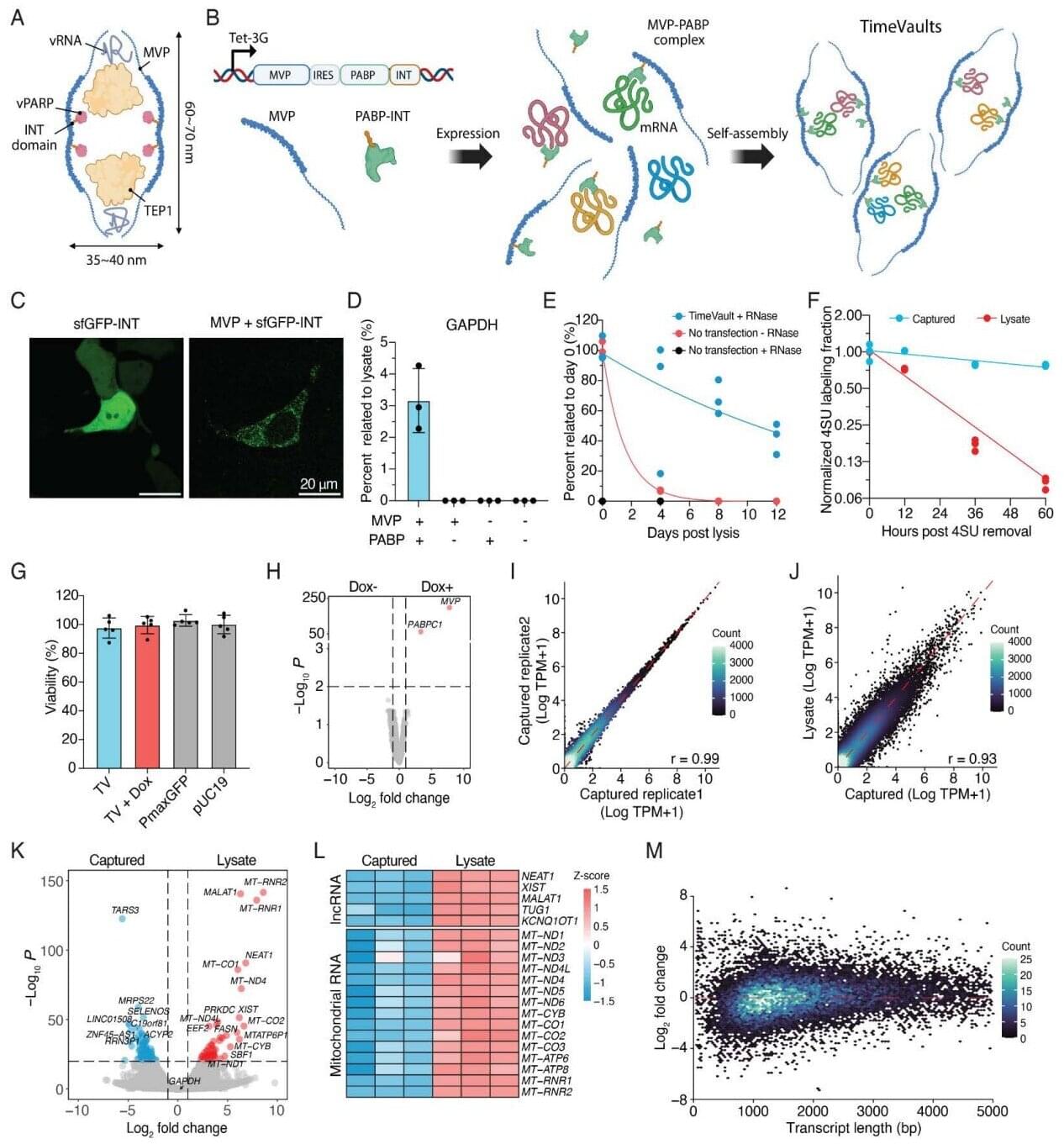
Scientists can peer into cells to get a limited view of their activity using microscopes and other tools. However, cells and the molecular events within them are dynamic, and developmental processes, disease progression and certain molecular cues are still difficult to discern. Ideally, scientists could leverage a system to obtain an unbiased record of a genome’s functional output, showing how cells respond to different conditions over time to gain useful insights. Now, it seems a group of researchers may have found a way to do just that.
A new study, published in Science, describes a technique to utilize mysterious cellular structures, called “vault particles,” to gather up mRNA by encapsulating and protecting it from degradation. This results in an ability to capture information, like transient stress responses and gene expression changes, and read it out at a later time.