The last time you scrubbed a streaky window or polished a porcelain appliance, you probably used a chemical called ammonia.
Also known as ammonium hydroxide when mixed with water, ammonia is more than a common household cleaner. More than 170 million metric tons of it are produced globally every year, with most of it ending up as fertilizer for corn, cotton and soybeans.
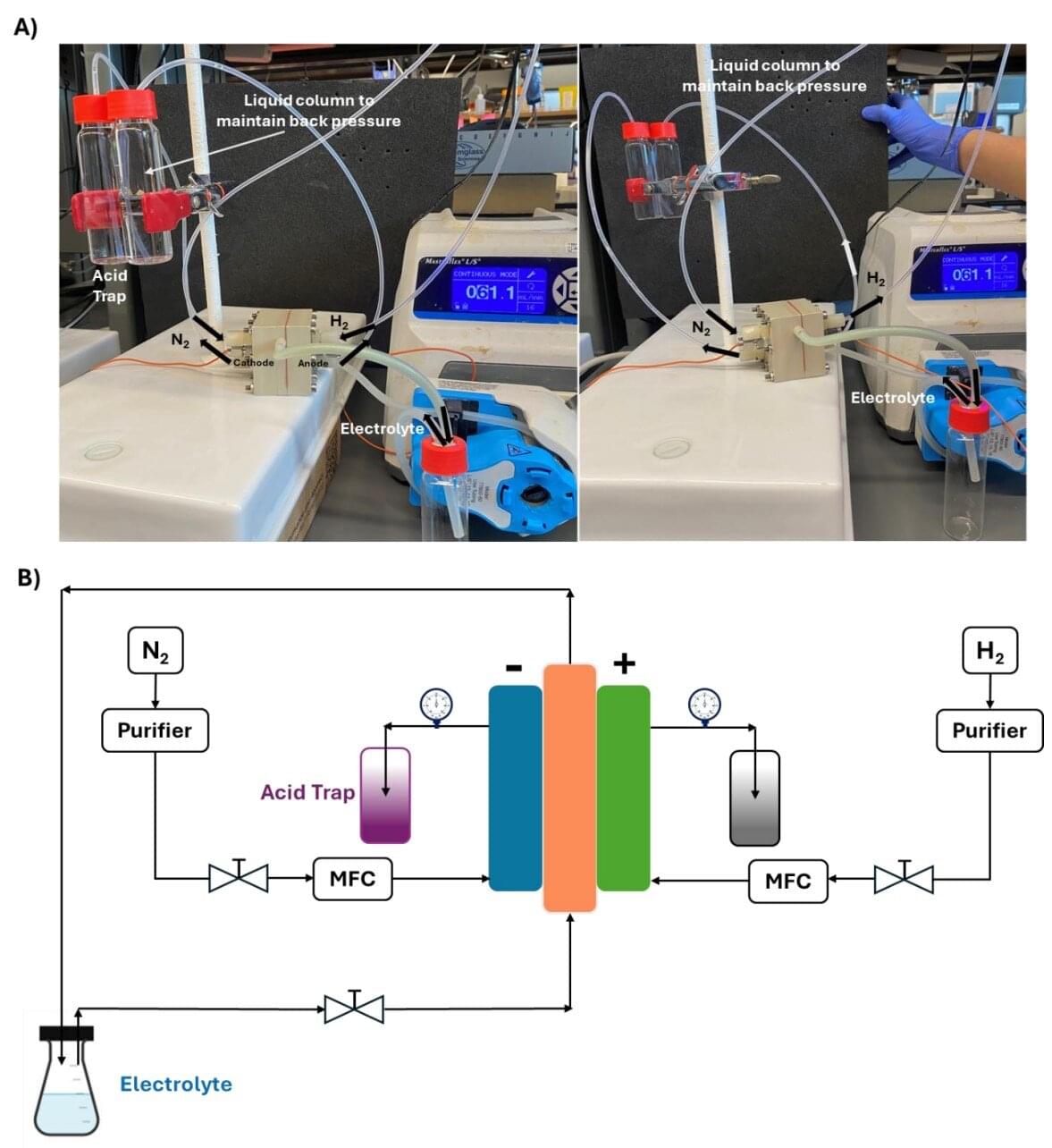
UIC researchers are scaling up a system for farmers to produce ammonia in their own backyards. The method, which uses renewable electricity and Earth’s natural resources, appears in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.