Researchers have engineered Clostridium sporogenes to selectively target and consume oxygen-deprived tumor cores. Pre-clinical testing is planned to evaluate the novel cancer therapy approach.


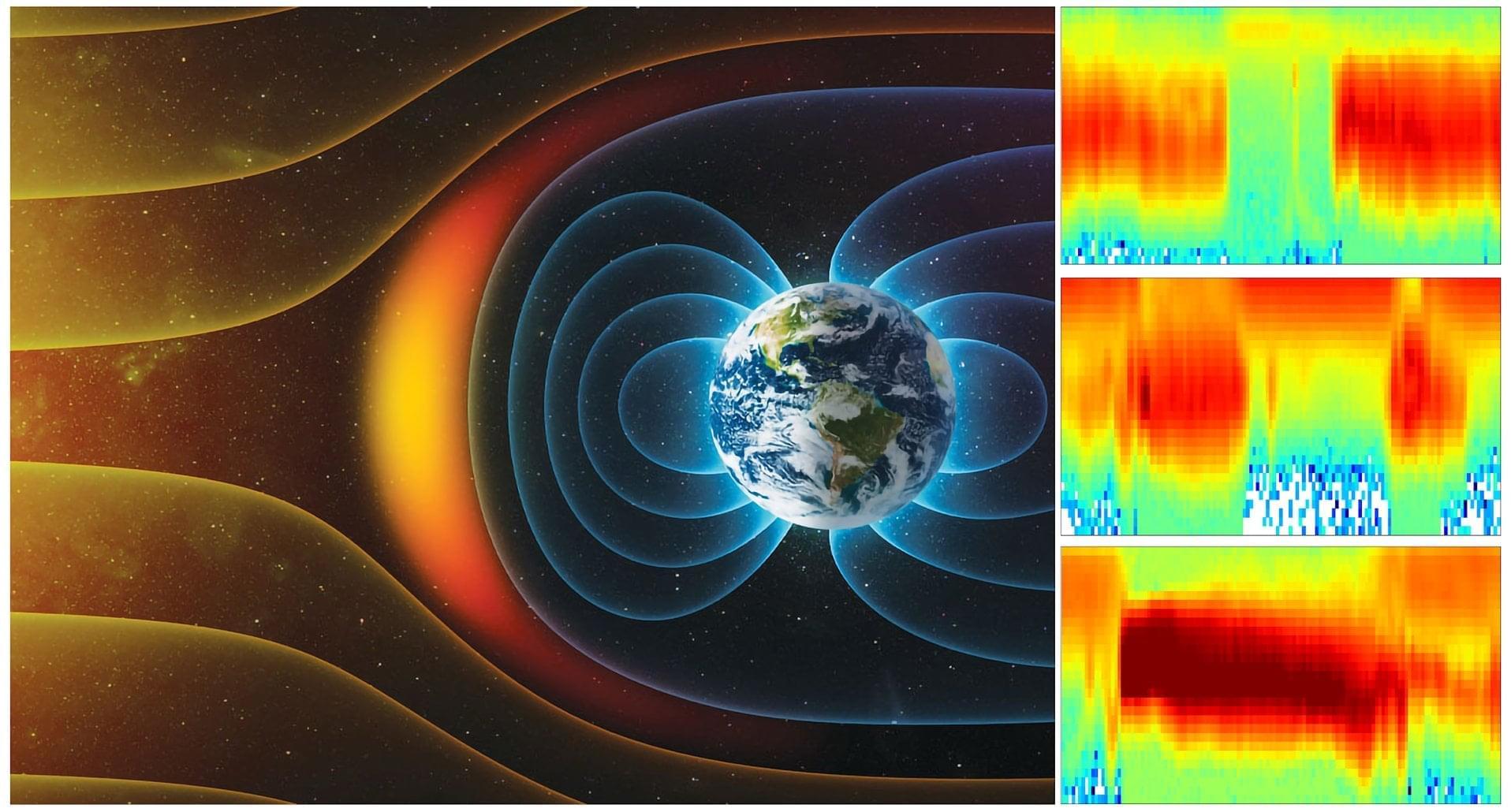
Earth’s magnetic shield is shifting in dramatic ways. New data from ESA’s Swarm satellites show that the South Atlantic Anomaly — a vast weak spot in Earth’s magnetic field — has grown by nearly half the size of continental Europe since 2014. Even more striking, a region southwest of Africa has begun weakening even faster in recent years, hinting at unusual activity deep within Earth’s molten outer core.

What started as a fun experiment to create a decorative diamond “owl” for distinguished guests has evolved into a scalable manufacturing process for electronics.
Researchers at Rice University have developed a bottom-up method for growing patterned diamond surfaces to cool electronics.
