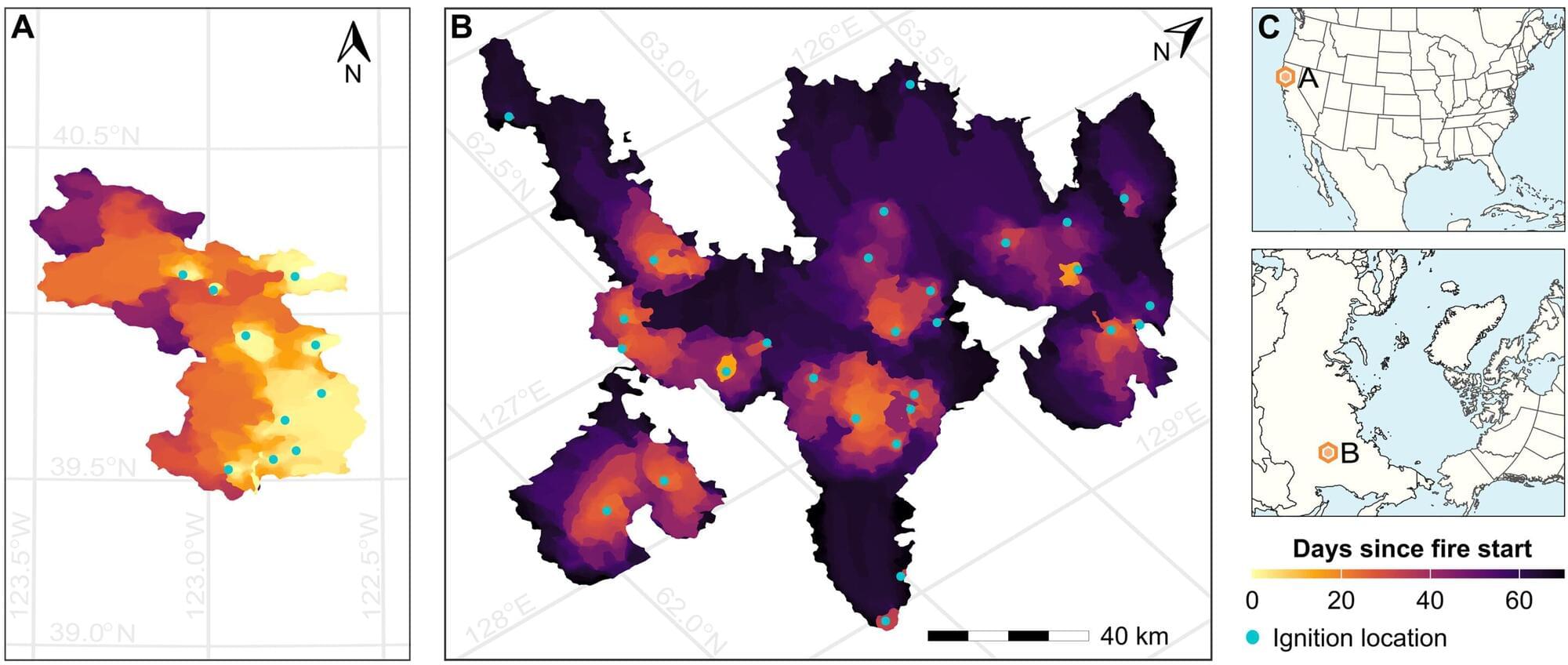
Multi-ignition wildfires are not overly common. But when individual fires do converge, the consequences can be catastrophic. The largest fire on record in California, the 2020 August Complex fire, grew from the coalescence of 10 separate ignitions.
In a new study, published in Science Advances, researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), the University of California (UC), Irvine and collaborators examine multi-ignition fires, calculating their impact and modeling the mechanisms behind them by leveraging the Department of Energy’s flagship Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM). The work shows that when flames combine, they are disproportionately destructive: They spread faster, last longer, generate stronger atmospheric events and strain firefighting resources.
In California, the study found that multi-ignition fires make up only 7% of the total number of fires, but they contribute to 31% of the burned area in the state.