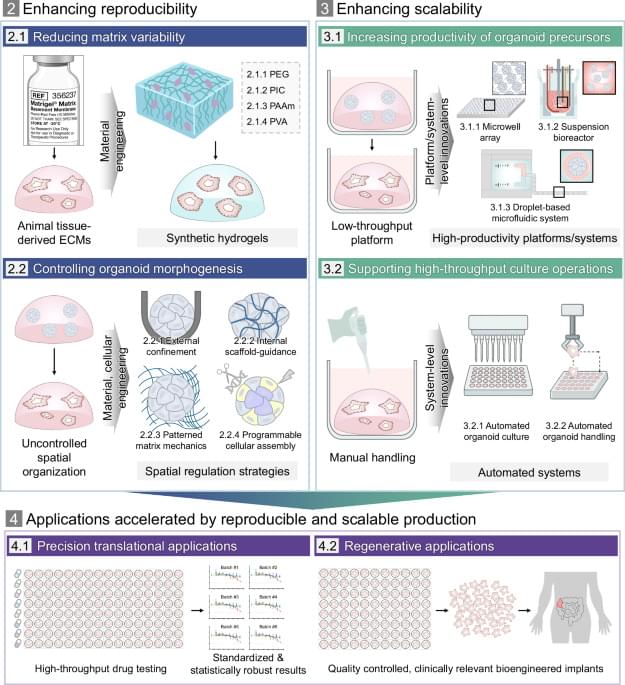
In response to these prevailing limitations and in alignment with global standardization trends, a range of engineering strategies has been developed, shifting the paradigm from organoid culture to organoid manufacturing by enabling reproducible and scalable organoid production. These strategies broadly focus on two goals: improving reproducibility by minimizing uncontrolled variation in the culture environment as well as by regulating intrinsic morphogenetic processes, and enhancing scalability by increasing productivity and throughput. To this end, recent advances can be categorized into three major domains: cellular engineering approaches that regulate morphogenetic processes through programmed cell organization; material-based strategies that establish defined and controllable environmental cues; and platform-or system-level innovations that enable high-throughput and automated workflows. Together, these innovative engineering advances mark aion toward more standardized, efficient production workflows.