The technique enables diamonds to be integrated directly into devices, reducing operating temperatures by 23°C (41°F).
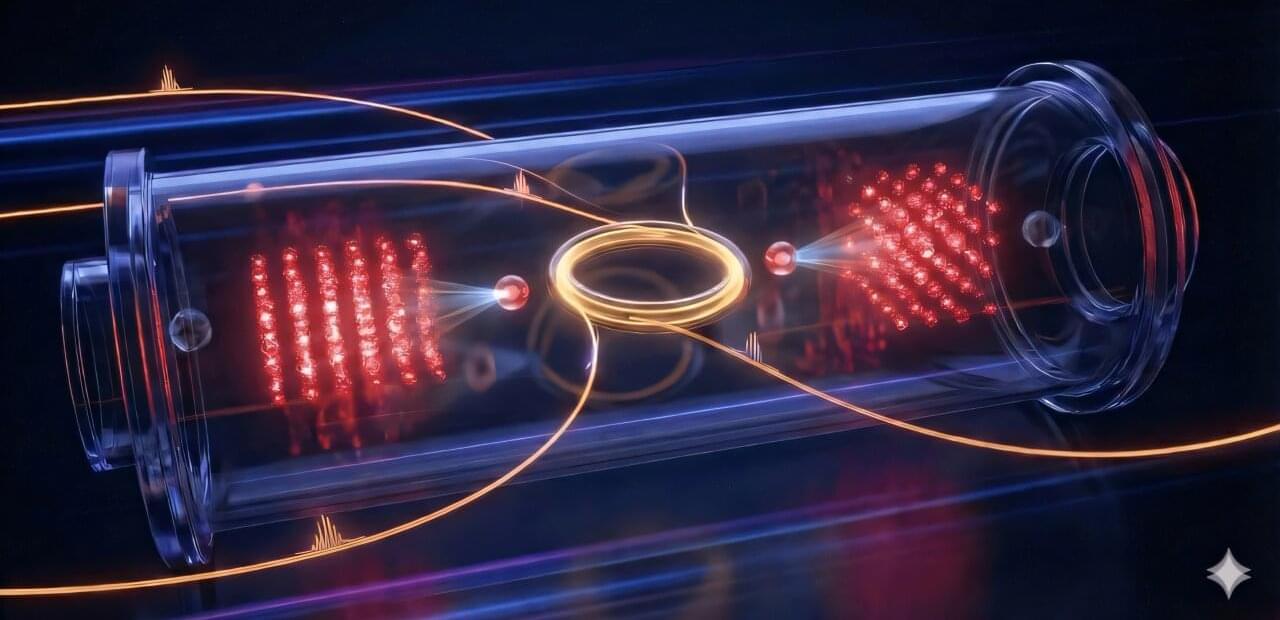
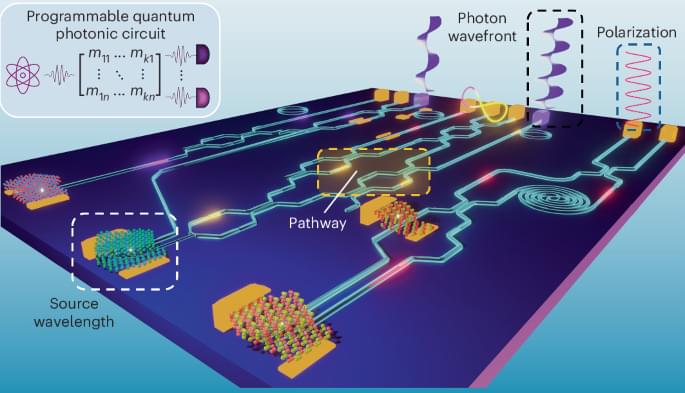
Quantum technologies, devices and systems that operate leveraging quantum mechanical effects, could tackle some tasks more reliably and efficiently than any classical technology could. In recent years, some researchers have been trying to realize quantum networks to scale up the size of quantum computers, which essentially consist of several connected smaller quantum processors.
The devices in a quantum network are connected via entanglement, a quantum effect via which distant quantum particles become inextricably linked and share a single correlated state. One way to create entanglement between different atomic quantum computers is to use an atom-cavity interface, a system in which atoms interact with light inside an optical cavity.
Over two decades ago, two physicists at the University of Aarhus introduced a protocol designed to produce high-quality entangled states, reliably connecting devices in a network. Despite its potential, this framework, known as the state-carving (SC) protocol, was found to only succeed in 50% of cases, which has so far prevented its application on a large scale.
An exploration of the physics and science behind time travel and the enormous implications of it.
My Patreon Page:
https://www.patreon.com/johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:
https://www.youtube.com/eventhorizonshow.
Music: