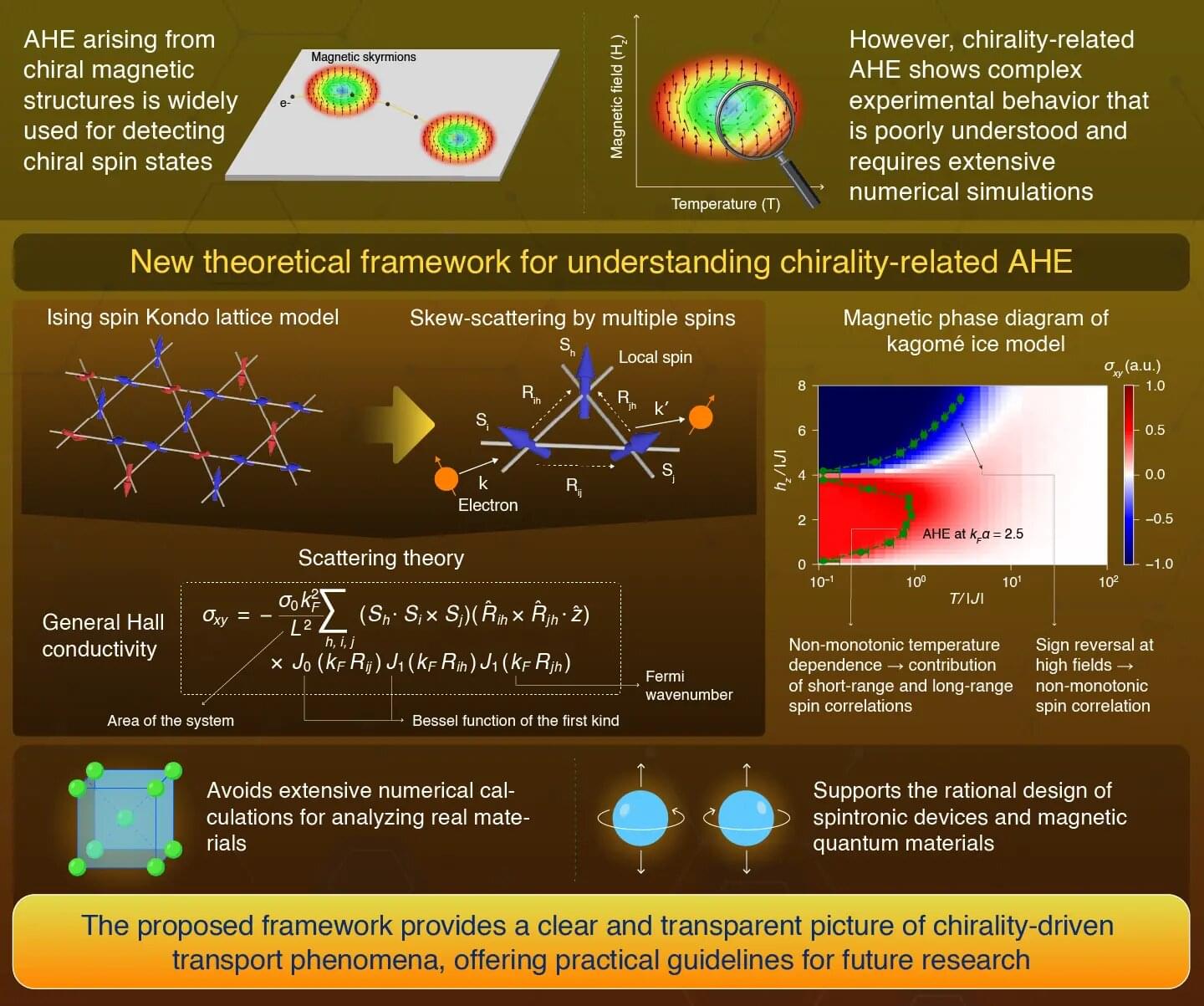
A new framework for understanding the nonmonotonic temperature dependence and sign reversal of the chirality-related anomalous Hall effect in highly conductive metals has been developed by scientists at Science Tokyo. This framework provides a clear picture of the unusual temperature dependence of chirality-driven transport phenomena, forming a foundation for the rational design of next-generation spintronic devices and magnetic quantum materials.
Magnetic materials exhibit a variety of intriguing properties during their magnetization process that reflect their magnetic states and excitations. These properties are studied by applying an external magnetic field to the material, producing the magnetization curve. Magnetic metals additionally demonstrate rich behavior in transport phenomena, referring to the flow of charge, heat, or spin under the influence of magnetic fields.
However, some of these behaviors are difficult to probe using the magnetization curve. The anomalous Hall effect (AHE) is one such effect. In the AHE, when an electric current passes through a magnetic metal, a voltage perpendicular to the current arises even in the absence of an external magnetic field. By contrast, in the traditional Hall effect, such a transverse voltage appears only when an external magnetic field is applied.